Feed aggregator
Uchi Embedded Solutions at electronica and productronica 2024: Pioneering Tools and Components for Embedded Systems and IoT Development
At Electronica and Productronica 2024, ELE Times caught up with Mr. Babu Ayyappan, Managing Director of Uchi Embedded Solutions. He shared insights about their focus on embedded systems and IoT development, quality assurance, and experiences at the event.
ELE Times: Let’s start by understanding what Uchi Embedded Solutions does and the product portfolio you have displayed at the event this year.
Mr. Babu Ayyappan: Good evening. At Uchi Embedded Solutions, we focus on tools and components for embedded systems and IoT development. It’s a niche field. For instance, an embedded system developer may require tools like debugging and programming tools. We cater to that segment. In IoT development, the process often begins by selecting the chip for development. One of the key products we are promoting is the ESP32 chip, which is widely used in IoT applications. These two segments—embedded systems and IoT—are our primary focus areas.
ELE Times: You’ve mentioned embedded solutions and IoT. Are there any specific trends or changes you’ve observed in these fields over the years?
Mr. Babu Ayyappan: I wouldn’t say there’s anything drastically new, but these fields have always demanded high-quality products. Embedded system developers often face challenges in selecting the right tools because of the plethora of options available in the market. We try to address this by offering global tools that are economical and come from well-known, reliable brands. At events like this, we aim to promote these quality products and grab the audience’s attention.
ELE Times: Can you elaborate on your sales network and distribution channels?
Mr. Babu Ayyappan: Certainly. As a distribution company, we’ve partnered with about 12 vendors from countries like Taiwan, the UK, the US, Germany, and China. We keep our product lines limited to around 12, focusing on quality over quantity. Operating from Bangalore, we manage our sales across India. Thanks to modern connectivity, this model works efficiently. For marketing, we employ a one-man-show approach in major cities like Pune, Mumbai, and Delhi, where we have residential engineers covering the market. This setup works well for us.
ELE Times: Quality and safety are always critical when it comes to components. How does Uchi ensure these aspects in its products?
Mr. Babu Ayyappan: As a distributor, our primary responsibility is to bring quality products to India. We carefully select companies based on their market reputation and business practices. Today, with globalization, anyone can purchase products from anywhere. However, the same product—say, a branded product from Espressif—can be sourced from multiple suppliers. At Uchi, we work directly with authorized distributors. We don’t go through third-party mediators to save costs or speed up imports because we can’t vouch for their practices. By maintaining direct relationships with trusted suppliers, we ensure we import only quality products. That’s the extent of control we have as a distributor in a vast global market.
ELE Times: How has your experience at this year’s event been? Did it meet your expectations, and what are your future plans?
Mr. Babu Ayyappan: Exhibitions serve multiple purposes for us. They allow us to meet customers we might not otherwise encounter, reconnect with existing ones, and engage new prospects. Consistent participation also strengthens our brand reputation, signaling industry commitment. While immediate ROI isn’t always guaranteed, the long-term benefits make the effort worthwhile. Overall, it has been a rewarding experience.
The post Uchi Embedded Solutions at electronica and productronica 2024: Pioneering Tools and Components for Embedded Systems and IoT Development appeared first on ELE Times.
CES 2025: Approaches towards hardware acceleration

Edge computing has naturally been a hot topic at CES with companies highlighting a myriad of use cases where the pre-trained edge device runs inference locally to produce the desired output, never once interacting with the cloud. The complexity of these nodes has grown to not only include multimodal support with the fusion and collaboration between sensors for context-aware devices but also multiple cores to ratchet up the compute power.
Naturally, any hardware acceleration has become desirable with embedded engineers craving solutions that ease the design and development burden. The solutions vary where many veer towards developing applications with servers in the cloud that are then virtualized or containerized to run at the edge. Ultimately, there is no one-size-fits-all solution for any edge compute application.
It is clear that support for some kind of hardware acceleration has become paramount for success in breaking into the intelligent embedded edge. Company approaches to the problem run the full gamut from hardware accelerated MCUs with abundant software support and reference code, to an embedded NPU.
Table 1 highlights this with a list of a few companies and their hardware acceleration support.
|
Company |
Hardware acceleration |
Implemented in |
Throughput |
Software |
|
NXP |
eIQ Neutron NPU |
select MCX, i.MX RT crossover MCUs, and i.MX applications processors |
32 Ops/cycle to over 10,000 Ops/cycle |
eIQ Toolkit, eIQ Time Series Studio |
|
STMicroelectronics |
Neural-ART Accelerator NPU |
STM32N6 |
up to 600 GOPS |
ST Edge AI Suite |
|
Renesas |
DRP-AI |
RZ/V2MA, RZ/V2L, RZ/V2M |
– |
DRP-AI Translator, DRP-AI TVM |
|
Silicon Labs |
Matrix Vector Processor, AI/ML co-processor |
BG24 and MG24 |
– |
MVP Math Library API, partnership with Edge Impulse |
|
TI |
NPU |
TMS320F28P55x, F29H85x, C2000 and more |
Up to 1200 MOPS (on 4bWx8bD) Up to 600 MOPS (on 8bWx8bD) |
Model Composer GUI or Tiny ML Modelmaker |
|
Synaptics |
NPU |
Astra (SL1640, SL1680) |
1.6 to 7.9 TOPS |
Open software with complete GitHub project |
|
Infineon |
Arm Ethos-U55 micro-NPU processor |
PSOC Edge MCU series, E81, E83 and E84 |
– |
ModusToolbox |
|
Microchip |
AI-accelerated MCU, MPU, DSC, or FPGA |
8-, 16- and 32-bit MCUs, MPUs, dsPIC33 DSCs, and FPGAs |
– |
MPLAB Machine Learning Development Suite, VectorBlox Accelerator Software Development (for FPGAs) |
|
Qualcomm |
Hexagon NPU |
Oryon CPU, Adreno GPU |
45 TOPS |
Qualcomm Hexagon SDK |
Table 1: Various company’s approaches for hardware acceleration.
Synaptics, for instance, has their Astra platform that is beginning to incorporate Google’s multi-level intermediate representation (MLIR) framework. “The core itself is supposed to take in models and operate in a general-purpose sense. It’s sort of like an open RISC-V core based system but we’re adding an engine alongside it, so the compiler decides whether it goes to the engine or whether it works in a general-purpose sense.” said Vikram Gupta, senior VP and general manager of IoT processors and chief product officer, “We made a conscious choice that we wanted to go with open frameworks. So,whether it’s a Pytorch model or a TFLite model, it doesn’t matter. You can compile it to the MLIR representation, and then from there go to the back end of the engine.” One of their CES demos can be seen in Figure 1.

Figure 1: A smart camera solution showing the Grinn SoM that uses the Astra SL1680 and software from Arcturus to provide both identification and tracking. New faces are assigned an ID and an associated confidence interval that will adjust according to the distance from the camera itself.
TI showcased its TMS320F28P55x C2000 real-time controller (RTC) MCU series with an integrated NPU with an arc fault detection solution for solar inverter applications. The system performs power conversion while at the same time doing real-time arc fault detection using AI. The solution follows the standard process of obtaining data, labeling, and training the arc fault models that are then deployed onto the C2000 device (Figure 2).

Figure 2: TI’s solar arc fault detection edge AI solution
One of Microchip’s edge demos detected true touches in the presence water using its mTouch algorithm in combination with their PIC16LF1559 MCU (Figure 3). Another solution highlighted was in partnership with Edge Impulse and used the FOMO ML architecture to perform object detection in a truck loading bay. Other companies, such as Nordic Semiconductor, have also partnered with Edge Impulse to ease the process of labeling, training, and deploying AI to their hardware. The company has also eased the process of leveraging NVIDIA TAO models to adapt well-established AI models to a specific end-application on any Edge-Impulse-supported target hardware.

Figure 3: Some of Microchip’s edge AI solutions at CES 2025. Truck loading bay augmented by AI in partnership with Edge Impulse (left) and a custom-tailored Microchip solution using their mTouch algorithm to differentiate between touch and water (right).
Aalyia Shaukat, associate editor at EDN, has worked in the design publishing industry for six years. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering from Rochester Institute of Technology, and has published works in major EE journals as well as trade publications.
Related Content- CES 2025: A Chat with Siemens EDA CEO Mike Ellow
- Software-defined vehicle (SDV): A technology to watch in 2025
- ADI’s efforts for a wirelessly upgraded software-defined vehicle
- CES 2025: Moving toward software-defined vehicles
The post CES 2025: Approaches towards hardware acceleration appeared first on EDN.
Tektronix soldering videos put online
 | submitted by /u/Linker3000 [link] [comments] |
3 different displays
 | I thought it was interesting that my parents' new car has 3 different types of electronic display! Some kind of LED/dot matrix in the center console, LCD on the instrument panel, and a normal (tiny) pixelated screen up on the dash. [link] [comments] |
Dev kit uses backscatter Wi-Fi for low-power connectivity

HaiLa Technologies has introduced the EVAL2000 development board, featuring its BSC2000 passive backscatter Wi-Fi chip and ST’s STM32U0 MCU. The platform empowers developers and researchers to create ultra-low-power connected sensor applications over Wi-Fi.

The BSC2000 is a monolithic chip that combines analog front-end and digital baseband components to implement HaiLa’s backscatter protocol for 802.11 1-Mbps Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) over Wi-Fi. By using backscattering, it enables low-power communication by reflecting existing Wi-Fi signals instead of generating its own. This allows devices to transmit data with minimal energy consumption. Leveraging readily available, standard Wi-Fi infrastructure, the BSC2000 backscatter Wi-Fi chip collects and transmits sensor data with power efficiency that extends the life of battery-operated sensors.
The EVAL2000 development board accelerates prototyping with GPIO, I2C, and SPI sensor interfaces. Sensor integration is handled through firmware on the MCU. The kit also includes an onboard temperature/humidity sensor.
The BSC2000 EVAL2000 development kit is available for preorder, with shipping anticipated for Q1 2025. For more information on the backscatter Wi-Fi chip and development kit, click here.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Dev kit uses backscatter Wi-Fi for low-power connectivity appeared first on EDN.
SoC supports multiple wireless protocols

The Talaria 6 family of SoCs from InnoPhase provides Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth 6.0, Thread, and Zigbee connectivity, along with PSA Level 2 and Level 3 security. Powered by an Arm Cortex-M33 processor and a rich peripheral suite, the SoCs offer the computational performance needed for real-time, on-chip edge AI tasks, including predictive maintenance, sensor analytics, and smart power management.

Talaria 6 wireless SoCs support Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and are Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) ready, achieving ultra-low power and high-performance connectivity. Integrated digital CMOS radio technology ensures robust throughput in noisy, high-density environments, making them well-suited for smart thermostats, video cameras, and sensors.
Single and dual-band options (2.4 GHz/5 GHz) offer flexible band selection based on use case and network conditions. IEEE 802.11be extensions and multi-link operation improve throughput, lower latency, and increase reliability in congested environments.
Additionally, the SoCs support Bluetooth 6.0, Bluetooth Classic, Thread, and Zigbee mesh networks, enabling seamless integration with a wide range of IoT devices. To protect against cybersecurity threats, Talaria 6 devices feature hardware-based encryption, secure boot, and tamper resistance, safeguarding sensitive data and meeting PSA Level 2 and Level 3 security standards.
The INP6120 2.4-GHz Wi-Fi 6 SoC is expected to sample in Q2 2025, with production starting in Q4 2025. The INP6220 dual-band 2.4/5-GHz Wi-Fi 6 SoC will sample in the second half of 2025, with production beginning in the first half of 2026.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post SoC supports multiple wireless protocols appeared first on EDN.
Synaptics partners with Google to advance edge AI

Synaptics is pairing Google’s ML core with its Astra AI-native hardware and open-source software to simplify context-aware IoT device development. The MLIR-compliant core on Astra hardware accelerates AI processing for vision, image, voice, sound, and other modalities. This combination enables intuitive interaction in wearables, appliances, entertainment systems, embedded hubs, monitoring, and control across consumer, automotive, enterprise, and industrial applications.

The Astra AI-native compute platform for IoT integrates scalable, low-power edge compute silicon with open-source, user-friendly software, robust tools, a strong partner ecosystem, and wireless connectivity. Built on Synaptics’ expertise in neural networks, proven AI hardware, and compiler design for IoT, the platform also supports a wide range of modalities with refined in-house solutions. Google’s ML core, a highly efficient open-source machine learning core, is MLIR-compliant, enhancing compatibility with modern compilers.
For more information about Synaptics’ Astra embedded processors for AI-native IoT, click here.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Synaptics partners with Google to advance edge AI appeared first on EDN.
Mitsubishi samples high-voltage IGBT modules

Mitsubishi announced that it has begun shipping samples of two new S1-Series high-voltage IGBT modules rated at 1.7 kV. These two components are useful for large industrial equipment, such as railcars and DC power transmitters. With proprietary IGBT devices and advanced insulation structures, the S1-Series modules enhance reliability, minimize power loss, and reduce thermal resistance, supporting more reliable and efficient operation of inverters in large industrial equipment.

The S1-Series incorporates Mitsubishi’s Relaxed Field of Cathode (RFC) diode, increasing the Reverse Recovery Safe Operating Area (RRSOA) by 2.2 times over previous models, improving inverter reliability. Additionally, an IGBT element with a Carrier Stored Trench Gate Bipolar Transistor (CSTBT) structure reduces power loss and thermal resistance, enabling more efficient inverter operation. The upgraded insulation structure boosts insulation voltage resistance to 6.0 kVRMS—1.5 times higher than earlier products—allowing more flexible insulation designs for compatibility with a broader range of inverter types.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Mitsubishi samples high-voltage IGBT modules appeared first on EDN.
imec reports first full wafer-scale fabrication of electrically pumped GaAs-based nano-ridge lasers on 300mm silicon
Teledyne Imaging Sensors places repeat order for Riber MBE 412 cluster system
New R&S SMW200A and R&S SMM100A vector signal generators feature significantly improved EVM performance
Rohde & Schwarz has upgraded its industry leading R&S SMW200A vector signal generator and its midrange counterpart, the R&S SMM100A. With significant enhancements in error vector magnitude (EVM) performance, the evolved R&S SMW200A is a robust choice for both 5G NR FR3 research and high demand RF applications like power amplifier testing. The instrument now also includes a new RF linearization software option, which uses digital pre distortion to optimize EVM at high output power. The R&S SMM100A has also been upgraded with improved EVM capabilities.
Rohde & Schwarz has introduced the latest evolution of its two vector signal generators, the signature R&S SMW200A for the most demanding applications, and its midrange counterpart, the best-in-class R&S SMM100A. Besides a redesigned front panel and user interface, the R&S SMW200A has been equipped with modified microwave hardware for enhanced error vector magnitude (EVM) performance as well as higher output power in the frequency range above 20 GHz. This addresses the demands of 5G NR FR2 research and RF component and module testing.
This upgrade comes with an RF linearization software option R&S SMW-K575, which utilizes digital pre distortion technology to optimize EVM at high output power. This ensures high accuracy and stability, even for complex modulation schemes in the entire frequency range.
These key upgrades also extend to the R&S SMM100A, the midrange counterpart of the R&S SMW200A. The R&S SMM100A also comes with a new low phase noise option, R&S SMM B709. With this option, the R&S SMM100A can provide, for example, an EVM performance better than –53 dB for an IEEE802.11be signal with a bandwidth of 320 MHz.
Customers with previous models of the R&S SMW200A or R&S SMM100A can also benefit from the new performance enhancements offered by R&S SMx-K575 RF linearization: Rohde & Schwarz offers retrofit options through a simple service and calibration process.
Gerald Tietscher, Vice President of Signal Generators, Power Supplies and Meters at Rohde & Schwarz, says: “With increasing data rates and modulation scheme complexity, achieving low EVM is critical for ensuring stability and robustness in wireless connectivity applications. The latest evolution of our R&S SMW200A and R&S SMM100A vector signal generators is a testament to our commitment to making our art
of signal generation even better. With their superior RF characteristics and exceptional EVM performance, these instruments are a pivotal resource for handling the requirements of the most advanced test applications.”
The post New R&S SMW200A and R&S SMM100A vector signal generators feature significantly improved EVM performance appeared first on ELE Times.
Smart Clothes Definition, Working, Technology & Applications
Smart clothes, also known as e-textiles or wearable technology, are garments embedded with sensors, actuators, and other electronic components that enable them to interact with the wearer and environment. These clothes can monitor various health parameters, provide connectivity, and even adapt to the user’s needs.
How Do Smart Clothes Work?
Smart clothes work through integrated sensors and actuators that can detect physical movements, environmental factors, and biological signals. These sensors collect data such as heart rate, body temperature, moisture levels, posture, or even muscle activity. The data is then transmitted to a connected device (like a smartphone or cloud server) for analysis and real-time feedback. Smart fabrics may also have embedded conductive threads that allow them to transmit electrical signals.
Some smart clothes are powered by flexible batteries, solar cells, or energy harvested from movement (like piezoelectric materials), making them lightweight and functional.
Smart Clothes Technology
The core technologies in smart clothes include:
- Conductive fabrics and threads: Materials capable of transmitting electricity, enabling the integration of sensors and circuits into fabrics.
- Flexible sensors: Lightweight sensors that measure things like temperature, pressure, motion, and even muscle activity.
- Wireless communication: Bluetooth, NFC, or Wi-Fi to send data from the clothes to external devices.
- Power sources: Small batteries or energy-harvesting systems like solar cells or kinetic energy converters.
Smart Clothes Applications
- Health and Fitness Monitoring: Smart clothes like heart rate-monitoring shirts, posture-correcting jackets, and smart sports bras help track and analyze physical activity, vital signs, and performance metrics in real-time.
- Medical and Rehabilitation: Some garments are designed for patients, offering features like tracking vital signs, muscle movements, and even aiding muscle stimulation.
- Safety: Smart clothes can include features like LED lights for better visibility for cyclists, workers, and runners, and GPS for tracking.
- Fashion and Aesthetics: Garments with integrated displays that change patterns or colors based on the environment or user input.
- Climate Control: Thermal adaptive clothing adjusts to body temperature, providing cooling or heating effects.
- Workplace Use: In sectors like construction, smart clothing can alert workers about their posture, fatigue, or physical stress.
Smart Clothes Advantages
- Health Monitoring: They enable continuous monitoring of health metrics like heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature, which can be used for preventive health care.
- Improved Performance: Athletes and fitness enthusiasts can track performance and adjust their training based on real-time data.
- Enhanced Safety: In work environments, smart clothes can provide early warnings about hazardous conditions, track worker location, or improve visibility.
- Personalized Comfort: With adaptive features, smart clothes can adjust their temperature, moisture level, or fit according to environmental conditions and personal preferences.
- Convenience: The integration of technology into clothes reduces the need to carry separate gadgets and can be more discreet and comfortable compared to wearables like watches or fitness bands.
Smart clothes continue to evolve, combining the worlds of fashion, health, technology, and convenience into one seamless experience.
The post Smart Clothes Definition, Working, Technology & Applications appeared first on ELE Times.
The battery-management technology that will strengthen our grid
Semiconductor innovations in battery systems are leading to energy storage adoption
Takeaways
- Power grids weren’t designed to handle new types of electricity demands and supplies.
- Battery energy storage systems are key to transforming and protecting the grid.
- Innovation in battery-management and high-voltage semiconductors help grids get the most out of battery storage.
The growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the transition to more renewable energy sources are reducing our more-than-century-long reliance on fossil fuels. Electric utilities are increasingly turning to solar panels and wind turbines rather than natural gas-fueled turbines to generate the electricity needed to charge EVs, as well as help power our homes and businesses. Together, these trends are poised to bring us closer to a sustainable energy future.
Those same trends also pose a big challenge to the electricity grid. Demand can vary throughout the day – and so can supplies of solar and wind energy based on changes in the weather. That’s why batteries are becoming an essential component of the grid.
“Batteries can fill in the gap when it’s cloudy and the wind dies down,” said Richard Zhang, a Virginia Tech professor who teaches power electronics and has worked in the grid and energy industry for 25 years. “And batteries improve the economics of electricity because they can be charged during off-peak times, providing electricity for charging EVs at peak times.”
Getting batteries to safely, reliably and cost-effectively store and release the large amounts of electricity running through the grid is a complex challenge. That’s where our company’s expertise in providing advanced battery-management semiconductor solutions can make a big difference.
“The bigger, higher-voltage batteries used in the grid require better thermal management and more precise monitoring,” said Samuel Wong, our company’s vice president and general manager of Battery Management Solutions. “Effectively managing those batteries requires understanding battery chemistry and adapting high-performance semiconductor devices to safely get the most out of each battery.”
Smoothing out the gridThe adoption of solar and wind generation and EVs is good news for the planet, Richard said. The problem is that power grids weren’t originally designed to handle these new types of electricity demands on available energy.
“Getting people to switch to EVs is easier today than it was just a few years ago,” he said. “Now the growing issue is getting the electricity infrastructure to handle them, alongside other energy demands.”
The challenge, Samuel said, is grid instability – in other words, fluctuations in electricity generation and usage. Variations in energy supply occur in solar and wind generation, especially the complete loss of solar power at night. Supply and demand swings may also occur from the charging routines of EV owners.
“If everyone comes home in the evening and plugs in their EVs for the night, the grid might not be able to handle it,” he said.
Samuel and Richard, like most power experts, agree on the solution to grid instability: energy storage systems (ESS). Storage systems – usually in the form of batteries – can capture and hold excess energy in the grid when supply is high and demand is low, and then make it available at other times. You may be picturing the relatively small, light battery cells used in EVs. But for the grid, an ESS might consist of a railroad-car-sized stack of bigger, heavier cells that each can operate at as much as 4 megawatt-hours (MWh) – enough energy to power thousands of homes.
Staging storage systems at different points in the grid optimizes their ability to distribute enormous amounts of electricity to neighborhoods when and where they’re needed. That can mean placing an ESS alongside a solar panel farm, where it can soak up the excess energy during the day and then pump it back out to the grid at night. Or, an ESS placed in a community can more easily grab energy from local rooftop solar panels and later supply the extra electricity needed to charge nearby EVs. “An ESS can serve as a local reservoir for the community,” Samuel said.
Managing battery and system performanceAt the heart of storage systems are high-voltage battery modules – typically lithium-iron phosphate cells – capable of generating enormous amounts of heat if charged or discharged too quickly. These modules can also have shortened lifetimes if completely depleted too often.
Monitoring temperature and charge in these batteries requires extremely precise semiconductors, such as the BQ79616 industrial battery monitor, Samuel said. That’s because even tiny fluctuations in temperature and voltage can signal that a battery may need attention.
“You have to get to millivolt accuracy to know how much charge is left in a battery,” he said.
Our company’s extensive experience in ultra-precise battery monitors is proving essential in helping the ESS industry produce systems that can supply the grid with vital battery-management data. The results can have a big impact on the cost-effectiveness of a grid ESS, Samuel said.
“If you can only measure the charge in a 10-MWh ESS with 5% accuracy, then you can’t safely use more than 9.5 MWh,” he said. “Our battery monitors can get the accuracy measurement to 1%, which enables you to use 9.9 MWh.”
In addition to accurate battery monitoring, grid-scale energy storage systems such as the ones integrated with solar panel farms require efficient high-voltage power conversion that help reduce power losses when transferring power to and from the grid. These systems also rely on sensing and isolation technologies that help maintain system safety and stability, which is critical for managing electricity flow as high as 1500 V.
Impacting the futureFor the foreseeable future, innovation in battery ESS looks to be the key to transform and protect the grid from the variabilities coming from solar and wind energy, as well as EV charging.
“It’s really exciting to contribute to strengthening the grid with innovations in energy storage,” Samuel said. “We can already do a lot today, and we’ll be able to do a lot more as we build out tomorrow’s smart grid.”
The post The battery-management technology that will strengthen our grid appeared first on ELE Times.
ROHM samples 1kW-class high-power IR laser diode
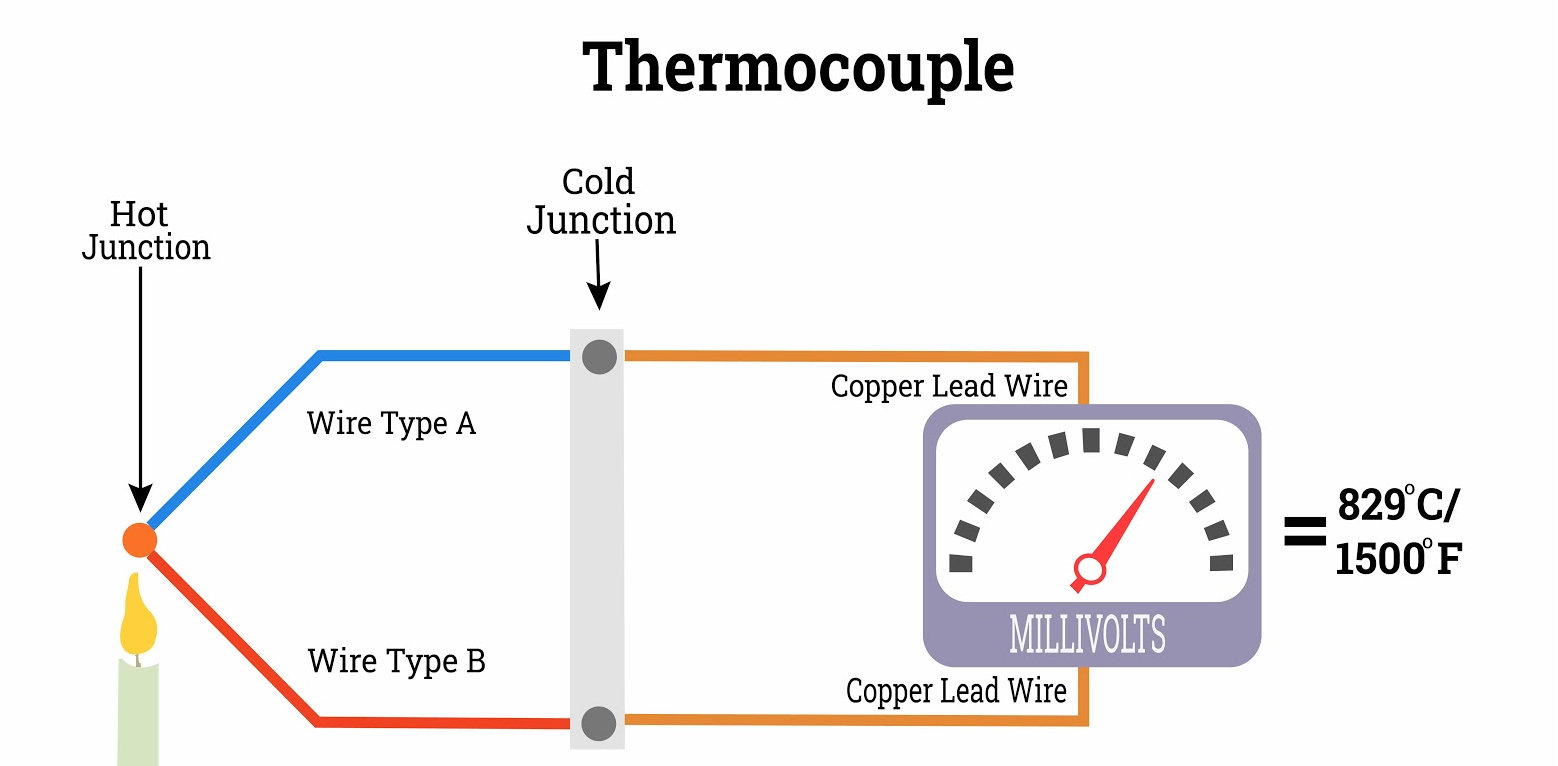
RTD vs Thermocouple vs Thermistor: Understanding Temperature Sensors
Temperature sensors are critical components in a variety of industries, from manufacturing and automotive to healthcare and environmental monitoring. Among the most common temperature-sensing devices are Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs), thermocouples, and thermistors. Each of these sensors has unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations, making them suitable for different applications. This article provides a detailed comparison to help you choose the right sensor for your needs.
- Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs)
RTDs measure temperature by correlating the resistance of a material (usually platinum) to temperature. Platinum is preferred because of its stability and linear resistance-temperature relationship.
Key Features of RTDs:
- Accuracy: RTDs deliver exceptional precision, typically within ±0.1°C.
- Stability: They provide outstanding consistency and reliable performance over long durations.
- Temperature Range: Commonly operate effectively between -200°C and 600°C.
- Linearity: RTDs exhibit a near-linear relationship between resistance and temperature, simplifying data interpretation.
Advantages:
- Highly precise and reliable.
- Extended operational life with negligible performance degradation over time.
- Suitable for industrial and laboratory settings.
Limitations:
- Expensive compared to thermocouples and thermistors.
- Fragile and sensitive to physical shocks and vibrations.
- Requires external circuitry for resistance measurement.
- Thermocouples
Thermocouples generate an electrical voltage that reflects the temperature gradient between two dissimilar metal junctions and a reference point. The voltage generated is interpreted to identify the corresponding temperature.
Key Features of Thermocouples:
- Versatility: Available in various types (e.g., Type J, K, T, E) to suit specific applications.
- Temperature Range: Capable of measuring temperatures from -200°C to over 2000°C, depending on the type.
- Durability: Resistant to mechanical stress and high temperatures.
Advantages:
- Wide temperature range.
- Cost-effective, especially for high-temperature applications.
- Their rapid response is attributed to a low thermal mass, enabling quick detection of temperature changes.
Limitations:
- Less accurate than RTDs, with typical errors of ±2°C to ±5°C.
- Requires regular calibration for precise measurements.
- Voltage signals are small and can be affected by electrical noise.
- Thermistors
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors made from ceramic or polymer materials. Their resistance decreases (Negative Temperature Coefficient, NTC) or increases (Positive Temperature Coefficient, PTC) significantly with temperature changes.
Key Features of Thermistors:
- Sensitivity: Extremely sensitive to small temperature changes.
- Temperature Range: Typically operate within -50°C to 150°C.
- Size: Compact and easy to integrate into electronic systems.
Advantages:
- High sensitivity enables precise detection of small temperature changes.
- Low cost and compact design.
- Quick response time.
Limitations:
- Limited temperature range.
- Non-linear response, requiring complex calibration.
- Thermistors tend to have lower durability in extreme or harsh environments when compared to RTDs and thermocouples.
Comparison Table
| Feature | RTD | Thermistor | Thermocouple |
| Accuracy | High (±0.1°C) | High in a limited range | Moderate (±2°C to ±5°C) |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 600°C | -50°C to 150°C | -200°C to 2000°C |
| Durability | Fragile | Moderate | Highly durable |
| Cost | Expensive | Economical | Affordable to mid-range |
| Response Time | Intermediate | Quick | Rapid |
| Linearity | Near-linear | Non-linear | Non-linear |
Choosing the Right Sensor
Selecting a temperature sensor hinges on its intended use:
- RTDs: Preferred for applications needing high precision and consistent performance, such as in labs, industrial setups, and HVAC systems.
- Thermocouples: Well-suited for high-temperature or challenging environments, including metal forging, kilns, and aviation.
- Thermistors: Ideal for compact, cost-sensitive applications like household devices, medical instruments, and consumer gadgets.
Conclusion
RTDs, thermocouples, and thermistors are essential tools for temperature measurement, each with distinct strengths and weaknesses. Understanding their characteristics and applications ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency in your projects. Whether you prioritize precision, range, or durability, selecting the appropriate sensor will significantly impact the success of your temperature-sensitive processes.
The post RTD vs Thermocouple vs Thermistor: Understanding Temperature Sensors appeared first on ELE Times.
Setting a new standard for electronics in space
Learn about our collaboration with NASA and industry leaders in developing radiation-hardened, plastic packaging for space electronics, known as QML Class P, to power missions with size, weight and power in mind.
As curiosity and innovation drive space exploration forward, constraints for size, weight and power continue to tighten. To design for space, you have little to no room for error. And increasing space exploration activities by public and private entities, whether in Earth’s orbit or way beyond, requires continued collaboration and improvements.
Recently, our company worked with NASA and other industry experts to lead the development of a new plastic packaging standard for space electronics, known as Qualified Manufacturers List Class P (QML Class P). Electronics in space must meet government standards set forth in the QML, ranging from radiation-tolerant or radiation-hardened devices in either ceramic or plastic packaging. The QML provides assurance that parts will operate as intended in the harsh environments of space.
“The QML Class P packaging standard enables more advanced computing in space, such as how satellites and other spacecraft can autonomously process data and make decisions in orbit as opposed to beaming data back down to Earth,” said Javier Valle, product line manager for space power at our company. “More processing capability also requires greater power. With TI’s QML Class P portfolio, we increase the efficiency of the power supply while reducing the size of the overall package, resulting in much higher power density.”
The QML exists with its many classes to ensure predictability in designs, meeting qualification and certification according to government standards, but new standards such as Class P are introduced as our knowledge and use cases advance. The QML Class P standard enables the use of radiation-hardened plastic packaging for power-management, processor, communications and high-speed integrated circuits (ICs) in satellites, rovers and other spacecraft.
Bring space up to speed through plasticCeramic packaging has often been the go-to, reliable option, as it meets a variety of government agency specifications in the United States. Manufacturers of ceramic-packaged space electronics have released ICs to the market under a qualification known as QML Class V.
Until QML Class P, there had been no standardized, radiation-hardened equivalent for plastic packaging.
Earlier forms of plastic packaging standards have also been especially vulnerable to a process known as outgassing. Outgassing describes a process when the harsh temperature and vacuum conditions of space vaporize organic compounds, which can deposit onto electronics causing them to fail. Depending on the severity, the effects of outgassing can interrupt or completely end missions.
Advancements in manufacturing and testing procedures have helped address the consequences of outgassing and other environmental concerns in space. However, these improvements can vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, and consequentially, were not enough to reassure space operators about the reliability of new, unfamiliar technologies without standardization.
In repeatedly hearing from customers that the industry needed a QML standard for plastic packaging, our company assembled a group of more than three dozen experts from industry and standardization bodies.
Looking further ahead with TISpace operators can now easily transition from a radiation-tolerant electronic design using our Space Enhanced Plastic portfolio to a radiation-hardened design with our QML Class P portfolio, without any hardware change given our pin-to-pin compatibility.
TI’s QML Class P certified portfolio offers solutions across the entire spacecraft electrical power system (EPS), from solar panels all the way to point of load power supplies, and the portfolio is growing.
As we continue to navigate the future of space exploration, designing for space brings unlimited possibilities and solutions as endless as space itself. We have more than six decades of experience in creating solutions for space, and we look forward to helping you engineer the next frontier.
The post Setting a new standard for electronics in space appeared first on ELE Times.
STMicroelectronics Announces Timing for Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2024 Earnings Release and Conference Call
STMicroelectronics, a global semiconductor leader serving customers across the spectrum of electronics applications, announced that it will release its fourth quarter and full year 2024 earnings before the opening of trading on the European Stock Exchanges on Thursday, January 30, 2025.
The press release will be available immediately after the release on the Company’s website at www.st.com.
STMicroelectronics will conduct a conference call with analysts, investors and reporters to discuss its fourth quarter and full year 2024 financial results and current business outlook on January 30, 2025, at 9:30 a.m. Central European Time (CET) / 3:30 a.m. U.S. Eastern Time (ET).
A live webcast (listen-only mode) of the conference call will be accessible at ST’s website https://investors.st.com and will be available for replay until February 14, 2025.
The post STMicroelectronics Announces Timing for Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2024 Earnings Release and Conference Call appeared first on ELE Times.
Spent the weekend making a logic simulation
 | submitted by /u/flippont [link] [comments] |
ADI’s efforts for a wirelessly upgraded software-defined vehicle
In-vehicle systems have massively grown in complexity with more installed speakers, microphones, cameras, displays, and compute burden to process the necessary information and provide the proper, often time-sensitive output. The unfortunate side effect of this complexity is the massive increase in ECUs and subsequent cabling to and from its allocated subsystem (e.g., engine, powertrain, braking, etc.). The lack of practicality with this approach has become apparent where more OEMs are shifting away from these domain-based architectures and subsequently traditional automotive buses such as local interconnect network (LIN), controlled area network (CAN) for ECU communications, FlexRay for x-by-wire systems, and media oriented transport (MOST) for audio and video systems. SDVs rethink underlying vehicle architecture so that cars are broken into zones that will directly service the vehicle subsystems that surround it locally, cutting down wiring, latency, and weight. Another major benefit of this are over-the-air (OTA) updates using Wi-Fi or cellular to update cloud-connected cars, however bringing ethernet to the automotive edge comes with its complexities.
ADI’s approach to zonal architecturesThis year at CES, EDN spoke with Yasmine King, VP of automotive cabin experience at Analog Devices (ADI). The company is closely working with the underlying connectivity solutions that allow vehicle manufacturers to shift from domain architectures to zonal with ethernet-to-edge (E2B) bus, automotive audio bus (A2B), and gigabit multimedia serial link (GMSL) technology. “Our focus this year is to show how we are adding intelligence at the edge and bringing the capabilities from bridging the analog of the real world into the digital world. That’s the vision of where automotive wants to get to, they want to be able to create experiences for their customers, whether it’s the driving experience, whether it’s the back seat passenger experience. How do you help create these immersive and safe experiences that are personalized to each occupant in the vehicle? In order to do that, there has to be a fundamental change of what the architecture of the car looks like,” said King. “So in order to do this in a way that is sustainable, for mobility to remain green, remain long battery range, good fuel efficiency, you have to find a way of transporting that data efficiently, and the E2B bus is one of those connectivity solutions where it’s it allows for body control, ambient lighting.”
E2B: Remote control protocol solution 10BASE-T1S solutionBased on the OPEN alliance 10BASE-T1S physical layer (PHY), the E2B bus aims at removing the need for MCUs centralizing the software to the high performance compute (HPC) or central compute (Figure 1). “The E2B bus is the only remote control protocol solution available on the market today for the 10BASE-T1S so it’s a very strong position for us. We just released our first product in June of this past year, and we see this as a very fundamental way to help the industry transform to zonal architecture. We’re working with the OPEN alliance to be part of that remote control definition.” These transceivers will integrate low complexity ethernet (LCE) hardware for remote operation and, naturally, can be used on the same bus as any other 10BASE-T1S-compliant product
BMW has already adopted the E2B bus for their ambient lighting system, King mentioned that there has already been further adoption by other OEMs but they were not public yet. “The E2B bus is one of those connectivity solutions where it allows for body control, ambient lighting. Honestly, there’s about 50 or 60 different applications inside the vehicle.” She mentioned how E2B is often used for ambient lighting today but there are many other potential applications such as driver monitoring systems (DMSs) that might detect a sleeping driver via the in-vehicle biometric capabilities to then respond with a series of measures to wake them up, E2B allows OEMs to apply these measures with an OTA update. Without E2B, you’d have to not only update the DMS, but you’d have to update the multiple nodes that are controlling the ambient light. The owner might have to take it back into the shop to apply the updates, it just takes longer and is more of a hassle. With E2B, it’s a single OTA update that is an easy, quick download to add safety features so it’s more realistic to get that safer, more immersive driver experience.” The goal for ADI is to move all the software from all edge nodes to the central location for updates.

Figure 1: EDN editor, Aalyia Shaukat (left) and VP of automotive cabin experience, Yasmine King (right) in front of a suspension control demo with 4 edge nodes sensing the location of the weighted ball, sends the information back to the HPC to send commands back to control the motors.
A2B: Audio system based on 100BASE-T1Based upon the 100BASE-T1 standard, the A2B audio follows a similar concept of connecting edge nodes with a specialization in sound limiting the installation of weighty shielded analog cables going to and from the many speakers and microphones in vehicles today for modern functions such as active noise cancellation (ANC) and road noise cancellation (RNC). “We have RNC algorithms that are connected through A2B, and it’s a very low latency, highly deterministic bus. It allows you to get the inputs from, say, the wheel base, where you’re listening for the noise, to the brain of the central compute very quickly.” King mentioned how audio systems require extremely low latencies for an enhanced user experience, “your ears are very susceptible to any small latency or distortion.” The technology has more maturity than the newer E2B bus and has therefore seen more adoption, “A2B is a technology that is utilized across most OEMs, the top 25 OEMs are all using it and we’ve shipped millions of ICs.” ADI is working on a second iteration of the A2B bus that multiplies the data rate of the previous generation, this is likely due to the maturation of the 1000BASE-T1 standard for automotive applications that is meant to reach 1 Gbps. When asked about the data rate King responded, “I’m not sure exactly what we are publicly stating yet but it will be a multiplier.”
GMSL: Single-wire SerDes display solutionGMSL is the in-vehicle serializer/deserializer (SerDes) video solution that shaves off the significant wiring typically required with camera and subsequent sensor infrastructure (Figure 2). “As you’re moving towards autonomous driving and you want to replace a human with intelligence inside the vehicle, you need additional sensing capabilities along with radar, LiDAR, and cameras to be that perception sensing network. It’s all very high bandwidth and it needs a solution that can be transmitted in a low-cost, lightweight cable.” Following a similar theme as the E2B and A2B audio buses, using a single cable to manage a cluster display or an in-vehicle infotainment (IVI) human-to-machine interface (HMI) minimizes the potential weight issues that could damage range/fuel efficiency. King finished by mentioning one overlooked benefit of lowering the weight of vehicle harnessing “The other piece that often gets missed is it’s very heavy during manufacturing, when you move over 100 pounds within the manufacturing facilities you need different safety protocols. This adds expense and safety concerns for the individuals who have to pick up the harness where now you have to get a machine over to pick up the harness because it’s too heavy.”

Figure 2: GMSL demo aggregating feeds from six cameras into a deserializer board going into a single MIPI port on the Jetson HPC-platform.
Aalyia Shaukat, associate editor at EDN, has worked in the design publishing industry for six years. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering from Rochester Institute of Technology, and has published works in major EE journals as well as trade publications.
Related Content
The post ADI’s efforts for a wirelessly upgraded software-defined vehicle appeared first on EDN.