Збирач потоків
Chip antennas boost Wi-Fi and UWB signal integrity

Three chip antennas from Taoglas—the ILA.257, ILA.68, and ILA.89—provide Wi-Fi 6/7, ultra-wideband (UWB), and ISM connectivity. Manufactured using a low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) process, the antennas deliver high radiation efficiency and frequency stability in ultra-compact packages. According to Taoglas, they also require a smaller keep-out area than competing antennas.

The ILA.257 is a 3.2×1.6×0.5-mm antenna for Wi-Fi 6/7, providing tri-band coverage across 2.4 GHz, 5.8 GHz, and 7.125 GHz with strong radiation efficiency and stable signal integrity. Its small footprint and minimal keep-out area make it well-suited for wearables, portable electronics, and industrial IoT devices.
Engineered for UWB operation from 6 GHz to 8.5 GHz, the ILA.68 3.2×1.6×1.1-mm antenna delivers a stable omnidirectional radiation pattern with consistent repeatability and low insertion loss. It supports applications such as indoor positioning, access control, and short-range radar in space-constrained IoT and automotive systems.
Designed for the 868-MHz and 915-MHz ISM bands, the ILA.89 supports global LPWAN and LoRa deployments with up to 47.9% radiation efficiency and 0.56 dBi peak gain. Its 4.0×12.0×1.6-mm footprint, simple layout, and regional variants help reduce design complexity and speed time-to-market for small IoT devices.
The ILA.257, ILA.68, and ILA.89 antennas are now available from Taoglas and its authorized distributors.
The post Chip antennas boost Wi-Fi and UWB signal integrity appeared first on EDN.
Handheld enclosures add integrated cable glands

OKW now offers CONNECT fast-assembly handheld plastic enclosures with optional integrated cable glands, making it easier to install power and data cables.
Cost-effective CONNECT is ideal for network technology, building services, safety engineering, IoT/IIoT, medical devices, analytical instruments, data loggers, detectors, sensors, test and measurement.
 (Source: OKW Enclosures Inc.)
(Source: OKW Enclosures Inc.)
CONNECT’s two case shells snap together for fast and easy assembly: no screws are required. This offers the choice of two ‘fronts’: one shell is convex – perfect for LEDs – while the other is flat and recessed for a compact display or membrane keypad. Inside the flat shell there are mounting pillars for PCBs and components.
CONNECT enclosures feature open apertures at each end. For these, design engineers can specify a combination of ASA+PC blank end panels and soft-touch TPE cable glands with integrated strain relief. Cable diameters from 0.134“ to 0.232“ are accommodated. The two long sides provide ample space for USB connectors.
These UV-stable ASA+PC (UL 94 V-0) enclosures are available in six sizes from 2.36″ x 1.65″ x 0.87″ to 6.14″ x 2.13″ x 0.87″. The standard colors are off-white (RAL 9002) and black (RAL 9005). Custom colors are also available.
The cable glands come in volcano (gray) and black (RAL 9005). The end parts are off-white (RAL 9002) and black (RAL 9005). Other accessories include wall holders, rail holding clamps for round tubes up to ø 1.26″, and self-tapping screws.
OKW can supply CONNECT fully customized. Services include machining, lacquering, printing, laser marking, decor foils, RFI/EMI shielding, and installation and assembly of accessories.
For more information, view the OKW website: https://www.okwenclosures.com/en/Plastic-enclosures/Connect.htm
The post Handheld enclosures add integrated cable glands appeared first on EDN.
DSO-TC3 Oscilloscope Test with Signal Generator - Signal Test - Sine wav...
 | We used the following circuit elements for measurement trials: [link] [comments] |
Coherent expands silicon carbide platform from 200mm to 300mm
ROHM launches 13–65mΩ SiC MOSFETs in TOLL package
Through-hole connector resolves surface-mount dilemma

Manufacturing of a modern component-laded printed circuit board (PCB) is an amazing fusion and coordination of diverse technologies. There’s the board as substrate itself, the stencils and masks that enable precise placement of solder paster, and the pick-and-place mechanical system that places components (both ICs and passive ones) on the appropriate lands with pinpoint precision and repeatability, all culminating in most cases in a sophisticated reflow-soldering process.
Most of the loaded components use surface mount technology (SMT) and tiny contacts to their respective lands on the PCB. However, it wasn’t always an SMT world. In the early days of PCBs, the situation was somewhat different. Most of the components were dual inline package (DIP) ICs and passives with tangible wire leads, where their connections went through holes in the board (Figure 1).

Figure 1 Dual-inline package (DIP) was dominant in the early days of ICs and is still favored by makers and DIY enthusiasts; but most devices are no longer offered this way, nor can they be. Source: Wikipedia
Not only did this require costly drilling of hundreds and thousands of space-consuming holes, but component installation was a challenge. The loaded board—with these through-hole components mounted on one side only—went through a wave-soldering process which soldered the leads to the tracks on the bottom of the board.
The advent of SMT
The use of surface-mount technology began in the 1960s, when it was originally called “planar mounting”. However, surface mount technology didn’t become popular until the mid-1980s, and even as recently as 1986; surface-mount components represented only around 10% of the total market. The technique took off in the late 1980s, and most high-tech electronic PCBs were using surface mount devices by the late 1990s.
SMT enables smaller components, higher board densities, use of top and bottom sides of the board for components, and a reflow soldering process. Today, active and passive components are offered in SMT packages whenever possible, with through-hole packages being the exception. SMT devices can be placed using an automated arrangement, while many larger through-hole ones require manual insertion and soldering. Obviously, this is costly and disruptive to the high-volume production process.
The demand for SMT versions is so overwhelming that many products are available only in that package type. SMT makes possible many super-tiny components we now count on; some are just a millimeter square or smaller.
Due to the popularity of SMT, vendors often announce when they have managed to make a former through-hole component into a SMT one. Doing so is not easy in many cases for ICs, as there are die-layout, thermal, packaging, and reliability issues.
There are also transitions for passives. For example, Vishay Intertechnology recently announced that it has transformed one of its families of axial-leaded safety resistors into surface-mount versions using a clever twisting to the leads in conjunction with a T-shaped PCB land pattern (Figure 2). This is not a trivial twist because these resistors must also meet various safety and regulatory mandates for performance under normal and fault conditions while being compatible with automated handling.

Figure 2 Transforming this leaded safety resistor from a through-hole to SMT device involved much more than a clever design as the SMT version must meet a long list of stringent safety-related requirements and tests. Source: Vishay
In other cases, vendors of leaded discrete devices such as mid-power MOSFETs have announced with fanfare that they have managed to engineer a version with the same ratings in an SMT package. No question about it; it’s a big deal in terms of attractiveness to the customer.
What about the SMT holdouts?
Despite the prevalence of, and desire for, SMT devices, some components are not easily transformed into SMT-friendly packaging that is also compatible with reflow soldering. Larger connecters for attaching discrete terminated wires to wiring blocks are a good example. If they were SMT devices, the stress they endure would flex the board and weaken their soldered connections as well as affect the integrity of the adjacent components. Their relatively large size also makes SMT handling a challenge.
But that dilemma is seeing some resolution. Connector vendor Weidmüller Group has developed what it calls through-hole reflow (THR) technology. These are terminal-block connectors for discrete wires that do require PCB holes and through-hole mounting for mechanical integrity. Yet, it can then be soldered using the standard reflow process along with other SMT devices on the board.
One of the vendor’s families with this capability was developed for Profinet applications and supports Ethernet-compliant data transmission up to 100 Mbps (Figure 3).

Figure 3 One of the available families of THR connector blocks is for Profibus installations. Source: Weidmüller
These connector blocks use glass-fiber-reinforced liquid crystal polymer (LCP) bodies to guarantee a high level of shape stability. The favorable temperature properties of the material (melting point of over 300°C) and the in-built pitch space (stand-off) of 0.3 mm (minimum) are well-suited for the solder-paste process. They come in choice of two pin lengths of 1.5 mm and 3.2 mm to precisely match board thickness, all with very tight tolerance on dimensional stability and pin centering (Figure 4).

Figure 4 The connector pin must have the right length and precise centering for reliable contact. Source: Weidmüller
The reflow wondering profile is like the ones required for other SMT components, so the entire board can be soldered in one pass (Figure 5).

Figure 5 The recommended reflow soldering profile for these THR connectors matches the profile of other SMT devices. Source: Weidmüller
Another connector family supports various USB connections (Figure 6).

Figure 6 A range of THR USB connectors is also available. Source: Weidmüller
With these THR connectors, you get the mechanical integrity of through-hole devices alongside the manufacturing benefit of automatic insertion (Figure 7) and reflow soldering. There is no need for a separate step to manually insert the connector and have a separate soldering step. You can also use them for through-hole wave-soldering as well, if you prefer.

Figure 7 Even the larger-block THR connectors can be automatically inserted using SMT pick-and-place systems. Source: Weidmüller
Connectors such as these will undoubtedly lower manufacturing costs while not compromising performance. Once again, it’s a reminder of the vital role and impact of mechanical know-how and material-science expertise to less-visible, low-glamour yet important advances in our “electronics” industry.
 Bill Schweber is a degreed senior EE who has written three textbooks, hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. Prior to becoming an author and editor, he spent his entire hands-on career on the analog side by working on power supplies, sensors, signal conditioning, and wired and wireless communication links. His work experience includes many years at Analog Devices in applications and marketing.
Bill Schweber is a degreed senior EE who has written three textbooks, hundreds of technical articles, opinion columns, and product features. Prior to becoming an author and editor, he spent his entire hands-on career on the analog side by working on power supplies, sensors, signal conditioning, and wired and wireless communication links. His work experience includes many years at Analog Devices in applications and marketing.
Related Content
- Consumer Connectors Get Ruggedized
- Be aware of connector mating-cycle limits
- Give Me Back My External Wi-Fi Antenna Connector, Please
The post Through-hole connector resolves surface-mount dilemma appeared first on EDN.
Infineon enhances Electreon’s wireless in-road EV charging with silicon carbide technology
The Oura Ring 4: Does “one more” deliver much (if any) more?

The most surprising thing to me about the Oura Ring 4, compared to its Gen3 predecessor, is how similar the two products are in terms of elemental usage perception. Granted, the precursor’s three internal finger-orientation bumps:

are now effectively gone:

and there are also multiple internal implementation differences between the two generations, some of which I’ll touch on in the paragraphs that follow. But they both use the same Android and iOS apps, generate the same data, and run for roughly the same ~1 week between charges.
One key qualifier on that last point: I bought them both used on eBay. The Ring 4, which claims 8 days of operating life when new, may have already accumulated more cycles from prior-owner usage than was the case with the Gen3 forebear, which touts 7 days’ operating life when new.
Smart ring “kissing cousins”They look similar, too: the Gen3 in “Brushed Titanium” is the lower of the two rings on my left index finger in the following photos, with the Ring 4 in “Brushed Silver” above it:


And here’s the Ring 4 standalone, alongside my wedding band:

A smart ring enthusiast’s detailed analysis of the two product generations, complete with an abundance of comparative captured-data results, is below for those of you interested in more of an on-finger relative appraisal than I was able (and, admittedly, willing) to muster:
Sensing enhancementsPerhaps the biggest claimed innovation with the newer Ring 4 is Smart Sensing:
Smart Sensing is powered by an algorithm that works alongside the research-grade sensors within Oura Ring 4 to respond to each member’s unique finger physiology, including the structure and distinct features of your finger (i.e. skin tone, BMI, and age).
The multiple sensors form an 18-path multi-wavelength photoplethysmography (PPG) subsystem, which adjusts dynamically to your lifestyle throughout the day and night.
As the functional representation in this conceptual video suggests:
there are two multi-LED clusters, each supporting three separate light wavelengths (red, green and infrared), with corresponding reception photodiodes in the rectangular structures to either side of each cluster (three structures total):


To complete the picture, here’s the inner top half of my Ring 4:

Six total LEDs, outputting to three total photodiodes, translates to 18 total possible light path options (which is presumably how Oura came up with the number I quoted earlier), with the optimal paths initially determined as part of the first-time ring setup:






and further fine-tuning is dynamically done while the ring is being worn, including compensating for non-optimum repositioning on the finger per the earlier-mentioned lack of distinct orientation bumps in this latest product generation.
What are the various-wavelength LEDs used for? Generally speaking, the infrared ones are capable of penetrating further into the finger tissue than are their visible-light counterparts, at some presumed tradeoff (accuracy, perhaps?). And specifically:
- Red and infrared LEDs measure blood oxygen levels (SpO2) while you sleep.
- Green and infrared LEDs track heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) 24/7, as well as respiration rate during sleep.
All three LED types were also present with the Gen3 ring, albeit in a different multi-location configuration than the Ring 4 (albeit common to both the Heritage and Horizon Gen3 styles):


The labeling in the following Ring 4 “stock” image, by the way, isn’t locationally or otherwise accurate, as far as I can tell; the area labeled “accelerometer” is actually a multi-LED cluster, for example, and in contrast to the distinct “Red And Infrared…” and “Green And Infrared…” labels in the stock image, both of the clusters actually contain both green and red (plus infrared) LEDs:

Also embedded within the ring is a 3D accelerometer, which I’ve just learned, thanks to a Texas Instruments technical article I came across while researching this writeup, is useful not only for counting steps (along with, alas, keystrokes and other finger motions mimicking steps) but also “used in combination with the light signals as inputs into PPG algorithms.”


And there’s also a digital temperature sensor, although it doesn’t leverage direct skin contact for measurement purposes. Instead, it’s a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor whose (quoting from Wikipedia) “resistance decreases as temperature rises; usually because electrons are bumped up by thermal agitation from the valence band to the conduction band”.
Battery life optimizationsAs noted in the public summary of a recent Ring 4 teardown by TechInsights, the newer smart ring has a higher capacity battery (26 mAh) than its Gen3 predecessor, which is likely a key factor in its day-longer specified operation between recharges. Additionally, the Ring 4’s Smart Sensing algorithms further optimize battery life as follows:
In order to optimize signal quality and power efficiency, Oura Ring 4 selects the optimal LED for each situation, instead of burning several LEDs simultaneously.
and
Smart Sensing also helps maximize the battery life of Oura Ring 4 by dynamically adjusting the brightness of the LEDs, using the dimmest possible setting to achieve the desired signal quality. This allows the battery life of Oura Ring 4 to extend up to eight days.
Here, for example, is a dim-light photo of both green LEDs in action, one in each cluster:

Generally speaking, the LEDs are active only briefly (when they’re illuminated at all, that is) and I haven’t yet succeeded in grabbing my smartphone and activating its camera in time to capture photos of any of the other combinations I’ve observed and note below. They include:
- Single green LED (either cluster)
- Concurrent single green and single red LEDs (one from each cluster), and
- Both single (either cluster) and dual concurrent (both clusters) red LED(s)
I’ve also witnessed transitions from bright to dim output illumination, prior to turnoff, for both one and two concurrent green LEDs, but not (yet, at least) for either one or both red LED(s). And perhaps obviously, the narrow-spectrum eyes-and-brain visual sensing and processing subsystem in my noggin isn’t capable of discerning infrared (or even near-IR) emissions, so…
Third-party functional insightsOperating life between integrated battery recharges, which I’ve already covered, is key to wearer satisfaction with the product, of course, as is recharge speed to “full” for the next multi-day (hopefully) wearing period.
But for long-term satisfaction, a sufficiently high number of supported recharge cycles prior to effective battery expiration (and subsequent landfill donation) is also necessary. To wit, I’ll close with some interesting (at least to me) information that I indirectly (and surprisingly, happily) stumbled across.
First off, here’s what the Ring 4 looks like in the process of charging on its inductive dock:
In last month’s Oura Gen3 write-up, I shared a photo of the portable charging case (including an integrated battery) that I’d acquired from Doohoeek via Amazon, with the dock mounted inside. Behind it was the Doohoeek charging case for the Oura Ring 4. They look the same, don’t they?


That’s because, it turns out, they are the same, at least from a hardware standpoint. Requoting what I first mentioned last month, the “development story (which I got straight from the manufacturer) was not only fascinating in its own right but also gave me insider insight into how Oura has evolved its smart ring charging scheme for the smart ring over time. More about that soon, likely next month.
Here’s the Ring 4 and dock inside the second-generation Doohoeek case (which, by the way, is also backwards-compatible with the Gen3 ring and dock):

And as promised, here’s the full back-and-forth between myself (in bold) and the manufacturer (in italics) over Amazon’s messaging system:
As I believe you already realize, while Doohoeek’s first-generation battery case that I’d bought from you through Amazon works fine with the Oura Gen3, it doesn’t (any longer, at least) work with the Ring 4. For that, one of Doohoeek’s second-generation battery cases is necessary. Can you comment on what the incompatibility was that precluded ongoing reliable operation of the original battery case with the Ring 4 charging dock (although it still works fine for the Gen3)? A USB-PD handshaking issue between your battery and the charging dock? Or was it something specific to the ring itself?
Hi Brian,
thank you for your question! Here’s a brief technical explanation of the Ring 4 compatibility issue with our original charging case:
Our first-gen charging case used a smart current-detection algorithm to determine charging status. Under normal conditions, when the ring reached full charge, the current would drop and remain consistently low—triggering our case to stop charging. This worked flawlessly with Oura Gen3 and initially with the Ring 4.
However, after a recent Oura firmware update, the Ring 4 began exhibiting unstable current draw patterns during charging—specifically, prolonged periods of low current followed by unexpected current spikes, even when the ring was not fully charged. This behavior caused our case to misinterpret the ring as “fully charged” and prematurely terminate charging.
To resolve this, we redesigned our charging logic in the updated version to implement a more robust timing-based backup protocol.
We appreciate your interest and hope this clarifies the engineering challenge we addressed!
Best,
Doohoeek Support Team
This is perfect! It was obvious to me that whatever it was, it was something that a firmware update couldn’t resolve, and I’d wondered if ring-generated current draw variances were to blame. I suspect the Ring 4 is doing this to maximize battery life over extended charge cycle counts. Thanks again!
p.s…I also wonder why you didn’t change the product naming, box labeling, etc. so potential buyers could have reassurance as to which version they’d be getting?
Hi Brian,
Thank you for your insightful feedback — you’ve clearly thought deeply about how these systems interact, and we really appreciate that.
Yes, the current behavior on the Ring 4 appears optimized for long-term battery longevity 
Regarding your question about naming and packaging:
We actually had already mass-produced the outer shells and packaging for old version when Oura pushed the update that changed the charging behavior. Rather than discard those components (and create unnecessary waste), we decided to prioritize a firmware-level fix and use the same exterior.
That’s why the outside looks identical, but the internal charging behavior is now completely updated.
If you’d like to confirm whether your unit is the latest version, you can check the FNSKU barcode on the package:
Old version (no longer in production) ONLY used: X004HYCA09
New version (may change in future production) currently used: X004Q62DV9
Customers can also contact us with a photo of the label, and we’d be happy to verify it for them personally.
Thanks again for your support and sharp eyes.
Best,
Doohoeek Support Team
Very interesting! So it IS possible to firmware-retrofit existing units. Would that require a unit shipment back to the factory for the update, or did you consider developing a Windows-based (for example) update utility for customer upgrade purposes (by tethering the battery case’s USB-C input to a computer)?
Hi Brian,
Great question.
Unfortunately, a firmware update is not possible for units that have already been shipped. The hardware design does not support customer-side or even a cost-effective return-to-factory update process.
The only practical solution we could implement was to correct the firmware in all newly produced units moving forward, which is what you have received.
We appreciate your understanding!
Best,
Doohoeek Support Team
And with that, having recently passed through 2,000 words, I’ll wrap up for today. Stay tuned for the aforementioned teardown-to-come (on a different Ring 4; I plan to keep using this one!), and until then, I as-always welcome your thoughts in the comments!
—Brian Dipert is the Principal at Sierra Media and a former technical editor at EDN Magazine, where he still regularly contributes as a freelancer.
Related Content
- The Smart Ring: Passing fad, or the next big health-monitoring thing?
- Can a smart ring make me an Ultrahuman being?
- Does (wearing) an Oura (smart ring) a day keep the doctor away?
- RingConn: Smart, svelte, and econ(omical)
The post The Oura Ring 4: Does “one more” deliver much (if any) more? appeared first on EDN.
ROHM launches SiC MOSFETs in TOLL package that achieves both miniaturization and high-power capability
ROHM has begun mass production of the SCT40xxDLL series of SiC MOSFETs in TOLL (TO-Leadless) packages. Compared to conventional packages (TO-263-7L) with equivalent voltage ratings and on-resistance, these new packages offer approximately 39% improved thermal performance. This enables high-power handling despite their compact size and low profile. It is ideal for industrial equipment such as server power supplies and ESS (Energy Storage Systems) where the power density is increasing, and low-profile components are required to enable miniaturized product design.
In applications like AI servers and compact PV inverters, the trend toward higher power ratings is occurring simultaneously with the contradictory demand for miniaturization, requiring power MOSFETs to achieve higher power density. Particularly in totem pole PFC circuits for slim power supplies, often called “the pizza box type,” stringent requirements demand thicknesses of 4mm or less for discrete semiconductors.
ROHM’s new product addresses these needs by reducing component footprint by approximately 26% and achieving a low profile of 2.3mm thickness – roughly half that of conventional packaged products. Furthermore, while most standard TOLL package products are limited by a drain-source rated voltage of 650V, ROHM’s new products support up to 750V. This allows for lower gate resistance and increased safety margin for surge voltages, contributing to reduced switching losses.
The lineup consists of six models with on-resistance ranging from 13mΩ to 65mΩ, with mass production started in September 2025 (sample price: $37.0/unit, tax excluded). These products are available for online purchase from online distributors such as DigiKey, MOUSER, and Farnell. Simulation models for all six new products are available on ROHM’s official website, supporting rapid circuit design evaluation.
Product Lineup
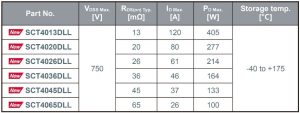
Application Examples
・Industrial equipment: Power supplies for AI servers and data centers, PV inverters, ESS (energy storage systems)
・Consumer equipment: General power supplies
The post ROHM launches SiC MOSFETs in TOLL package that achieves both miniaturization and high-power capability appeared first on ELE Times.
📰 Газета "Київський політехнік" № 43-44 за 2025 (.pdf)
Вийшов 43-44 номер газети "Київський політехнік" за 2025 рік
Asia-Pacific Takes the Lead in AI Adoption Across Manufacturing
Courtesy: Rockwell Automation
Manufacturing around the world has undergone a significant transformation with the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. With dynamic market conditions and pressures to optimize operations across the supply chain, more businesses today are turning to technology to meet the demands of an increasingly competitive market.
To get a better understanding of the smart manufacturing landscape and how manufacturers are leveraging these new technologies, the latest edition of the State of Smart Manufacturing report (SOSM) surveyed more than 1,500 manufacturing decision makers across industries from 17 countries, including Asia Pacific nations Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, and South Korea.
Now in its 10th edition, the report offers a global perspective on today’s challenges and tomorrow’s opportunities, highlighting how smart manufacturing and emerging technologies are fostering resilience and shaping the future.
How AI is Challenging the Status Quo in the Asia Pacific
Rich in resources with the resilience to constantly adapt and innovate, Asia Pacific (APAC) is setting the pace for manufacturing and industrial growth around the world. There is strong digitization momentum across the region, as AI and smart manufacturing technologies are no longer buzzwords but have become mission-critical to drive quality, agility, and growth.
This year’s survey is proof that the focus has shifted from experimentation to execution, where more manufacturers have adopted a tech-first mindset. Nearly half of manufacturers are already scaling AI to address workforce gaps, cybersecurity risks, and evolving sustainability targets, and APAC organizations investing in generative and causal AI increased 10% year-over-year.
The growing maturity in how businesses view AI is noticeable, moving towards becoming a strategic enabler rather than a supplementary tool. Trust in AI has deepened, with 41% of those surveyed in APAC having plans to increase automation in the workplace to address workforce shortage and bridge the skills gap. Organizations are no longer primarily using AI for predictive maintenance. They are now leveraging these capabilities for other, more sophisticated, autonomous operations such as quality assurance and adaptive control, which help to reduce human error and enhance real-time decision-making.
AI in Cybersecurity
With the rapid adoption of digital technologies, cybersecurity has become a growing concern across industries, including manufacturing. Globally, it now ranks as the second most significant external obstacle for manufacturers. In the APAC region, cybersecurity is top of the list, alongside inflation and rising energy costs.
In response, businesses are accelerating their use of AI, adopting smart manufacturing technologies to digitize operations, and upskilling existing talent to stay competitive and minimize cybersecurity risks. They are also hiring with new priorities, whereby cybersecurity skills and standards have become an in-demand capability.
Understanding the need for secure-by-design architectures and real-time threat detection capabilities, Rockwell Automation has developed a series of threat intelligence and detection services, helping manufacturers to stay ahead of the evolving cybersecurity frameworks and industry standards.
Transforming the Workforce with AI
Alongside AI, the workforce, too, is evolving. Just as AI can support business needs, it requires a skilled workforce to adapt these technologies to deliver real business value. Manufacturers across APAC are looking to AI to increase automation and make workflows more efficient, while looking for employees with strong analytical thinking skills to take on more value-added tasks. While challenging, the SOSM report reveals that the need for more skilled workers is not a uniquely regional issue but a global concern, affecting industries in both developed and emerging markets.
On the upside, the skills gap in APAC has narrowed slightly from the previous year, with only 29% of respondents in 2025 citing skills gap as a challenge compared to the 31% in 2024. This suggests that investments in talent development and education are beginning to pay off.
Delivering More Sustainable Business Outcomes for the Long Run
As an industry, manufacturing consumes lots of energy. As manufacturers across the region become more invested in their ESG goals, they are driven to improve business efficiencies in pursuit of sustainability and resource conservation. Over half (55%) stated that improving efficiencies is the top reason to pursue better sustainability, up from 39% last year. By improving workflow efficiencies through automation and technologies like AI, businesses are saving on business costs while supporting better energy management.
As the 2025 State of Smart Manufacturing report shows, AI is no longer a distant promise for the Asia Pacific—it is a powerful catalyst actively reshaping how the region builds, protects, and grows. From strengthening cybersecurity and elevating workforce capabilities to enabling smarter energy use and more sustainable operations, APAC manufacturers are demonstrating what it means to move from digital ambition to digital action.
With technology adoption accelerating and confidence in AI deepening, the region is well-positioned to define the next era of global manufacturing. Those who continue to invest in talent, innovation, and secure, future-ready systems will not only overcome today’s challenges but also lead the transformation of industry for years to come.
The post Asia-Pacific Takes the Lead in AI Adoption Across Manufacturing appeared first on ELE Times.
Smartphone production grows 9% in Q3/2025, driven by seasonal demand and new product releases
День Донора 2025
День донора в КПІ ім. Ігоря Сікорського 2025 це 📌 35 учасників донорського відбору та 🩸 11,25 літрів крові!!!
Will AI Consume the World’s Electricity? Addressing AI Data Center Demands with Advanced Power Semiconductors
Courtesy: RoHM
AI’s unprecedented advancement is reshaping our world, but this transformation comes with the urgent challenge of sharply rising energy demands from data center infrastructure.
In response, Japan has launched an ambitious national strategy—the ‘Watt-Bit Initiative’—spearheaded by the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI). This comprehensive program aims to establish Japan as a global leader by developing ultra-efficient data centers strategically distributed across the nation. Through collaborative platforms like the ‘Watt-Bit Public-Private Council,’ METI is orchestrating a unified effort among key sectors—energy providers, telecommunications, data center operators, and semiconductor manufacturers—to turn this vision into reality.
Will AI Consume the World’s Electricity?
The explosive growth of generative AI technologies like ChatGPT has triggered an unprecedented surge in data center energy demands. Training and inference of complex AI models require enormous computational resources, supported by high-performance servers operating continuously around the clock.
This escalating demand for electricity not only places a significant strain on local environments but also raises concerns about the stability of the power supply. As AI continues to advance, the limitations of conventional power supply systems are becoming increasingly apparent.
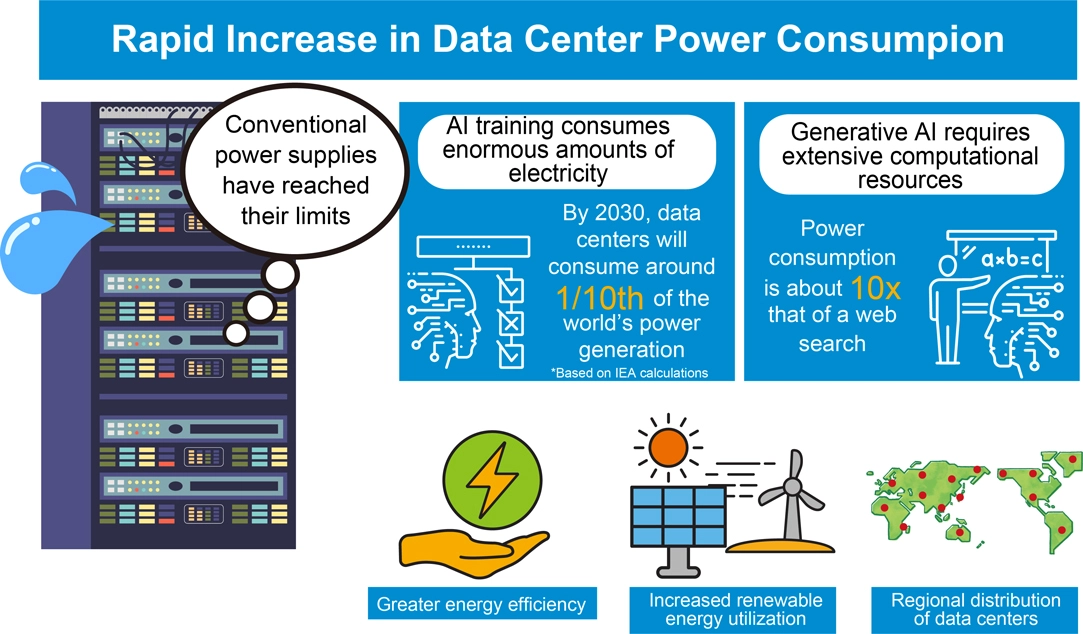
Against this backdrop, three urgent challenges emerge: improving energy efficiency, expanding the use of renewable energy, and optimizing the regional distribution of data centers. Achieving a sustainable society requires moving away from fossil fuel dependency and embracing renewable sources such as solar and wind power.
Utilizing Renewable Energy in Data Centers
Data centers, now an indispensable part of modern infrastructure, are at a major turning point.
Traditionally, urban data centers have been concentrated in metropolitan hubs like Tokyo to ensure low-latency communication for services requiring high-speed data access, including finance, healthcare, and edge computing. However, the surge in power consumption driven by AI adoption, coupled with the need for robust business continuity (BCP) in the face of large-scale natural disasters, is accelerating the shift toward decentralizing data centers into suburban areas.
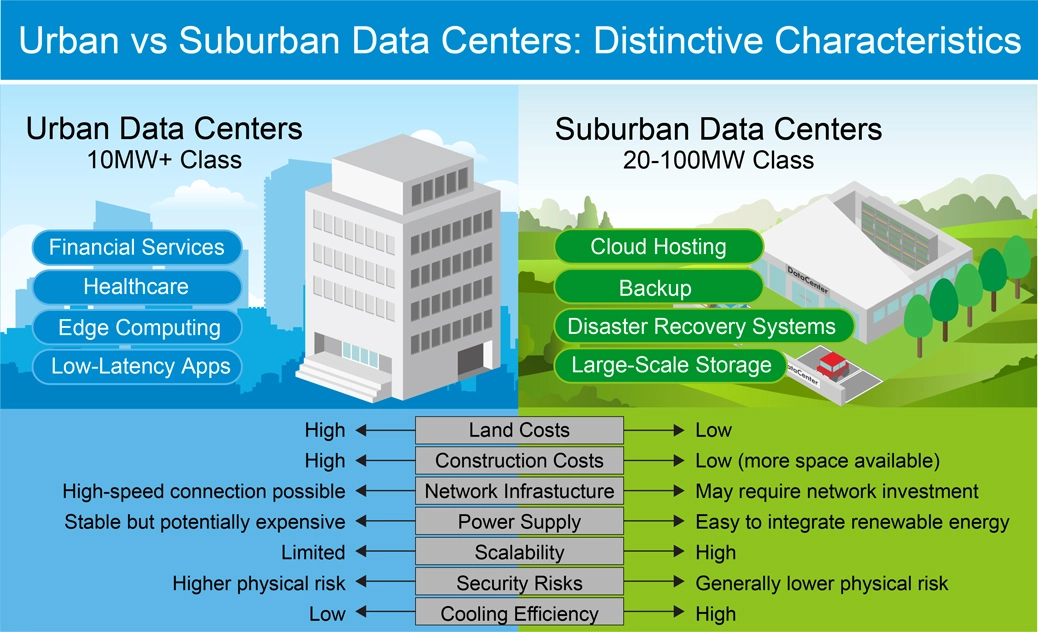
These new sites offer compelling advantages beyond just abundant available space. They enable seamless integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power, benefit from surplus grid capacity for stable electricity, and leverage natural cooling from climate and water resources, dramatically reducing operational costs. As a result, suburban facilities are increasingly being adopted for modern workloads such as cloud hosting, backup, disaster recovery, and large-scale storage.
The Future of Server Rack Expansion
Urban data centers face severe land constraints, and even suburban data centers, where securing large plots is relatively easier, are approaching their limits in available space for server deployment.
To overcome this, server racks are evolving into high-density AI server racks designed to house a greater number of high-performance servers efficiently. Rather than expanding the total number of server racks, the industry is moving toward high-density configurations equipped with more CPUs, GPUs, and other functional boards, significantly boosting the computing power per rack to maximize performance within limited space.
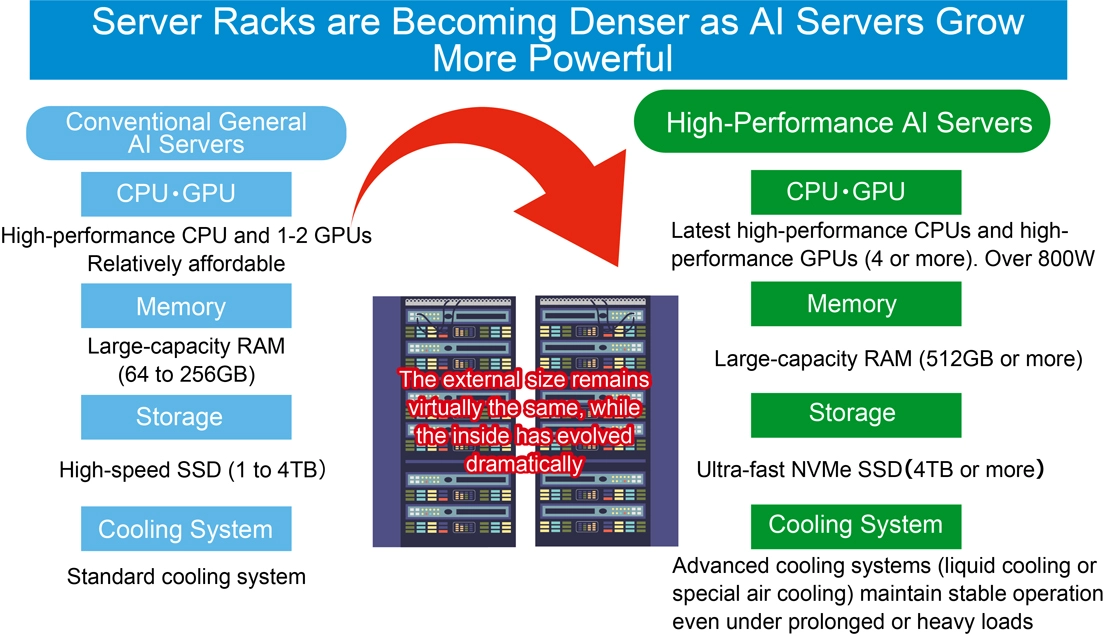
While the external appearance of server racks remains largely unchanged, their internal storage capacity has increased several fold.
This leap in performance and density demands a fundamental transformation of power delivery systems. Conventional multi-stage power conversion introduces significant energy losses, making efficient supply increasingly difficult. As a result, innovations such as reducing conversion stages and adopting high-voltage direct current (HVDC) architectures are gaining momentum, driving the need for SiC and GaN power semiconductors. ROHM, together with other industry leaders, is advancing technologies that support this transformation, enabling both higher performance and greater energy efficiency across entire data centers.
- Are Today’s Power Systems Sufficient?
The sharp rise in power consumption of high-performance AI servers—particularly GPUs—is forcing a fundamental redesign of existing data center power architectures. Conventional multi-stage power conversion incurs significant conversion losses, making efficient power delivery increasingly difficult.

In today’s data centers, high-voltage AC is supplied and gradually stepped down through multiple transformers and rectifiers before finally being converted into the low-voltage DC required by servers. Each stage of this process incurs losses, ultimately reducing overall efficiency. To address these challenges, data centers are expected to undergo key transformations aimed at enhancing both power conversion efficiency and reliability.
- Reducing Power Conversion Stages
A growing trend is the integration of multiple conversion processes—for example, converting high-voltage AC directly to DC, or stepping down high-voltage DC directly to the voltage used by servers. This approach significantly reduces the number of conversion steps, minimizing energy losses, enhancing overall system efficiency, and lowering the risk of failures.
- Supporting High-Voltage Input/High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Power Supplies
Server rack input voltages are shifting from traditional low-voltage 12VDC and 48VDC to higher levels such as 400VDC, and even 800VDC (or ±400VDC). Operating at higher voltages reduces transmission current, enabling lighter busbar designs.
At the same time, the adoption of HVDC systems is gaining momentum. Unlike conventional AC-based architectures, HVDC delivers DC power directly to server racks, reducing the need for multiple AC/DC conversion stages. This approach enhances energy efficiency, enables more flexible power management and bidirectional transmission, and simplifies integration with renewable energy sources.
- Increasing Adoption of SSTs (Solid State Transformers)
Transformer equipment is evolving from traditional designs to SSTs (Solid State Transformers) that leverage semiconductor technology. SSTs are expected to play a key role in significantly miniaturizing conventional equipment.
- Growing Demand for SiC/GaN Power Semiconductors
Building high-efficiency, high-voltage power systems requires performance levels that exceed the capabilities of conventional silicon (Si) semiconductors. This has made SiC and GaN power semiconductors indispensable. These advanced devices enable low-loss, high-frequency, high-temperature operation under high-voltage input conditions, greatly contributing to both the miniaturization and efficiency of power systems.

Moreover, as these technologies advance, their benefits extend beyond power systems to individual devices within server racks, further improving overall energy efficiency.
ROHM is accelerating the development of solutions for next-generation servers. In addition to existing products such as SiC/GaN/Si IGBTs, isolated gate drivers, cooling fan drivers, SSD PMICs, and HDD combo motor drivers from the EcoSiC, EcoGaN, and EcoMOS series, we are also developing high-current LV MOS, isolated DC-DC converters, DC-DC converters for SoCs/GPUs, and eFuses.
Power Semiconductors Driving Next-Generation AI Data Centers
- SiC Devices Ideal for High Voltage, Large Current Applications
SiC devices are particularly well-suited for sets requiring high voltages and currents. As server rack input voltages continue to rise, conventional 54V rack power systems face increasing challenges, including space limitations, high copper usage, and significant power conversion losses.
By integrating ROHM’s SiC MOSFETs into next-generation data center power systems, superior performance can be achieved in high-voltage, high-power environments. These devices reduce both switching and conduction losses, improving overall efficiency while ensuring the high reliability demanded by compact, high-density systems.
This not only minimizes energy loss but also reduces copper usage and simplifies power conversion across the entire data center.
- GaN Devices that Provide Greater Efficiency and Miniaturization
While SiC excels in high-voltage, high-current applications, GaN demonstrates outstanding performance in the 100V to 650V range, providing excellent breakdown strength, low on-resistance, and ultra-fast switching.
AI servers process far greater volumes of data than general-purpose servers, requiring high-performance GPUs, large memory capacity, and advanced software. This leads to higher power consumption, making efficient cooling and thermal management increasingly critical.
To address these challenges, GaN HEMTs – capable of high-speed switching (high-frequency operation) – are being integrated into power supply units to minimize power loss. This delivers major gains in power conversion efficiency, translating to substantial energy savings, lower operating costs, and reduced environmental footprint.
What’s more, GaN devices offer high current density, enabling a size reduction of approximately. 30-50% compared to conventional silicon devices. This not only improves space efficiency in power supplies and chargers, but also simplifies thermal design.
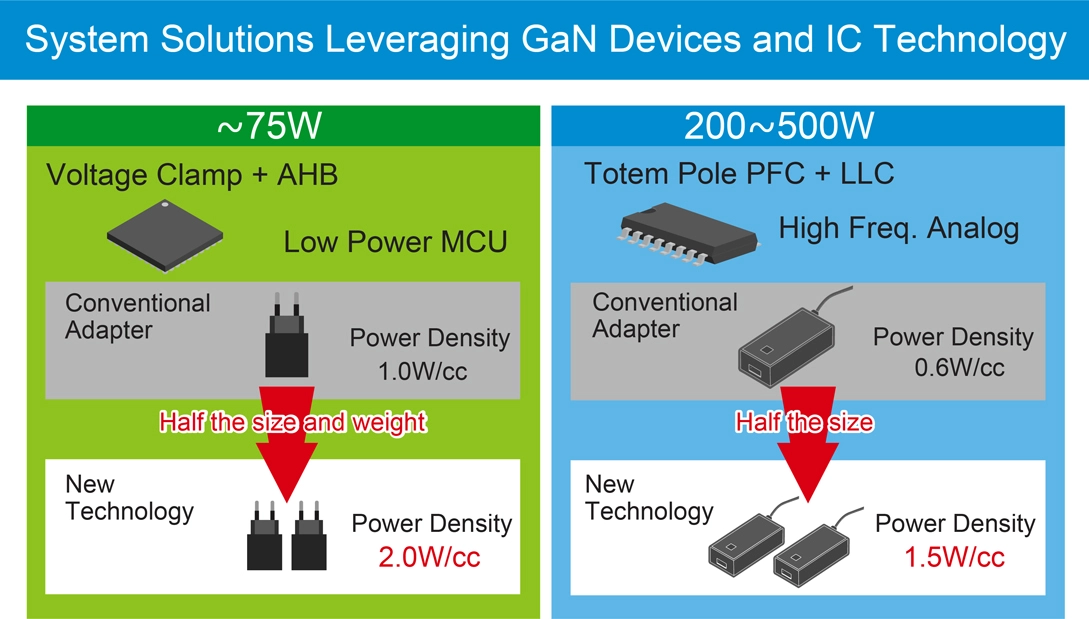
By reducing unit size and making effective use of freed-up space, the load on cooling systems can be alleviated, supporting overall system miniaturization and improved reliability. In addition, GaN’s high durability and suitability for high-frequency applications make it an ideal choice for data centers.
ROHM has succeeded in shortening the pulse width to as little as 2ns utilizing proprietary Nano Pulse Control technology, further enhancing the switching performance of GaN devices. Through the EcoGaN series, ROHM is expanding its lineup to meet the needs of AI data centers demanding compact, highly efficient power systems. The portfolio includes 150V and 650V GaN HEMTs, gate drivers, and integrated solutions that combine these components.
Conclusion
The evolution of AI, which shows no signs of slowing, comes with an inevitable surge in power demand.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global data center electricity consumption is expected to more than double in the next 5 years, reaching approximately 945 billion kWh. Around half of this demand is projected to be met by renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, signaling a major shift in how energy is generated and consumed in the power-hungry data center sector. Technologies like photovoltaics (PV) and energy storage systems (ESS) are gaining traction as essential components of this transformation.
ROHM is actively contributing to this transition with a broad portfolio of advanced power semiconductor technologies, including SiC and GaN devices. These solutions enable high-efficiency power systems tailored for next-generation AI data centers. ROHM is also accelerating the development of new products to meet evolving market needs, supporting a more sustainable and prosperous AI-driven future.
The post Will AI Consume the World’s Electricity? Addressing AI Data Center Demands with Advanced Power Semiconductors appeared first on ELE Times.
Filtronic awarded £1.2m funding to develop 550W Ka-band solid-state power amplifiers
STMicroelectronics streamlines smart-home device integration with industry-first Matter NFC chip
STMicroelectronics has unveiled a secure NFC chip designed to make home networks faster and easier to install and scale, leveraging the latest Matter smart-home standard. ST’s ST25DA-C chip lets users add lighting, access control, security cameras, or any IoT device to their home network in one step by tapping their phone. The chip is the first commercial solution fulfilling newly published enhancements in Matter—the latest open-source standard now making smart home devices secure, reliable, and seamless to use.
“The integration of NFC-based onboarding in Matter 1.5 is a timely enhancement to the smart home experience. Our market-first ST25DA-C chip leverages this capability to simplify device commissioning through tap-to-pair functionality. This reduces setup complexity, especially for installations that are difficult to access, thanks to NFC-enabled battery-less connectivity. This aligns well with the broader momentum in the smart home market to serve consumers who increasingly prioritize ease of use, interoperability, and security. NFC-enabled Matter devices are positioned to play a key role in driving even greater adoption,” said David Richetto, Group VP, Division General Manager, Connected Security at STMicroelectronics.
“Matter is an important standard for the smart-home industry, enabling seamless communication across devices, mobile apps, and cloud services. Its primary benefit is simplifying technology for non-expert consumers, which could help accelerate adoption of connected devices. The new STMicroelectronics’ ST25DA-C secure NFC chip is one example of next generation chipset that supports this standard, providing device makers with tools to develop the next generation of smart-home products,” said Shobhit Srivastava, Senior Principal Analyst at Omdia.
Technical information
Enhanced usability: ST’s new NFC Forum Type 4 chip significantly improves the user experience, leveraging NFC technology present in most smartphone devices. NFC-enabled device commissioning is faster, more reliable, and secure compared to conventional pairing using technologies such as Bluetooth® or QR codes, which are not always possible.
The ST25DA-C secure NFC tag can operate cryptographic operations required for Matter device commissioning using energy harvesting from the RF field. This mechanism allows users to jump-start adding unpowered devices to the smart home network. It also simplifies the installation of multiple accessories in parallel.
Focused on security: The ST25DA-C brings strong security to smart homes, leveraging ST’s proven expertise in embedded secure elements for protecting assets with device authentication, secure storage for cryptographic keys, certificates, and network credentials.
Based on Common Criteria-certified hardware, the ST25DA-C also targets certification to the GlobalPlatform Security Evaluation Standard for IoT Platforms (SESIP level 3).
The post STMicroelectronics streamlines smart-home device integration with industry-first Matter NFC chip appeared first on ELE Times.
Mitsubishi Electric India to Showcase Breakthrough Power Semiconductor Technologies at PCIM India 2025
Mitsubishi Electric India, is set to introduce its flagship cutting edge Power Semiconductor Devices and technology to the Indian market. MEI Participation in PCIM Asia New Delhi 2025 reinforces the company’s commitment on delivering high-efficiency semiconductor solutions to support India’s growing demand in the area of Home appliances, Railway, xEV, renewable energy and industrial Applications.
Visitors at PCIM India 2025 will experience the new DIPIPM platform that integrates inverter circuitry, gate-drive functions and protection features into a single module. These modules enable compact designs and improved system safety. Available in both IGBT and SiC-based versions, the latest Compact DIPIPM and SLIMDIP families are suited for applications such as room air conditioners, washing machines, commercial HVAC, solar pumping and light industrial drives.
Mitsubishi Electric India will also showcase a wider product portfolio, including high-voltage HVIGBT modules, LV100 and NX industrial power modules, and automotive-grade semiconductor platforms engineered for Utility-scale solar inverters, wind converters, EV charging & powertrains, Railway traction converters, HVDC transmission and induction heating. Alongside the Power Modules, Mitsubishi Electric India will also display its latest bare-die SiC MOSFETs and RC-IGBT technology which enables optimal structure, low loss, and high reliability devices for xEV- traction and charging applications.
| Product Line | Key Features |
| DIPIPM (Dual In-line Package Intelligent Power Module) | *Offers CSTBT & RC-IGBT chip technologies in a wide line-up *Available in 600V and 1200V, 5A–100A *Includes SiC-MOSFET variants and new Compact DIPIPM & SLIMDIP series |
| LV100 & NX Power Modules | *Industry-standard IGBT & SiC modules with 7th/8th gen CSTBT chipset and SLC packaging *Voltage: 1200V/1700V/2000V; Current: 225A–1800A *Includes new 8th gen LV100 & NX models |
| HVIGBT (High-Voltage IGBT) | *Modules for traction and power transmission *Voltage options: 1700V, 3300V, 4500V, 6500V; Current: 400A–2400A *High-voltage SiC up to 3300V/175A–800A *Includes new XB Series |
| Power Modules for Automotive | *Designed with integrated cooling fins and DLB technology *The Line-up of 2 in 1 circuit & 6 in 1 circuit with latest SiC & RC-IGBT chip technologies *Available in 750V/1300V, 350A–800A with on-chip current and temperature sensing *Includes new J3 Series |
Speaking on the participation, Mr. Hitesh Bhardwaj, General Manager/Business Head, Semiconductors & Devices, Mitsubishi Electric India said: “India is entering a decisive phase of Power Electronics across mobility, renewable energy infrastructure. With the introduction of latest Si and SiC semiconductor technologies to the domestic market, we aim to empower Indian manufacturers with smarter, more efficient and more reliable technologies. Our long-term vision is to support the country’s innovation ecosystem and contribute to sustainable growth across industry and society.”
With India’s manufacturing ecosystem evolving toward higher energy efficiency standards and smarter power architectures, Mitsubishi Electric India’s latest offering strengthens access to globally proven semiconductor innovation tailored for future-ready applications.
The post Mitsubishi Electric India to Showcase Breakthrough Power Semiconductor Technologies at PCIM India 2025 appeared first on ELE Times.
ASMPT Wins New Orders for Nineteen Chip-to-Substrate TCB Tools to Serve AI Chip Market
ASMPT announced it had won new orders for 19 Chip-to-Substrate (C2S) TCB tools from a major OSAT partner of the leading foundry serving the AI chip market.
ASMPT is the sole supplier and Process of Record (POR) of C2S TCB solutions for this customer, supporting their high-volume manufacturing requirements. These latest systems will enable their next-generation C2S bonding for logic applications as compound die sizes get larger. This demonstrates the customer’s continued confidence in ASMPT’s technological leadership and production-proven capabilities. Looking ahead, ASMPT is well-positioned to secure additional orders in the future.
This continued momentum for ASMPT’s flagship Thermo-Compression Bonding (TCB) solutions reinforces its position as the industry’s leading provider of advanced packaging solutions for artificial intelligence and high-performance computing applications.
“The TCB market is experiencing transformational growth driven by AI and HPC applications,” said Robin Ng, Group CEO, ASMPT. “Our comprehensive technology portfolio spanning chip-on-wafer, chip-on-substrate, and HBM applications positions ASMPT uniquely to support our customers’ most demanding advanced packaging roadmaps. This latest win validates our technology leadership and highlights the market’s recognition of our ability to deliver production-ready, scalable platforms.”
With the largest TCB installed base worldwide consisting of more than 500 tools, ASMPT is strategically positioned to capture between 35% to 40% of an expanded TCB market. ASMPT recently expressed confidence that the TCB Total Addressable Market (TAM) projection will exceed US$1 billion by 2027, bolstered by recent news about AI ecosystem investments.
The post ASMPT Wins New Orders for Nineteen Chip-to-Substrate TCB Tools to Serve AI Chip Market appeared first on ELE Times.
Microchip Halves the Power Required to Measure How Much Power Portable Devices Consume
Battery-operated devices and energy-restricted applications must track and monitor power consumption without wasting power in the process. To solve this challenge, Microchip Technology announced two digital power monitors that consume half the power of comparable solutions based on typical operating conditions at 1024 samples per second. The PAC1711 and PAC1811 power monitors achieve this efficiency milestone while also providing real-time system alerts for out-of-limit power events and a patent-pending step-alert function for identifying variations in long-running averages.
The 42V, 12-bit single-channel PAC1711 and 16-bit PAC1811 monitors are housed in 8- and 10-pin Very Thin Dual Flat, No-Lead (VDFN) packages, respectively, that are pin- and footprint-compatible with the popular Small Outline Transistor (SOT23)-8 package. This compatibility simplifies second-sourcing for developers, while streamlining upgrades and integration into existing systems.
“Until now, portable devices and a variety of energy-constrained applications have needed to burn a significant amount of valuable power to measure how much they are consuming,” said Keith Pazul, vice president of Microchip’s mixed-signal linear business unit. “Unlike many existing solutions, Microchip’s power monitors function as independent ‘watchdog’ peripherals, eliminating the need for the MCU to handle power monitoring tasks. These monitors allow the MCU or host processor to remain dormant until a significant power event occurs such as needing an LCD screen to power on.”
The PAC1711 and PAC1811 power monitors’ step-alert capability keeps a running average of voltage and current values. If there is a significant, user-defined variation, it will notify the MCU to act on it. The devices keep a rolling average, and any new sample can trigger an alert. A slow-sample pin option is available, which can delay the power usage sampling to every eight seconds and further conserve power.
An accumulator register in the power monitor can be used to manage logistical items, track system battery aging or time to recharge, and provide the short-term historical data for long-term power usage that the MCU can be programmed to act on. Both current monitor integrated circuits sense bus voltages from 0 to 42 volts and can communicate over an I2C interface. They are well-suited for first- or second-source options in computing, networking, AI/ML and E-Mobility applications.
The post Microchip Halves the Power Required to Measure How Much Power Portable Devices Consume appeared first on ELE Times.
India needs up to 15,000 crore more investment for PCB manufacturing: JS Gujral, MD, Syrma SGS
In the budget for 2021, the Indian government sanctioned Rs. 76,000 crores for the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM). Today, after nearly five years, there is a need for an additional investment of Rs. 10,000-15,000 crores in the next two to three years to boost domestic PCB manufacturing to reduce import dependency below 50%, according to JS Gujral, MD, Syrma SGS.
Currently, India demands PCBs worth nearly Rs. 50,000 crores, and only 10% of that demand is met locally, while the rest is fulfilled through imports from China, Taiwan and other nations. The aim is to increase the production to a worth of Rs. 20,000 in the next three years when the demand itself will rise to Rs. 70,000 worth.
From the many factors holding India back, the raw material bottle neck is a significant problem. Raw materials make up for nearly 60% of the total cost of the PCB. Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) is one of the primary materials used in PCB manufacturing. It covers nearly 27% of that raw material cost. While India is gradually progressing towards its complete domestic manufacturing, there are other burdens such as the copper foil, pre pregs, and specialized chemicals. These three are largely imported which add to the exorbitant costs of PCBs manufactured in India, making them costly and less competitive in the global market.
Experts recommend the increase in domestic supply for copper foils and necessary raw materials alongside CCL to maintain the competitiveness of locally produced PCBs to meet both national and international demands.
The post India needs up to 15,000 crore more investment for PCB manufacturing: JS Gujral, MD, Syrma SGS appeared first on ELE Times.





