Збирач потоків
The Next Phase of Energy Storage: When Batteries Start Working with the Grid
Authoredby: Rajesh Kaushal, Energy Infrastructure & Industrial Solutions (EIS) Business Group Head, India & SAARC, Delta Electronics India
For decades, the electricity grid operated on a simple principle: power had to be generated at the exact moment it was consumed. Coal plants, gas turbines, and hydro stations were dispatched to follow demand, and the grid was built around predictability and centralised control.
That principle is now being fundamentally rewritten.
As renewable energy becomes central to India’s power system, variability has entered the equation at an unprecedented scale. Solar and wind generation do not follow traditional load curves, and their growing share is changing how grids must be designed and operated. In this new reality, energy storage, particularly Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), is moving from being a supporting technology to becoming a core grid asset.
We are entering the next phase of energy storage, where batteries no longer sit on the sidelines but actively work with the grid.
From Backup to Backbone
In its early years, energy storage in India was largely viewed as backup power, used during outages or in niche, isolated applications. That perception is changing rapidly.
Today, batteries are expected to play a much broader role:
- Smoothing renewable variability
- Managing peak demand
- Deferring transmission upgrades
- Providing frequency and voltage support
- Enabling faster and more resilient grids
According to projections from the Central Electricity Authority, India will require over 82 GWh of total energy storage by 2026–27, with BESS contributing nearly 35 GWh, rising to 411 GWh total by 2031–32, with batteries accounting for over 236 GWh.
These are not incremental additions. They signal a structural shift in how the power system will be planned, operated, and stabilised.
When Policy Meets Scale
A key indicator of this transition is policy clarity and rapidly declining costs.
Recent tariff-based competitive bidding shows that the cost of BESS has plummeted from around ₹10.18 per kWh to approximately ₹2.1 per kWh, assuming two daily cycles. Based on market trends and utilisation patterns, the cost at 1.5 cycles per day is expected to be around ₹2.8 per kWh. This aligns closely with average solar tariffs, making storage increasingly competitive.
India’s policy framework supports this transition:
- Viability Gap Funding schemes supporting 13,220 MWh of BESS capacity with ₹3,760 crore, and an additional 30 GWh with ₹5,400 crore support through the Power System Development Fund.
- Inter-State Transmission System (ISTS) charges waiver for co-located BESS projects for 12 years and graded waivers for non-co-located projects.
- The PLI “National Programme on Advanced Chemistry Cell (ACC) Battery Storage” aims to establish 50 GWh of domestic Advanced Chemistry Cell manufacturing capacity, including 10 GWh for grid-scale applications to reduce import dependency and future costs.
These mechanisms are accelerating adoption and enhancing affordability, shifting storage from pilot projects to mainstream system planning.
Storage Enters Grid Planning
Perhaps the clearest indicator of maturity is how storage is now treated in national planning.
Nearly 47 GW of BESS capacity has already been considered in India’s transmission planning horizon up to 2032. This is a profound change. Batteries are no longer “add-ons” installed after the grid is built. They are being planned alongside transmission lines, substations, and renewable corridors.
This integration unlocks new possibilities:
- Managing congestion without building new lines
- Firming renewable power at the point of injection
- Providing local grid support closer to demand centres
In effect, storage becomes a flexible, digital asset embedded within the physical grid.
When Batteries Start Talking to the Grid
The next phase of energy storage is not defined by chemistry alone. It is defined by intelligence.
A battery that simply charges and discharges on a timer is useful. A battery that communicates with the grid in real time is transformative.
Advanced power electronics, grid-forming inverters, and intelligent control systems allow BESS to:
- Respond instantly to frequency deviations
- Stabilise weak grids with high renewable penetration
- Coordinate with solar and wind plants to deliver dispatchable power
- Support black start and islanding operations
This is where energy storage stops being passive infrastructure and starts behaving like an active grid participant.
At Delta, our energy infrastructure approach is built around this convergence, where power electronics, automation, and digital control come together. Batteries are no longer isolated assets. They operate as part of a wider ecosystem that includes inverters, energy management systems, EV charging infrastructure, and grid interfaces.
Beyond Utilities: Storage Touches Everyday Life
While much of the discussion around BESS focuses on utilities and large-scale projects, the impact of grid-integrated storage is far broader.
For industries, it means improved power quality and reduced exposure to peak tariffs.
For cities, it means greater resilience during extreme weather events.
For renewable developers, it means predictable revenues and bankable projects.
For consumers, it ultimately means a cleaner, more reliable power supply.
Energy storage is becoming an invisible enabler, rarely noticed when it works well, but critical to system reliability when it is absent.
India’s Unique Opportunity
India’s energy transition is happening at a scale and speed few countries have attempted. Peak demand continues to rise, renewable capacity is expanding rapidly, and electrification is accelerating across transport, industry, and households.
This creates a unique opportunity. Instead of retrofitting storage into an aging grid, India can design a future-ready system where renewables, batteries, and digital infrastructure are integrated from the outset.
But success will depend on how well technology, policy, and execution align:
- Clear market signals for ancillary services
- Standards for grid-forming and hybrid systems
- Long-term visibility for manufacturers and developers
- Skill development for operating a more complex, digital grid
A Grid That Thinks, Responds, and Adapts
The next phase of energy storage is not only about adding battery capacity. It is about how the grid itself is designed and operated.
Future power systems will need to sense conditions in real time, respond quickly to changes in demand and supply, and adapt to increasing variability from renewable sources. When batteries are fully integrated into grid operations, they can support frequency regulation, peak management, and network stability more effectively than standalone assets.
India has already begun moving in this direction. Energy storage is being considered within transmission planning, renewable integration strategies, and market mechanisms. The focus now shifts from adoption to optimisation: how efficiently storage can be deployed, controlled, and scaled to deliver maximum system value.
In the years ahead, the grid’s role will extend beyond power delivery. It will increasingly manage energy flows dynamically, with storage playing a central role in enabling reliability, flexibility, and long-term sustainability.
The post The Next Phase of Energy Storage: When Batteries Start Working with the Grid appeared first on ELE Times.
TOYOTA Selects Infineon’s SiC Power Semiconductors for its New, “bZ4X”
Infineon Technologies announced that CoolSiC MOSFETs (silicon carbide (SiC) power MOSFETs) have been adopted in the new bZ4X model from Toyota, the world’s largest automaker. Integrated into the on-board charger (OBC) and DC/DC converter, the SiC MOSFETs leverage the material’s advantages of low losses, high thermal resistance, and high voltage capability to help extend driving range and reduce charging time.
“We are very proud that Toyota, one of the world’s largest automakers, has chosen Infineon’s CoolSiC technology. Silicon carbide enhances the range, efficiency and performance of electric vehicles and is therefore a very important part of the future of mobility,” said Peter Schaefer, Executive Vice President and Chief Sales Officer Automotive at Infineon. “With our dedication and our commitment to innovation and zero-defect quality, we are well-positioned to meet the growing demand for power electronics in electromobility.”
Infineon’s CoolSiC MOSFETs feature a unique trench gate structure that reduces normalised on-resistance and chip size, enabling reductions in both conduction and switching losses to contribute to higher efficiency in automotive power systems. In addition, optimised parasitic capacitance and gate threshold voltage enable unipolar gate drive, contributing to the simplification of drive circuits for automotive electric drive train and supporting high-density, high-reliability design for OBC and DC/DC converters.
The post TOYOTA Selects Infineon’s SiC Power Semiconductors for its New, “bZ4X” appeared first on ELE Times.
STMicroelectronics expands strategic engagement with AWS, enabling high-performance compute infrastructure for cloud and AI data
STMicroelectronics has announced an expanded strategic collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) through a multi-year, multi-billion USD commercial engagement serving several product categories. The collaboration establishes ST as a strategic supplier of advanced semiconductor technologies and products that AWS integrates into its compute infrastructure, enabling AWS to provide customers with new high-performance compute instances, reduced operational costs, and the ability to scale compute-intensive workloads more effectively.
As part of this expanded relationship, ST will work with AWS to optimise electronic design automation (EDA) workloads in the cloud. AWS’s scalable compute power enables silicon design acceleration, parallelises design tasks, and gives engineering teams the flexibility to handle dynamic compute demands and speed products to market.
Commercial Agreement
This engagement covers a broad range of semiconductor solutions leveraging ST’s portfolio of proprietary technologies. ST will supply specialised capabilities across high-bandwidth connectivity, including high-performance mixed-signal processing, advanced microcontrollers for intelligent infrastructure management, as well as analogue and power ICs that deliver the energy efficiency required for hyperscale data centre operations.
The collaboration will help customers reduce the total cost of ownership and bring products to market faster. ST’s specialised technologies help AWS address the increasing demands for compute performance, efficiency, and data throughput required to support growing AI and cloud workloads.
Jean-Marc Chery, ST President & CEO, commented: “This strategic engagement establishes ST as an important supplier to AWS and validates the strength of our innovation, proprietary technology portfolio, and proven manufacturing-at-scale capabilities. Our advanced semiconductor solutions will directly power AWS’s next-generation infrastructure, enabling its customers to push the boundaries of AI, high-performance computing, and digital connectivity. This collaboration positions us ideally for further scale-up across multiple market segments, from data centre infrastructure to AI connectivity, positioning ST at the centre of the AI revolution.”
ST has issued warrants to AWS for the acquisition of up to 24.8 million ordinary shares of ST. The warrants will vest in tranches over the term of the agreement, with vesting substantially tied to payments for ST products and services purchased by AWS and its affiliates. AWS may exercise the warrants in one or more transactions over a seven-year period from the issue date at an initial exercise price of $28.38.
The post STMicroelectronics expands strategic engagement with AWS, enabling high-performance compute infrastructure for cloud and AI data appeared first on ELE Times.
GaN Benefits in Motor Controls
By: Ester Spitale, Technical Marketing Manager, STMicroelectronics and Albert Boscarato, Application Lab Manager, STMicroelectronics

GaN benefits in different applications
The major challenge of power electronics today is dealing with the growing need for improved efficiency and power performance, and at the same time, the constant pursuit of cost and size reductions.
The introduction of Gallium Nitride (GaN) technology, a relatively new wide bandgap compound, moves in this direction, as it becomes increasingly available commercially, its use is growing tremendously.
With a better figure-of-merit (FOM), on-resistance RDS(on), and total gate charge (QG) than silicon counterparts, High-electron-mobility transistor (HEMT) devices based on gallium nitride (GaN) also offer a high drain to source voltage capability, zero reverse recovery charge and very low intrinsic capacitances.
The first application where GaN technology has spread is power conversion: GaN represents the leading solution for improving efficiency, making it possible to meet the most stringent energy requirements. The capability to work at higher switching frequencies enables higher power densities, and therefore reduction of the system dimensions, weight and cost.
Size and energy efficiency are also crucial in electronic motor designs: minimising conduction and switching losses in the drive is key for reducing energy waste.
Performance improvement in motor drivers relying on classic silicon MOSFETs and IGBTs is becoming more difficult as silicon technology approaches theoretical limits for power density, breakdown voltage, and switching frequency. Due to their superior electrical characteristics, GaN transistors are a valid alternative to MOSFETs and IGBTs in high-voltage motor control applications.
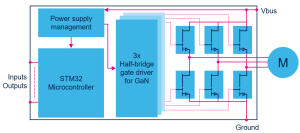 Simplified block diagram of a power inverter based on GaN transistors
Simplified block diagram of a power inverter based on GaN transistors
Fueling the next generation of motor inverters
GaN is promising important benefits even in applications operating at low frequencies (up to 20kHz). In the realm of home appliances, motor-driven systems such as washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, and vacuum cleaners rely heavily on motor inverters to control speed, torque, and efficiency. Unlike industrial servo or precision motors, the physical size of these motors is largely fixed due to mechanical and functional constraints. This means that the traditional approach of reducing overall system size by shrinking the motor itself is not feasible. Instead, improvements must be sought in the inverter and power electronics that drive these motors.
In this sense, it is important to point out that the benefit of GaN over traditional silicon transistors does not come from a single parameter that stands out. It is rather the sum of different aspects concatenating together.
GaN has a de facto negligible reverse recovery charge (Qrr) and low parasitic capacitances, which in turn enable working with slightly higher dV/dt. While the motor winding and insulation limit the maximum allowable dV/dt, GaN’s capability to operate at higher switching speeds allows designers to optimise switching edges carefully.
Moreover, a safe and drastic reduction of dead-time is also achievable without risking shoot-through faults. Time between high-side and low-side switching can be easily lowered by a factor of 10. This can improve inverter efficiency and reduce switching losses without compromising motor reliability.
As remarkable as it gets, the performance is not over yet. In fact, all these “little” improvements combined lead to what may be considered the most relevant of them all: the removal of the heatsink.
Kiss your heatsink goodbye
The considerable reduction in power dissipation allows designers to reduce or even remove bulky heatsinks in the inverter power stage. The assembly line may now require fewer steps in the manufacturing process. No heatsink also means no screws or mounting joints, thus avoiding mechanical failures that can appear when the appliance is already long in the field. An interesting potential saving of service and warranty costs.
The overall result is a more compact, lightweight, and cost-effective inverter design that fits better within the demanding and highly competitive space of the home appliances market.
 700 V GaN mounted on a motor inverter running without a heatsink
700 V GaN mounted on a motor inverter running without a heatsink
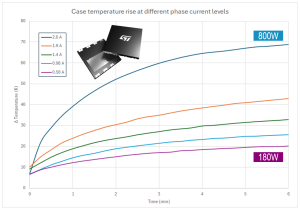
The waveforms show how smooth and cold a GaN can be. In the example above, the device under test has a typical RDS(on) of 80mΩ. The motor inverter runs at a switching frequency of 16 kHz, with a maximum dV/dt slightly under 10V/ns.
A power level of about 800 W can be safely achieved without incurring thermal runaway. The increase in temperature Δt is less than 70 °C, which leaves a good margin before reaching the maximum operating junction temperature (TJmax) of 150 °C.
This remarkable result is achieved without a heatsink, with GaNs mounted on and cooled down through a common 2-layer PCB.
STPOWER GaN Transistors
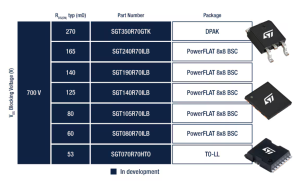
STPOWER GaN Transistors are intrinsically normally off, p-GaN gate e-mode transistors that offer a zero reverse recovery charge. ST offers today seven part numbers rated 700 V breakdown voltage (VDS), with typical on-resistance RDS(on) ranging from 270 mΩ down to 53 mΩ in DPAK, PowerFLAT 8×8, and TO-LL packages.
The portfolio is rapidly growing, adding on different packages, RDS(on) and breakdown voltage levels.
The post GaN Benefits in Motor Controls appeared first on ELE Times.
Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw inaugurates TI’s new, world-class R&D centre
Texas Instruments (TI) officially opened its new, state-of-the-art product research and development (R&D) centre in Bengaluru at an event commemorating the company’s 40-year presence in India. As the first multinational company to establish an R&D centre in India in 1985, TI has been instrumental in shaping India’s semiconductor landscape for four decades. The new 550,000-square-foot centre features a collaborative workspace dedicated to developing world-class chip designs. The centre includes an end-to-end reliability lab equipped with advanced testing capabilities for various environmental conditions, along with many other integrated circuit design labs.
Inaugurated by Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, Union Minister for Railways, Information & Broadcasting, Electronics & Information Technology, Government of India, alongside TI leaders, the new centre highlights the company’s strategic vision to propel semiconductor innovation and nurture world-class design talent. This expansion reinforces TI’s commitment to developing breakthrough analogue and embedded processing technologies while strengthening its support for the design ecosystem and its growing customer base in India.
Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, Union Minister for Railways, Information & Broadcasting; Electronics & Information Technology, Government of India, said, “I congratulate Texas Instruments on the inauguration of this world-class R&D centre in Bengaluru. TI has been a true pioneer in India’s semiconductor journey and stood as a testament to consistently nurturing the design talent ecosystem in India. The company’s expanded investment reinforces India’s position as a global hub for semiconductor design, development and supports our vision of building an innovation-led nation.”
Santhosh Kumar, president and managing director, TI India, said, “As we celebrate 40 years in India, this milestone reflects TI’s rich legacy and our strong commitment to the future. TI India’s product development and design teams drive research and breakthrough innovations for customers worldwide. Our world-class engineers are central to pioneering the next generation of semiconductor advancements.”
The company recently opened an additional sales office to strengthen its partnership with Indian customers, while the new R&D facility builds on its innovation capabilities in the region. With thousands of employees in India, TI continues to expand its presence in the region.
The post Union Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw inaugurates TI’s new, world-class R&D centre appeared first on ELE Times.
Veeco stockholders approve merger with Axcelis
Texas Semiconductor Innovation Fund grants Coherent $14m to accelerate scaled production of InP wafers
Bridging the design-to-deployment gap: How India can lead the next wave of connected device innovation
Hareesh Ramana, Chief Experience Officer, Sasken Group & President, Borqs Technologies (a Sasken Group company)
India is making significant strides in electronics manufacturing with the aim of 38% value addition within five years. The device manufacturing ecosystem has grown to a significant scale, but it still depends heavily on designs and reference architectures developed elsewhere.
Building domestic capability in electronic device design, especially IoT/connected device design, is critical to India’s ambition of becoming a major electronics manufacturing hub. India’s ambition to reach 38% value addition in electronics manufacturing will be driven not only by scaling assembly but by strengthening device design and systems engineering, which can contribute as much as 30-35% of the total value creation.
Need for in-house design capabilities:
A growing model in India’s connected-device ecosystem is design-led, end-to-end IoT product development anchored locally, covering silicon integration, embedded software, connectivity stacks, and certification. Companies like Borqs Technologies (now part of the Sasken Group) exemplify this approach, offering full-stack IoT design capabilities from within India. For OEMs, this can shorten development cycles, improve control over system integration, and reduce dependence on externally sourced IP and engineering capacity, especially in critical connectivity and compliance stages. Expanding these capabilities across the industry can help India move beyond contract manufacturing and toward the higher-value innovation layer where devices connect to data, analytics, and services.
Time to market gap:
Many IoT projects stall because hardware, firmware, cloud platforms, connectivity, and certification are handled by separate vendors with misaligned priorities.
Over the past decade, India’s product development ecosystem has matured to address these challenges, evolving from a cost-centric outsourcing base into a design-led innovation hub. Global OEMs and platform companies increasingly view India as a partner for rapid prototyping and co-innovation, not just low-cost assembly. Several end-to-end product engineering companies in India exemplify this shift by delivering integrated IoT solutions that shorten development cycles and align with global OEM roadmaps.
Integration as a strategic capability
Connected devices are no longer standalone products; they are endpoints of digital services. The differentiator is therefore systems integration across silicon, hardware, software, connectivity, and lifecycle management. A unified, end-to-end engineering model can enable:
- Faster debugging by tightening the feedback loop between hardware and software teams
- Fewer integration issues by reducing handoffs across multiple vendors
- Quicker prototyping and validation through coordinated design and test cycles
- More predictable certification and production ramp by planning compliance and manufacturability early
- A single accountable partner from concept through delivery and lifecycle management
This is particularly vital for industrial-grade devices where reliability, security, and compliance define adoption. Indian engineering firms with cross-layer capabilities are increasingly enabling platform-driven approaches that allow module reuse across verticals like automotive, energy management, and logistics.
AI and advanced technologies and product development:
Advanced technologies like AI, IoT, automation, digital twins, and cloud computing are transforming product development. AI-driven analytics reduce manual testing cycles, while digital twins simulate device behaviour under real-world conditions, enabling faster iteration and higher reliability.
Demand for software-defined vehicles, smart energy infrastructure, automated factories, and connected appliances is accelerating globally. Multinationals are expanding design centres and co-innovation programs in India to build products for both developed and emerging markets.
For India, the opportunity lies in moving beyond contract manufacturing to the high-value layer where devices meet data, analytics, and services. Mastery over sensors, edge intelligence, connectivity stacks, and lifecycle platforms can enable the country to capture a far greater share of the global electronics economy.
The coming decade will reward ecosystems that can bridge the design-to-deployment gap with reliability and speed. India has the talent, digital infrastructure, and entrepreneurial energy to lead this shift. The next step is an integrated approach that unites design, engineering, and manufacturing into a single innovation continuum.
The post Bridging the design-to-deployment gap: How India can lead the next wave of connected device innovation appeared first on ELE Times.
My first Project - Healthtracker
 | Hi everyone, This is my Healthtracker project. This will be my first real 6-Layer PCB I have designed using EasyEDA. I am using the nrf5340 for this low Power Bluetooth application paired with couple i2c peripherals for activitiy, heartrate, time & temp. So I don't run out of storage, I integrated infineon 8-Mbit FRAM. Power is supplied to various DC/DC Buck/Boost converters found at the top. I am planning to programm the SoC using the pinheaders and my DevKit. (pinheaders will be soldered out, after programming and Debugging). Oh, don't be confused with these many throughhole vias; JLCPCB curently doesn't support blind or buried vias.... Have a great day. [link] [comments] |
Wrap solder wick around TO-220 transistors' legs to unsolder it easily.
 | submitted by /u/1Davide [link] [comments] |
Thumbwheel switches: Turning numbers into control

Thumbwheel switches may evoke early digital design, yet their compact precision and tactile feedback keep them indispensable. From setting circuit-board addresses to configuring embedded parameters, they translate simple rotations into reliable numeric codes.
Whether selecting device IDs, adjusting ranges, or defining system values, thumbwheel switches deliver a straightforward interface that endures across industrial, consumer, and embedded applications.
Thumbwheel switches (often abbreviated as TWS) offer a straightforward, tactile method for setting numerical values in electronic instruments and control systems. Each wheel is marked with digits, allowing users to rotate and lock in precise entries without complex circuitry or software.
Their mechanical reliability, clear visual indication, and ease of use have made them a staple in applications ranging from laboratory test equipment to industrial control panels. By combining compact design with intuitive operation, thumbwheel switches continue to serve as a practical solution where accuracy and simplicity are paramount.
Rolling vs. clicking: Choosing your digital dial
While both convert a physical turn into a digital signal, the choice between a thumbwheel and a push-wheel switch comes down to how you prefer to drive your data. The rotary thumbwheel is the high-speed option, featuring a serrated edge that you roll with your thumb to flick through numbers in a single, fluid motion—ideal for quick adjustments across a broad range.
In contrast, the push-wheel is the precision specialist; it keeps the wheel protected behind a window and uses dedicated ‘+’ and ‘−’ buttons to advance the value one crisp click at a time. While the thumbwheel offers intuitive speed, the push-wheel provides tactile certainty and protection against accidental bumps, making it the go-to for industrial settings where every digit counts.

Figure 1 Rotary thumbwheel and push-button thumbwheel switches adjust numerical inputs by rotation or precision clicks. Source: Author
Sidenote: Although rotary thumbwheel and push‑button thumbwheel (push-wheel) switches differ in operation—one using a rotating wheel, the other plus/minus buttons—the term thumbwheel is widely applied as an umbrella designation for both types of digital input switches in industry.
Switch communication mechanisms
Beneath the surface, these switches speak a specific digital language through their pin configurations, typically utilizing binary coded decimal (BCD) or hexadecimal (Hex) outputs to communicate with your controller.
A BCD switch is the standard for human-readable interfaces, cycling strictly from 0 to 9; it’s the perfect fit for decimal-based inputs like a kitchen timer or a thermostat setpoint. However, if your project requires more density, a hexadecimal switch utilizes the same four output pins to provide 16 distinct positions (0–9 and A–F).

Figure 2 Example maps TWS positions to BCD code chart using 8421 pin logic. Source: Author
While both rely on the same 8-4-2-1 weighted logic—where internal contacts bridge a common pin to specific data lines to represent a value—BCD keeps things simple for the end-user, whereas hexadecimal is the preferred choice for technical tasks like setting device addresses or selecting complex software modes in a space-saving format.
As a quick aside, the 8-4-2-1 weighted logic is the most common form of BCD representation. Each decimal digit (0–9) is encoded into a 4-bit binary number, where the bit positions carry weights of 8, 4, 2, and 1 from left to right (MSB to LSB).
Thumbwheel switch output code variants
In practice, thumbwheel switches provide designers with multiple output code formats to match diverse digital system needs. The most common is BCD, where each decimal digit is encoded into a 4-bit binary value for straightforward interfacing with counters and microcontrollers.
Some switches offer decimal output, directly representing the digit without binary conversion. More specialized variants include BCD + Complement, which supplies both the normal BCD code and its inverted form for redundancy or error checking, and BCD Complement, which outputs only the inverted binary representation.
Certain models also support BCH hexadecimal coding, enabling representation of values 0–F in compact 4-bit hexadecimal form, useful in applications requiring extended coding beyond decimal digits. These output options give engineers flexibility to align switch signals with the encoding schemes of displays, logic circuits, or embedded systems, ensuring compatibility and efficient signal processing.
Thumbwheel switches: Key practical notes
In practice, each push-wheel/thumbwheel switch forms a single vertical segment, and multiple segments can be combined to build assemblies of varying sizes. The wheel or buttons enable digit selection from 0 through 9.
In a BCD thumbwheel switch, the common terminal (C) lies on one side, followed by weighted contacts for 8, 4, 2, and 1. Applying a small voltage, for instance 5 VDC, to the common allows the output value to be read by summing the weights of the contacts driven HIGH. For example, selecting digit 3 energizes contacts 1 and 2, both appearing at the common voltage.
Notably, diodes are incorporated into thumbwheel switches to isolate each weighted contact and prevent back-feeding between lines. This ensures that only the intended logic states contribute to the BCD output, protecting the switch and downstream logic from false readings or short circuits.

Figure 3 A practical example illustrates a BCD TWS with diodes installed. Source: Author
Equally important, pull-up and pull-down resistors establish defined default states for the contacts. A pull-up resistor ties an inactive line to logic HIGH, while a pull-down resistor ties it to logic LOW. Without these resistors, floating inputs could drift unpredictably, resulting in noisy or unstable outputs. Together, diodes and pull-up/pull-down resistors guarantee that BCD thumbwheel switches deliver clean, reliable, and unambiguous digital signals to the system.
Keep note at this point that datasheets for thumbwheel switches consistently caution against exceeding their specified voltage and current limits. These devices are usually intended for logic interfacing, with ratings of only a few volts and currents in the milliampere range. Operating them beyond these limits can lead to contact wear, unstable outputs, or permanent failure. As emphasized in manufacturer specifications, designers should strictly adhere to the stated ratings and apply recommended best practices to ensure reliable performance.
Also, it’s critical to distinguish between the Switch Rating and the Carry Rating when selecting a thumbwheel switch. The Switch Rating defines the maximum current allowed while the dial is in motion; exceeding this causes electrical arcing that can erode the gold plating on the contacts. In contrast, the Carry Rating is significantly higher because it applies only when the dial is stationary and the contacts are firmly seated, eliminating the risk of arcs.

Figure 4 Datasheet snippet highlights the key specifications of a thumbwheel switch. Source: C&K Switches
So, to maximize component life when interfacing with PLC inputs, many engineers employ cold switching. This involves adjusting the thumbwheel only when the circuit is de-energized, allowing the switch to operate within its higher carry capacity rather than its lower switching capacity. This practice eliminates the risk of electrical arcing across the contacts during transitions, thereby preventing signal noise and extending the operational life of the switch.
The click that counts
That marks the end of this quick take on thumbwheel switches. While we have covered a flake of theory and some essential practical pointers, there is always more to explore—from advanced BCD logic to creative modern retrofits. These switches may be a “classic” technology, but their reliability and tactile feedback still offer unique value in a touchscreen world.
What is your take? Are you planning to use thumbwheels in your next project, or do you have a favorite “old-school” component that still outperforms modern alternatives? Leave a comment below and share your experience; I would love to hear how you are putting these switches to work.
 T. K. Hareendran is a self-taught electronics enthusiast with a strong passion for innovative circuit design and hands-on technology. He develops both experimental and practical electronic projects, documenting and sharing his work to support fellow tinkerers and learners. Beyond the workbench, he dedicates time to technical writing and hardware evaluations to contribute meaningfully to the maker community.
T. K. Hareendran is a self-taught electronics enthusiast with a strong passion for innovative circuit design and hands-on technology. He develops both experimental and practical electronic projects, documenting and sharing his work to support fellow tinkerers and learners. Beyond the workbench, he dedicates time to technical writing and hardware evaluations to contribute meaningfully to the maker community.
The post Thumbwheel switches: Turning numbers into control appeared first on EDN.
I was losing my mind
 | I couldn't for the life of me understand why the multimeter was not reading correctly when using bananas to crocodile cables. Lesson learned: don't cheap out on cables. [link] [comments] |
Weekly discussion, complaint, and rant thread
Open to anything, including discussions, complaints, and rants.
Sub rules do not apply, so don't bother reporting incivility, off-topic, or spam.
Reddit-wide rules do apply.
To see the newest posts, sort the comments by "new" (instead of "best" or "top").
[link] [comments]
"PONG Behind Glas" - PONG SYZYGY E - A replica of the first globally popular video game
 | PONG has always fascinated me. A video game made entirely from logic blocks from the 74xx series. Without a processor, memory or software. After seeing an original PONG console at the Berlin Computer Game Museum, I set myself the goal of recreating one. And now it's finished. I didn't want to use the large arcade cabinet like the original as the ‘housing’, but something smaller that would focus on the circuit board. Because it is the ‘star’ of PONG. Ingeniously designed by Allen Alcorn, who went down in computer gaming history as the designer of PONG. But as I said, it's not a computer. I redesigned the circuit board from photos and templates. Conductor track by conductor track, component by component. The ICs are still relatively easy to obtain (I also recreated an Apple I, which was more difficult, or rather almost impossible nowadays). The control panel also had to be the same as the original, and of course a real coin validator had to be included. [link] [comments] |
"Mona Lisa" recreated using about 10,000 SMD components
 | This “Mona Lisa” was created as a technical demonstration by a by a Japanese company that provides PCB assembly (PCBA) services. Instead of using PCB traces or silkscreen artwork, this piece is built from about 10,000 1608-metric SMD components. The image is formed through the color variation of resistors, ceramic capacitors and other components, turning electronic parts into a high-resolution mosaic. [link] [comments] |
ESP32-S3 vision development board – component-level schematic overview
 | This post presents a component-level schematic overview of an ESP32-S3-based vision development board. The shared material focuses strictly on electronic circuit design and interconnection of active components, including the MCU core, power regulation, and peripheral interfaces. Primary active components shown in the schematic: - ESP32-S3-WROOM system-on-chip - DVP camera interface connected directly to the MCU - 6-axis IMU interfaced over I2C - MEMS microphone connected via I2S - SPI-based microSD card interface - Dedicated voltage regulation stages supplying RF, camera, and sensor domains The circuit design integrates vision, motion sensing, and wireless communication on a single ESP32-S3 platform. Power integrity, signal routing density, and pin multiplexing constraints are central factors influencing the schematic structure. The schematic is provided for component-level reference and electronic circuit visibility. Since it's newly created, it doesn't have a GitHub repository yet. [link] [comments] |
Just made this module that converts 12v to 5v or 3.3v (I know I have bad wiring)
 | submitted by /u/Vast_Image_4828 [link] [comments] |
PCB Art - Boston's Red Line
 | I love maps, transit, and DIY electronics- here is my recent project combining all three! I had an 8"x10" PCB manufactured with a custom map of Boston silkscreened on the front side. On this map, each station on the Red Line is marked by two LEDs- one for inbound and outbound trains. Data is streamed from the MBTA's API and displayed on the board, showing location, speed, or occupancy information. This version utilizes WS2812B-2020 LEDs and a very simple two-layer PCB. For future projects, I would be interested in using rear-mounted LEDs (such as SK6812-Es) for a more polished look. If you're interested in the project, all of the code, PCB files, and tutorials are open source: https://github.com/tomunderwood99/CharlieBoard [link] [comments] |



