ELE Times
R&S showcases its comprehensive embedded systems test solutions at embedded world 2026
Rohde & Schwarz will present its advanced test and measurement solutions for the embedded industry at embedded world Exhibition & Conference in Nuremberg, Germany. Visitors can find the T&M expert at booth 4-218 in hall 4 of the Nuremberg Exhibition Centre from March 10 to 12, 2026. There, they can delve into the company’s innovations designed to help engineers enhance device energy efficiency, expedite EMC compliance within the design process, speed up digital protocols debugging, and meet required regulatory standards for wireless interfaces.
Next generation oscilloscopes
At Embedded World, Rohde & Schwarz will showcase its ever-growing range of next-generation oscilloscopes, from MXO 3 to MXO 5, all powered by the same next-generation MXO-EP ASIC technology from Rohde & Schwarz, originally introduced with the MXO 4 in 2022. The latest addition, the compact MXO 3, comes with up to eight channels and offers a combination of features that rival higher-class oscilloscopes, such as a real-time capture rate of up to 99% and hardware-accelerated functionality on math, spectrum and zone trigger.
Ensuring reliability in power electronics
Combined with high voltage, current and optically isolated probes (R&S RT-ZISO), the eight-channel models of MXO 3 and MXO 5 extend their capabilities to power electronics applications. For power conversion, the instruments’ eight channels and 18-bit HD mode provide critical visibility into complex systems like motor drives and inverters, enabling precise measurements for efficiency and optimisation. Furthermore, they simplify power sequencing analysis with simultaneous multi-channel observation and deep memory of up to 500 Mpts, enabling longer recording durations and precise analysis of small signal events. Additionally, their fast spectrum analysis capability makes them excellent tools for quickly identifying EMI issues and noise sources.
EMI testing for embedded systems
Every electronic product and component is likely to emit conducted or radiated electromagnetic emissions. Especially for densely packed embedded systems, early debugging helps to isolate and correct EMI issues and accelerates time-to-market. As a leader in EMC testing, Rohde & Schwarz will present solutions that integrate EMI testing into the product design process. Visitors can learn how to use the R&S EPL1007 EMI test receiver in fast, accurate and reliable EMI pre-compliance and compliance measurements up to a frequency range of 7.125 GHz. The instrument offers device developers and conformance test houses the flexibility to upgrade with evolving needs – from preselection, including a preamplifier, up to a full CISPR 16-1-1 compliant test receiver.
Verifying signal integrity of digital designs
All hardware elements on a board layout are potential causes of signal degradation. To test the signal integrity on a PCB, Rohde & Schwarz will showcase its R&S ZNB3000 vector network analyser at embedded world, covering up to 40 GHz. This VNA, part of the new midrange family offering instruments with a maximum frequency range of up to 54 GHz, has redefined the standard for speed, precision and versatility with its industry-leading dynamic range, fast measurement speed, and scalable upgrades, perfectly suited for signal integrity applications. Visitors can experience the instrument’s advanced de-embedding techniques, which facilitate characterising the test fixture, extracting the S-parameters and de-embedding the test fixture in a user-friendly manner, with the signal quality visualised by a simulated eye diagram.
Testing of high-speed interfaces
High-speed digital interfaces are integral to electronic designs, with increasing data rates and integration density posing new challenges at the IC, board and system level. Trade show visitors will learn at the Rohde & Schwarz booth about powerful signal integrity test tools for system verification, debugging, and compliance testing for different high-speed busses. Rohde & Schwarz will showcase, for example, 1GBASE-T Ethernet compliance testing using the R&S RTO6 oscilloscope and related equipment to ensure that a 1 Gigabit Ethernet (1GbE) physical layer (PHY) transceiver meets the specifications outlined in the IEEE 802.3 standard. In a different setup, Rohde & Schwarz will showcase its R&S RTP164B oscilloscope for signal integrity testing on a multitude of standards, including DDR5 and USB3.2.
When it comes to automotive interfaces, the emerging standards, including Automotive Ethernet, OpenGMSL or ASA (Automotive SerDes Alliance), bring new challenges for design. Rohde & Schwarz already supports all of these new standards and will showcase comprehensive validation using the R&S RTP164B oscilloscope, featuring signal integrity debugging and automated compliance on ASA, as well as protocol decoding of 10Base-T1S to ensure robust and reliable link performance.
Battery life testing
Battery life is critical for battery-powered devices. Rohde & Schwarz will demonstrate in real time how the features of smart devices affect their power consumption. The setup is based on the R&S NGU source measure unit emulating a battery. The integrated analysis tool captures and visualises current across sleep-to-active transitions. In another application on battery testing with the R&S NGM202, cells will be charged and discharged to characterise battery behaviour and build accurate battery models.
Wireless connectivity testing
Embedded systems increasingly incorporate wireless connectivity as a core function. Thorough testing is essential to ensure reliable performance, interoperability and compliance with industry standards. The complexity of these standards requires specialised test equipment and expertise. The CMP180 radio communication tester from Rohde & Schwarz contains two analysers, two generators and two sets of eight RF ports in a single box and supports many cellular and non-cellular technologies across R&D, pre‑conformance and mass production. At embedded world, visitors will experience the CMP180 testing both Bluetooth LE and Wi-Fi 8 devices.
The platform already supports physical layer testing for the new Bluetooth LE Channel Sounding and new Bluetooth LE High Data Throughput (HDT) feature, a cornerstone for the next generation of Bluetooth Low Energy (LE), offering increased capacity, better energy efficiency, improved spectrum efficiency and enhanced reliability. Wi-Fi 8, based on the IEEE 802.11bn standard, sets new expectations for consistent, ultra-high-reliability and quality connectivity. Designed to support a growing number of connected devices and demanding applications like XR and industrial IoT, the CMP180 helps engineers navigate the technical complexities of 802.11bn throughout the entire device lifecycle in non-signalling mode with its advanced capabilities and broad bandwidth support.
Efficient production lines with tailored solutions
For production tests at component, module and system level, Rohde & Schwarz will showcase a rack-mounted test and measurement configuration, featuring the rack-optimised MXO 5C oscilloscopes and the PVT360A performance vector tester. This setup will demonstrate how tailored Rohde & Schwarz test solutions contribute to a production environment built for reliable validation, streamlined workflows and maximised throughput.
These and other test solutions for the embedded industry can be found at the Rohde & Schwarz booth 4-218 in hall 4 at the Embedded World Exhibition & Conference from March 10 to 12, 2026, in Nuremberg, Germany.
The post R&S showcases its comprehensive embedded systems test solutions at embedded world 2026 appeared first on ELE Times.
Toxics Link study Finds a Long Road to Circularity in India’s E-waste EPR Model
A new report by an environmental group, Toxics Link, reveals significant structural gaps in India’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework for e-waste. The study, titled “Long Road to Circularity,” warns that while the EPR model is a cornerstone of waste management, it currently fails to capture a vast range of critical minerals essential for India’s green transition.
The Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework mandates the recovery of only four metals—gold, copper, iron, and aluminium—leaving critical metals untapped. A vast range of valuable and critical metals, including neodymium, dysprosium, and lithium, are essential to strengthening resource security but is currently overlooked and lost.
In light of these concerns, the report examines current e-waste regulations and highlights critical challenges limiting their effective implementation. The report also underscores persistent issues, including low consumer awareness, poor financial traceability of e-waste flow and limited monitoring capacities. The study identifies several operational gaps. Key findings from the report include:
- The EPR portal currently lacks data on total market players and leaves small-scale manufacturers, online sellers, and grey-market importers outside the system.
- Information regarding non-compliance penalties and environmental compensation remains unavailable for the 2023–24 and 2024–25 fiscal years.
- Detailed data is accessible only to operators, resulting in limited public visibility into system performance.
- The current regulation does not identify and place responsibility on any individual stakeholder for the setting up of collection centres, thus making it extremely difficult for consumers to deposit their waste in the authorised e-waste stream.
- No incentive to producers and manufacturers adopting “green” product designs or for recyclers implementing high-quality, advanced recovery processes.
“While Extended Producer Responsibility is a cornerstone of India’s e-waste management framework, the principle alone cannot deliver the desired outcomes. It must be complemented by an effective and robust waste collection system, integrating the informal sector and the development of high-tech recycling facilities along with public awareness for advancing system transparency”, Satish Sinha, Associate Director, Toxics Link.
The report suggests the following key recommendations to plug some of the gaps in the
present system:
- Enhance system accountability and transparency by making data accessible to the
public. - Strengthen reverse supply chains and collection mechanisms to streamline the flow
of e-waste. - Expand consumer awareness on the advantages of e-waste recycling and the
importance of using authorised collection channels. - Integrate the informal sector into the e-waste management ecosystem.
Together, these measures can help build a stronger and more effective e-waste
management system.
The post Toxics Link study Finds a Long Road to Circularity in India’s E-waste EPR Model appeared first on ELE Times.
ESGDS’ AI platform slashes data processing time by 98% with MongoDB Atlas
ESG Data & Solutions (ESGDS) is a fast-growing Indian technology company. It builds tools to enable banks, investors, and other financial groups to track and analyse a company’s performance on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) issues.
With a vast range of covered topics and multiple providers employing different types of methodologies and taxonomies, ESG data sets are notoriously difficult to work with.
Because these analyses guide critical research and investment decisions, ESGDS developed ESGSure—a bespoke research platform built on MongoDB Atlas—to address the challenge.
THEIR CHALLENGE: Overcoming the relational model limitations to unlock AI scale
ESGSure collects points from over 20,000 companies and investors—these include annual reports and corporate filings, news, and client-specific questionnaires. The platform also tracks a range of other publicly available sources, including news articles, compliance records, and sanctions lists, among others. These resources come in various formats, including videos, PDFs, transactional data in APIs, and more.
Before moving to MongoDB Atlas, ESGDS relied on several other databases, including relational databases such as PostgreSQL and Pinecone for vector search workloads. As the use cases and data sets expanded, ESGDS encountered limitations.
“Our platform needs to process massive, diverse, and unstructured data sets, so we can then use a combination of large language models (LLMs), real-time data, and vector search capabilities to deliver AI-driven granular, personalised, and actionable insights for investors,” said Arun Doraisamy, Co-Founder and Chief Technology Officer at ESGDS. “We needed more flexibility, to reduce complexity, and do that at scale. This meant moving away from a relational model and onto a database model that fit our needs.”
Several limitations drove ESGDS to seek a new database:
- Lack of flexibility and scalability: Rigid legacy relational databases lacked the schema flexibility required to dynamically store and update ESGDS’s rapidly evolving datasets. This resulted in inconsistent insights that hindered analysts’ and investors’ ability to make timely and accurate data-driven decisions. Additionally, a lack of elastic scalability throttled ESGDS’s ability to handle continuous data growth, compromising its ambitious expansion plans.
- Delayed data insights: Stale data is a significant challenge for the ESG data analysis industry—by the time it is collected and analysed, ESG data can be up to a year old. To add to this challenge, manual ESG data review in ESGDS’s legacy database took an average of 2 to 3 days per company. ESGDS wanted to automate these processes to provide investors with real-time insights.
- Complex security and compliance: ESGDS manages sensitive, private datasets for its clients. Ensuring secure storage, data encryption, and compliance with ESG frameworks and regional requirements, such as GDPR, has become increasingly complex. With expansion into highly regulated countries on its roadmap, ESGDS knew this challenge would become acute.
- Limited global portability: ESGDS needed a data platform that would easily and efficiently power growth plans across Europe, Asia Pacific, and North America. It had to support a reliable, multi-cloud, and multi-region infrastructure.
“We needed a modern, flexible model with built-in AI capabilities that could meet our complex needs, and keep evolving to support our ambitious growth and diversification goals,” said Doraisamy.
The post ESGDS’ AI platform slashes data processing time by 98% with MongoDB Atlas appeared first on ELE Times.
Keysight Unveils 3D Interconnect Designer for Chiplet and 3DIC Advanced Package Designs
Keysight Technologies introduced 3D Interconnect Designer, a new addition to its Electronic Design Automation (EDA) portfolio. The solution addresses the mounting complexity of designing 3D interconnects for high-chiplet and 3DIC advanced packages used in AI infrastructure and data centre applications.
As chiplet architectures are increasingly adopted, engineers face complex 3D interconnect designs for multi-die and stacked-die applications, which traditional workflows struggle to handle efficiently. As a result, teams spend significant time manually optimising the interconnects that include vias, transmission lines, solder balls, and micro-bumps while ensuring signal and power integrity in densely packed systems. This results in more design spins and longer product development cycles, creating a bottleneck that can delay product launches and increase development costs.
Keysight EDA software streamlines the process with a dedicated workflow for designing and optimising 3D interconnects accurately. The tool handles complex geometries, including hatched or waffled ground planes, which are critical to overcome manufacturing and fabrication constraints, especially silicon processes such as interposers and bridges, in advanced package designs. By enabling engineers to quickly design, optimise, and validate 3D interconnects used in chiplets and 3DICs, it minimises iterations and speeds time-to-market.
Key benefits include:
- Accelerates Design Cycles: Streamlined automation removes time‑consuming manual steps in 3D interconnect design, minimising errors and boosting first‑pass success
- Reduced Compliance Risk: Validates designs against emerging standards such as UCIe and BoW, ex VTF (Voltage Transfer Function), early in the lifecycle, reducing the risk of late-stage failures that lead to costly redesigns
- Predicts Performance Accurately: Electromagnetic-based simulation provides precise electrical analysis of printed circuit boards (PCB) and package 3D interconnect designs
The solution integrates with Keysight’s EDA tools as well as supporting the standalone version, enabling teams to incorporate 3D interconnect design and optimisation into existing workflows. When combined with Chiplet PHY Designer, engineers can design and optimise 3D interconnects specifically for chiplets and three-dimensional integrated circuits (3DICs), ensuring accuracy and reducing costly iterations in multi-die systems.
Nilesh Kamdar, EDA Design and Verification General Manager at Keysight, said:
“With today’s complexity, manual 3D interconnect design and optimisation have become a significant bottleneck. By streamlining the process and providing early insights into potential issues like signal and power integrity, we’re enabling engineers to get products to market faster and deliver compliant designs on tighter timelines.”
The post Keysight Unveils 3D Interconnect Designer for Chiplet and 3DIC Advanced Package Designs appeared first on ELE Times.
Jodi Shelton, CEO of GSA – Launches A Bit Personal, a New Podcast Offering Rare, Candid Conversations with the Most Powerful Tech Leaders
Jodi Shelton, Co-Founder and CEO of the Global Semiconductor Alliance and Shelton Group, announced the launch of A Bit Personal, a new leadership-focused podcast that pulls back the curtain on the people shaping the future of global technology. Premiering today, the podcast offers an intimate, cinematic look at the personal stories, values, failures, and defining moments of the industry’s most powerful leaders – stories rarely heard beyond earnings calls and keynote stages.
Unlike traditional technology podcasts focused on products and platforms, A Bit Personal centres on the human behind the hardware. Through trust-based, unscripted conversations, Shelton encourages guests to share candid reflections on leadership, ambition, vulnerability, and the moments that shaped who they are today.
“These are the most fascinating people I know, and I can’t wait for you to hear their stories,” said Shelton. “This is A Bit Personal, and it’s going to be good.”
The inaugural season features nine weekly episodes and includes hard-hitting, first-of-their-kind conversations with industry icons such as NVIDIA Founder and CEO Jensen Huang and AMD Chair and CEO Lisa Su. Future episodes will further spotlight a female-led perspective in a traditionally male-dominated industry, with an upcoming series focused on women CEOs and their leadership journeys.
“Over the course of my career, I’ve had a front-row seat to the semiconductor industry’s evolution,” Shelton added. “The leaders who drive economic prosperity and human advancement have become public figures and cultural celebrities. The world wants to know who they are and what drives them. With A Bit Personal, I’m offering listeners a seat at the table – moving past product launches to explore the personal stories, values, failures, and triumphs of the boldest visionaries defining tomorrow.”
Produced with a film-forward, cinematic approach, the podcast blends creative visuals, behind-the-scenes moments, and deeply personal storytelling to deliver what Shelton describes as “not your father’s tech industry podcast.”
New episodes of A Bit Personal release weekly on Thursdays and are available on YouTube and all major podcast platforms. Listeners can also follow along for news and updates on A Bit Personal’s Instagram, TikTok, LinkedIn and X channels. Additionally, Jodi’s podcast A Bit Personal is planning to interview the CEOs of Indian semiconductor companies in its upcoming season. Guest announcements and appearances will be revealed gradually—stay tuned.”
The post Jodi Shelton, CEO of GSA – Launches A Bit Personal, a New Podcast Offering Rare, Candid Conversations with the Most Powerful Tech Leaders appeared first on ELE Times.
Is SDV Really an Automotive or Just A Software-based machine That Moves?
Speaking at the Auto EV Tech Vision Summit 2025, Rajeev Ved, Chief Growth Officer at Sasken Technologies Limited, took the Software-Defined Vehicle conversation away from surface-level features and into something far more foundational. While much of the industry debate revolves around autonomy levels, over-the-air updates, or larger infotainment screens, Ved stepped back and asked a more fundamental question: What does a car even mean in an SDV world?
For decades, automobiles have been sold through emotion. Freedom of mobility. Control over one’s journey. Aspiration for safety, performance, and status. These emotional anchors have shaped marketing, engineering priorities, and customer expectations alike. According to Ved, the SDV does not erase these emotions—it amplifies them. Adaptive driving systems increase control, predictive maintenance enhances reliability, and connected ecosystems elevate convenience. The “joy of driving” becomes algorithmically refined.
Software that Happens to Move
But beneath that emotional amplification lies a deeper transformation. An SDV is no longer merely a car with software added on. It is software orchestrating a machine, continuously connected to cloud systems, infrastructure, homes, offices, and other vehicles. At that point, the question shifts: is it a car enhanced by software, or is it a rolling software platform that happens to move from point A to point B?
Building such a vehicle, Ved argued, cannot be achieved by layering code over legacy architectures. It requires constructing the stack from the ground up. He described four foundational layers that together define a true SDV architecture.
The 4 Layers of SDV Architecture
In his address, Rajeev outlines what he described as the four architectural layers required to build a true Software-Defined Vehicle. At the foundation sits the Operational Foundation Layer—the tightly integrated hardware–software core that governs the vehicle’s mechanical systems. Here, distributed ECUs are consolidated into centralized domain controllers, allowing braking, propulsion, safety, and powertrain functions to operate as coordinated software-driven systems. Built above this is the Data & Intelligence Layer, where the vehicle continuously ingests sensor data, processes it at the edge, connects through V2X ecosystems, and interacts with cloud backends—transforming the car into a connected computational platform rather than an isolated machine.
Layered on top is the Services & Monetization Layer, where connectivity enables feature-on-demand models, adaptive insurance, predictive maintenance, and new lifecycle revenue streams. In this framework, the vehicle evolves from a one-time hardware product into a dynamic digital platform. At the apex lies the UI/UX & Infotainment Layer—the digital cockpit that defines the customer interface through immersive screens, augmented experiences, and ecosystem integrations. According to Ved, control of this layer will determine who ultimately owns the user relationship in the SDV era, making it one of the most strategically contested fronts in automotive transformation.
Cross-sectoral Expertise
Yet Ved cautioned that while the architecture evolves, foundational disciplines remain non-negotiable. Mission-critical standards, safety validation frameworks, and robust embedded software practices continue to underpin the stack. What changes is the scale of data pipelines, edge compute capabilities, cloud APIs, and monetization frameworks layered on top. Building for the SDV era requires expertise not only in automotive systems but in distributed computing, AI integration, and scalable digital services.
Conclusion
The larger implication of his address was clear. The SDV shift is not a feature race. It is a structural redesign of how vehicles are conceived, built, monetized, and experienced. Cars are evolving into distributed compute nodes, data platforms, and service ecosystems. The industry’s challenge is not merely to digitize the automobile, but to architect it as a layered, interoperable, and continuously evolving system.
The Software-Defined Vehicle is not an upgrade cycle. It is the redefinition of mobility itself.
The post Is SDV Really an Automotive or Just A Software-based machine That Moves? appeared first on ELE Times.
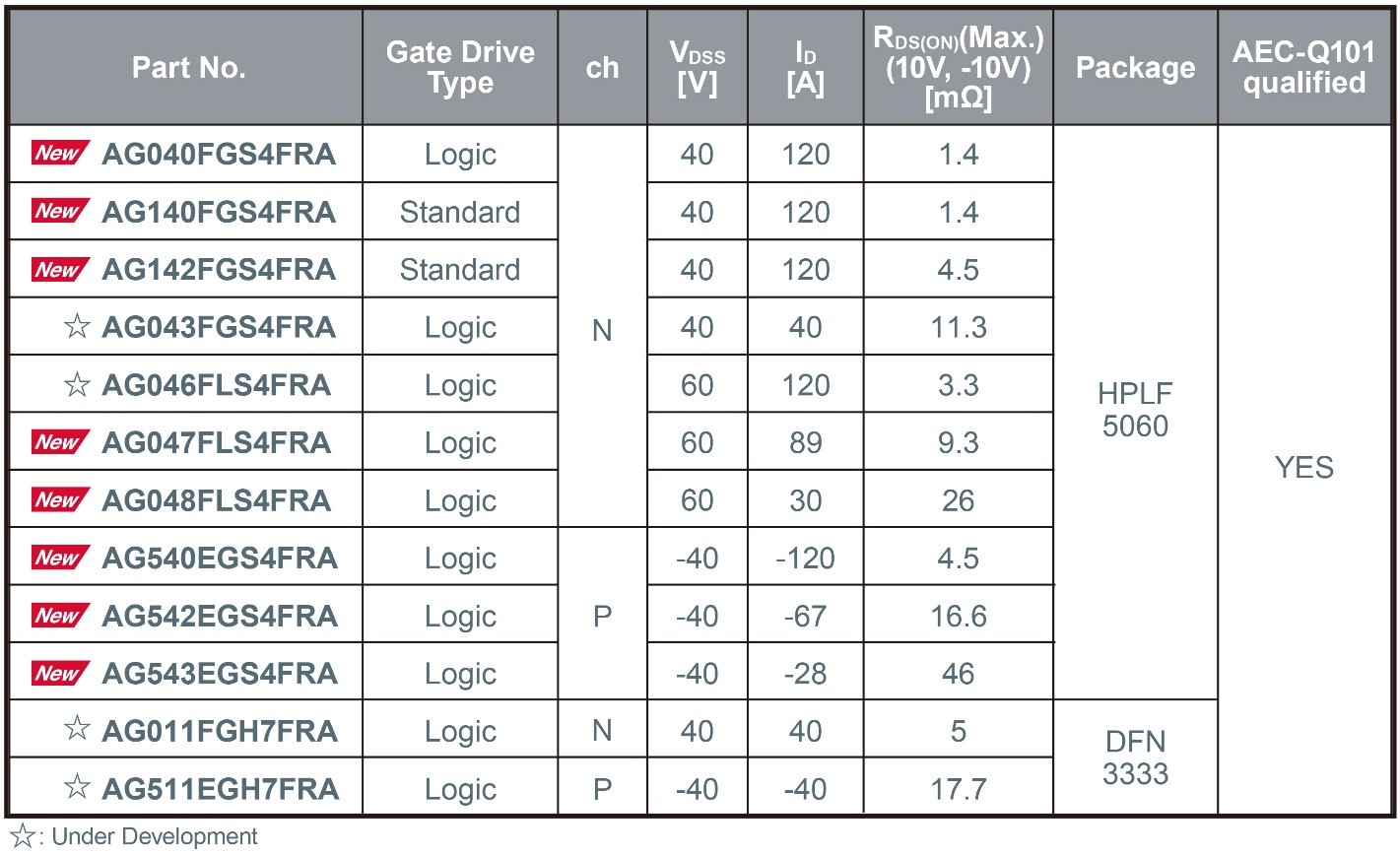
ROHM’s New Compact, Highly Reliable Package Added to Automotive 40V/60V MOSFET Lineup
ROHM has expanded its lineup of low-voltage (40V/60V) MOSFETs for automotive applications – such as main inverter control circuits, electric pumps, and LED headlights – by introducing the latest products adopting the new HPLF5060 package (4.9mm × 6.0mm).
In recent years, automotive low-voltage MOSFETs have been trending toward smaller packages, such as the 5060-size and even more compact options. However, this miniaturisation introduces significant challenges for achieving reliable mounting, primarily due to narrow terminal spacing and leadless designs.
To address these issues, the new HPLF5060 package offers a smaller footprint compared to the widely used TO-252 package (6.6mm × 10.0mm) while enhancing board-mount reliability through the adoption of gull-wing leads. Additionally, the use of copper clip junction technology enables high-current operation, making the HPLF5060 an ideal solution for demanding automotive environments.
Mass production of new products using this package began in November 2025 (sample price: $3.5/unit, excluding tax). Online sales have also started, and the products are also available for online purchase through online distributors such as DigiKey and Farnell.
In addition to expanding the lineup of products using this package, mass production of the smaller DFN3333 (3.3mm × 3.3mm) package, which employs wettable flank technology, is scheduled to begin around February 2026. Furthermore, development has commenced on a TOLG (TO-Leaded with Gull-wing) package (9.9mm × 11.7mm) to further expand the lineup of high-power, high-reliability packages.
The post ROHM’s New Compact, Highly Reliable Package Added to Automotive 40V/60V MOSFET Lineup appeared first on ELE Times.
The Rise of the AgentEngineer: How AI is Orchestrating the Future of Chip Design
While traditional Electronic Design Automation tools have been faithfully executing commands for decades, today’s agentic AI systems are rewriting the rulebook by thinking, iterating, and problem-solving autonomously across entire design workflows. Picture this: specialised AI agents functioning like a virtual design team—complete with their own CEO, CTO, and engineering specialists—orchestrating everything from RTL generation to physical design verification in feedback-driven loops that don’t just respond to errors, they anticipate and resolve them. This isn’t your standard chatbot-writes-some-code scenario; we’re talking about multi-agent architectures powered by Large Language Models that refuse to call it a day until every simulation passes. As the semiconductor industry grapples with a workforce crisis that threatens to bottleneck innovation, these AI systems are emerging as more than assistants; they’re becoming co-designers capable of exponentially multiplying engineering productivity. To understand how industry leaders are navigating this transformation from AI-assisted to AI-orchestrated design, we reached out to companies at the forefront of this revolution.
Architecture to Autonomy: Building Multi-Agent AI Systems for Chip Design
The semiconductor design floor is witnessing an unprecedented transformation where intelligent agents collaborate, critique, and refine work autonomously, like a seasoned design team operating at machine speed.
The Multi-Agent Architecture
Industry implementations structure these systems around specialised agent roles: RTL generation specialists handle code synthesis, verification agents scrutinise design correctness, and physical design agents optimise layouts. The orchestration framework manages task routing and dependencies, ensuring coherent workflow progression. Critically, these agents don’t replace existing EDA platforms; instead, they orchestrate them, invoking synthesis runs and analysing timing reports with minimal human intervention.

LLM Selection and Domain Adaptation
Behind these agents run Large Language Models serving as inference engines. The industry has split between proprietary models like GPT-4 and Claude, which offer robust reasoning capabilities, and open-source alternatives such as DeepSeek-Coder and Llama variants, providing customisation flexibility for high-volume workloads.
Raw LLMs produce generic code, but semiconductor design demands precision. Organisations implement two adaptation strategies: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) connects LLMs to design rule manuals, timing libraries, and verified IP repositories, grounding outputs in proven patterns. Domain-specific fine-tuning retrains models on millions of lines of verified RTL, enabling them to recognise design intent from terse specifications and suggest synthesis-aligned optimisations.
Talking about choosing the “right” LLM, 
Addressing Code Hallucination
The critical challenge remains code hallucination, plausible but incorrect outputs. Industry leaders deploy multi-layered validation: formal verification integration, simulation-in-the-loop refinement cycles, constraint-guided generation, and mandatory human review checkpoints for critical path logic. As one verification lead noted, AI-generated RTL receives the same scrutiny as junior engineer code, but iterates at 100x speed before human review.
“Hallucination is not a mysterious AI problem. It is the result of under-specified intent. We deal with it the same way we deal with junior engineers: through validation gates. Every AI-generated output passes through linting, simulation, coverage analysis, and equivalence checks. Nothing bypasses human review for critical design decisions. Trustworthy output comes from engineering discipline applied to AI, not from believing AI will magically become trustworthy,” added Gupta.
The technical architecture is maturing rapidly, but the true test ahead is scaling from engineer assistance to autonomous subsystem design, determining whether agentic AI becomes indispensable infrastructure or remains an expensive experiment.
AgentEngineer Revolution: Transforming Roles and Multiplying Productivity
The automation wave reshaping semiconductor design isn’t just changing workflows—it’s fundamentally redefining what it means to be a design engineer in 2026.
Quantifiable Productivity GainsEarly adopters report transformative productivity metrics. RTL generation rates have surged from approximately 50-100 lines per engineer-day in manual workflows to 500-1,000+ lines with AI assistance—a 10x improvement when measured by functional complexity rather than raw line count. Time-to-tapeout reductions range from 20-40% for complex SoC projects, with verification cycles seeing the most dramatic compression.
“The biggest gains have come from reducing friction, not replacing engineers. Tasks that previously required multiple iteration initial RTL structure, verification scaffolding, and early debug hypotheses now converge faster. We typically see meaningful schedule compression in early and mid-design phases, allowing teams to spend more time on optimisation, corner cases, and RF-digital interactions. This has increased our capacity to take on more complex mixed-signal and SoC programs without sacrificing rigour,” explains Anup Salva, CEO, Sasken Silicon.
Verification coverage metrics tell an equally compelling story. AI-driven testbench generation achieves 85-95% functional coverage in initial passes compared to 60-70% with manual approaches, while bug detection rates during pre-silicon validation have improved by 30-50%. One design team reported identifying critical corner-case failures that traditional directed tests missed entirely, caught by AI agents exploring unconventional stimulus patterns.
Perhaps most significant: engineering teams report handling 2-3x more concurrent design projects without proportional headcount increases, effectively multiplying organisational capacity during an industry-wide talent shortage.
The Evolving Engineer RoleThe shift from manual RTL coding to AI-orchestrated design is forcing a fundamental role transformation. Traditional design engineers spent 60-70% of their time writing and debugging code. Today’s “AgentEngineers” allocate that time differently: 40% on high-level architectural specification and constraint definition, 30% on AI output validation and refinement, 20% on system integration and optimisation, and just 10% on direct coding for critical path logic AI cannot yet handle reliably.
Talking on the evolving role of Engineers in the AI era, Srinivas Gupta, CEO, Silicon Patterns, emphasises that, “AI is not eliminating engineering roles, it is exposing who is adding real value. The role of the engineer is shifting from manual construction to intent definition, supervision, and judgment. Writing RTL is no longer the bottleneck; understanding what should be written and why is. Effective training is not about teaching “prompt engineering.” It is about teaching engineers how to reason clearly, review outputs critically, and understand failure modes. The best learning happens when AI is embedded directly into real project workflows, spec reviews, verification bring-up, debug, not in isolation.”
New competencies are emerging as essential: prompt engineering skills to communicate design intent effectively to LLM agents, AI system supervision capabilities to recognize when autonomous agents are diverging from design goals, and elevated architectural thinking to work at higher abstraction layers. The most successful engineers are those who transition from implementation experts to design orchestrators—defining what to build while delegating how to build it.
Training for TransformationOrganisations are implementing structured transition programs. Technical training covers AI model capabilities and limitations, effective prompt crafting for design specifications, and verification strategies for AI-generated code. Just as importantly, cultural training addresses the psychological shift from individual contributor to AI collaborator, teaching engineers when to trust autonomous outputs and when human judgment remains irreplaceable.
The semiconductor workforce crisis that threatened industry growth is being addressed not through massive hiring campaigns, but through radical productivity multiplication—a smaller cohort of AgentEngineers accomplishing what previously required entire design teams.
Trust, Validation, and the Road to 2026: Overcoming Deployment Challenges
Agentic AI’s technical promise confronts harsh deployment realities. The path from laboratory demonstration to production tapeout demands solving trust, integration, and scalability challenges that determine whether this technology revolutionises the industry or remains confined to pilot projects.
The Three Critical Deployment ChallengesIntegration Complexity tops the challenge list. Legacy EDA environments weren’t architected for AI orchestration—tool licenses limit concurrent sessions, APIs lack programmatic access depth, and design databases struggle with AI agents’ iterative read/write intensity. Organisations report 6-12 month integration timelines just to achieve basic agent-tool interoperability.
Trust and Validation Frameworks represent the existential challenge. For tape-out critical stages—final timing closure, DFT insertion, physical verification—engineers demand confidence levels AI systems cannot yet guarantee. One design director noted, “We can’t ship silicon that passes simulation but fails in production because an AI agent hallucinated a clock domain crossing fix.”
Organisational Resistance manifests subtly but persistently. Experienced engineers trained over decades resist delegating design authority to probabilistic systems. Version control becomes contentious when distinguishing human versus AI contributions. Accountability questions arise when AI-generated blocks cause post-silicon failures.
Building Trust Through ValidationSuccessful deployments implement rigorous validation hierarchies. AI-generated RTL undergoes formal equivalence checking against specifications, simulation coverage thresholds exceed 95% before human review, and critical paths receive mandatory expert sign-off regardless of AI confidence scores. Human-in-the-loop checkpoints gate progression, with engineers retaining veto authority at every stage.
Observability tools provide transparency into AI decision-making—logging which training examples influenced specific design choices, tracking confidence metrics for generated code segments, and flagging low-confidence outputs for immediate human review.
The 2026 Automation RoadmapIndustry consensus positions current systems at Level 2 on the five-level autonomy scale: capable assistants requiring continuous supervision. Reaching Level 4—autonomous subsystem design with minimal oversight—demands breakthroughs across multiple fronts.
Enhanced LLM reasoning must progress beyond pattern matching to genuine architectural trade-off analysis, understanding power-performance-area implications of micro-architectural choices. Memory systems need expansion to manage entire SoC contexts rather than isolated module designs. Formal methods integration must advance from post-generation validation to constraint-guided generation, preventing invalid designs rather than detecting them.
On the India front, Anup Salva, CEO, Sasken Silicon, notes that, “India’s advantage lies in its depth of engineering intuition, especially in areas like RF, analogue, and system-level integration. These are domains where AI works best as a multiplier, not a replacement. Over the next few years, we expect higher automation in well-understood design spaces, but always guided by engineers who understand the underlying physics and architecture. Progress will be driven more by better problem formulation and design discipline than by radical new tools.”
The competitive landscape trajectory appears clear: by late 2026, agentic AI will likely transition from a competitive differentiator to table stakes. Organisations not deploying these systems risk falling behind on time-to-market metrics. Yet the dominant paradigm will remain hybrid human-AI workflows rather than full autonomy—engineers orchestrating AI agents rather than being replaced by them, at least through this decade.
by: Shreya Bansal, Sub-Editor
The post The Rise of the AgentEngineer: How AI is Orchestrating the Future of Chip Design appeared first on ELE Times.
IIIT Hyderabad’s Smart Approach To Sand Mining Enforcement, Incorporating AI in Trucks
‘Truck art’ or the hand-painted ‘Horn Ok Please’, ‘Use Dipper at Night’ and the ‘Buri nazar waale tera mooh kala’ are an integral part of Indian highways. These artistic expressions, which lighten up many a road journey, also find an extension in hand-painted registration plates. However, such unstandardised lettering can prove to be a challenge for automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) systems. Most commercial ANPR systems are designed for standardised license plates. ANPR systems play a crucial role in modern governance, helping authorities monitor traffic, enforce regulations, prevent illegal transport, and improve public safety. From toll booths to traffic violations, ANPR enables real-time vehicle tracking without manual checks.
A Unique Number Plate Problem
Hence, when the Telangana IT Department approached IIIT-H, seeking an ANPR solution for the Telangana Mineral Development Corporation (TGMDC), their requirement was very different from typical commercial use cases.TGMDC was on the lookout for a cost-effective, robust solution tailored to monitor sand mining trucks, primarily to curb illegal mining and transport. “Typical license plates are actually easy to detect,” explains Dr. Veera Ganesh Yalla, CEO of iHub-Data and Adjunct Faculty at IIIT-H. But in India, especially with trucks, plates are often hand-painted, inconsistent, and highly variable. “They might follow black lettering on a yellow background, but from vehicle to vehicle, their design, the style, everything is unique,” he says, making off-the-shelf solutions for their detection both ineffective and expensive.

Building Smart, Not From Scratch
Commercial systems are typically very expensive, with per-camera costs of licensing and maintenance running into tens of lakhs. Leveraging prior research from Prof. Ravikiran Sarvadevabhatla’s team at the Centre for Visual Information Technology, IIIT-H, where a prototype license plate recognition system had been developed, the iHub-Data team took the research forward into real-world deployment. “The lab tech was more like a research prototype, not really for scaling or translation. So we decided to take it and see what we could do,” Dr. Yalla recalls. The team studied the workflow, rebuilt and strengthened the handwritten character recognition component. What’s unique is that they integrated the analytics as a plug-in into an open-source platform. ”If anybody wants to plug in our license plate technology into their platform, they can do it without having to rewrite their entire platform from scratch,” he notes.
Real-life Deployment
Their solution, named Vahan Eye, was piloted at Chityal on the Vijayawada–Hyderabad highway, where the team installed cameras, laid cables, and deployed the system end-to-end. The deployment tracks trucks entering Telangana and cross-checks them against a whitelist of nearly 40,000 approved vehicles. Tweaked specially to suit the needs of TGMDC, the solution offers customised dashboards. Since September, the system has been running continuously. Despite challenges such as low lighting at night and festival-related obstructions such as garlands covering the number plates, the algorithm has proven robust and continues to improve with live data.

From PoC to Public Impact
Built by a lean team of fewer than five engineers and powered by modern deep learning models, Vahan Eye demonstrates how lab research can be translated into an affordable, field-ready public solution. “Our IP is that we really figured out how to solve this whole handwritten license plate character problem,” says Dr. Yalla. Currently, the team is working on customising the solution for the Police Department for automatic detection of traffic violations by 2-wheelers.
Dr. Yalla, who began his career in the video surveillance industry with classical machine learning solutions that used support vector machines, explains that with advances in deep learning, more powerful algorithms such as YOLO and RF-Detr are now being applied, leading to significantly improved performance and accuracy. As he puts it, the goal is clear: prove the technology works, make it accessible at a fraction of commercial costs, and enable scalable adoption across government departments.
The post IIIT Hyderabad’s Smart Approach To Sand Mining Enforcement, Incorporating AI in Trucks appeared first on ELE Times.
Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, Larsen & Toubro, and Micron Join the IDTA
The India Deep Tech Alliance (IDTA) announced that Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, Larsen & Toubro, and Micron Technology have joined the Alliance. These additions further strengthen IDTA’s cross-sector collaboration model, which brings together investors, corporates, and technology-enabling partners to mobilise capital, technical expertise, market access, and policy engagement for the advancement of Indian deep tech startups.
With the addition of these global and Indian industry leaders, IDTA now spans artificial intelligence, semiconductor equipment, memory, materials, infrastructure engineering, and power systems, creating an integrated platform to support investment, technology collaboration, talent development, and startup commercialisation. With the shared goal of accelerating the growth of India’s deep tech economy, IDTA Corporate Strategic Partners aim to leverage their expertise to provide strategic and technology counsel to other IDTA members and emerging startups. Strategic advisory and ecosystem collaborations may include:
- Manufacturing and scale-up guidance for lab-to-fab transitions and production readiness.
- Technical talks, training, and access to expert resources.
- Collaborative research discussions and ecosystem initiatives with startups, researchers, and industry.
- Private industry input to policy dialogues related to national priority technology sectors.
- Mentorship, network access, and co-development opportunities in concert with investors.
IDTA is an industry-led consortium formed to mobilise capital and company-building expertise to help India-domiciled deep tech startups scale globally. It was formed to expand private sector support for strategic technology sectors, complementing the Government of India’s Research, Development & Innovation (RDI) Scheme.
This latest membership expansion follows NVIDIA joining IDTA as a Founding Member and Strategic & Technical Advisor, underscoring the Alliance’s ambition to build globally relevant, India-anchored deep tech capabilities at scale. Since its founding in September 2025, IDTA has expanded to a commitment of more than $2.5B USD in venture funding to Indian deep tech startups over the next five years, including a dedicated $1B USD allocation to Indian AI startups to be invested over the next three years. IDTA venture capital members have deployed $110M USD into 50+ companies over the past six months.
“The entry of Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, L&T, and Micron marks a pivotal step in moving India’s deep tech ambition from intent to execution,” said Arun Kumar, India Managing Partner of Celesta Capital and Chair of IDTA. “Together with NVIDIA’s role as a founding member and strategic advisor, this coalition brings unmatched depth across semiconductors, advanced manufacturing, infrastructure, and systems engineering. IDTA is designed to align capital, technology, and policy so that India can emerge not just as a participant, but as a trusted global hub for next-generation technologies.”
Quotes from New IDTA Corporate Strategic Partners:
Om Nalamasu, CTO, Applied Materials, said, “Applied Materials has a long history of working across industry, startups, academia, and research institutions to advance foundational technologies. As a materials engineering leader, we believe long‑term progress comes from sustained, ecosystem‑level collaboration. Through this alliance, we look forward to contributing our deep technology expertise to help build resilient ecosystems for India and the world.’’
Mr. Amar Kaul, Global CEO & Managing Director, CG Power, said, “India’s deep tech journey is entering a decisive phase, one where execution, industrial capability, and long-term partnerships will determine global relevance. CG Power’s participation in the India Deep Tech Alliance reflects our conviction that nation-building today requires strong, technology-led manufacturing ecosystems. Through IDTA, we look forward to contributing our expertise in industrial, power systems and semiconductors to create resilient and future-ready value chains that reinforce India’s position as a trusted global technology hub.”
Kevin Chen, Head of Lam Capital & Corporate Development, Lam Research, said: “Semiconductor manufacturing excellence depends on deep collaboration across equipment, materials, process technology, and talent. We look forward to engaging with IDTA to help Indian innovators navigate technology roadmaps, manufacturability, and global ecosystem linkages that accelerate from lab to fab.”
Prashant Chiranjive Jain, Head Corporate Centre, Larsen & Toubro, said: “The India Deep Tech Alliance represents a pivotal shift toward indigenous innovation. By synergising L&T’s engineering heritage with advanced capabilities in AI, design engineering, and quantum systems, we are committed to building a robust deep-tech ecosystem. We look forward to delivering cutting-edge solutions that position India as a global leader in the next generation of technology.”
Anand Ramamoorthy, Managing Director, Micron India, said: “Micron’s decision to join the India Deep Tech Alliance reflects our commitment to ecosystem-led collaboration to propel a vital economic engine for India. Micron’s technology and innovation expertise will play a vital role in helping advance globally competitive deep tech from India while aligning with IDTA’s support for the national RDI agenda and its focus on translating research into market impact.”
The post Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, Larsen & Toubro, and Micron Join the IDTA appeared first on ELE Times.
Manufacturing Breakthroughs in Chip Packaging Are Powering AI’s Future
Courtesy: Lam Research
With all the attention being given to AI, it’s easy to overlook some of the core technologies enabling its capabilities. Sure, a lot more people have now heard about NPUs, GPUs and the businesses that make them, but what about the companies that enable these cutting-edge AI accelerators to be manufactured?
The Complexity of Modern Chipmaking
While most people may not realise it, chip manufacturing is incredibly challenging and requires the level of scientific breakthroughs that have powered humanity’s most advanced achievements. I mean, we’re talking about bending the laws of physics to build components that are a thousand times smaller than a grain of sand. Oh, and doing so millions of times over at incredibly high levels of quality and consistency. Plus, with the extra demands that GenAI workloads are putting on today’s latest chips, the challenges are getting even tougher.
That’s why companies providing the equipment and technologies that enable the manufacturing of these advanced chips play an essential role in driving the advanced AI capabilities we are all starting to experience.
Without their work to overcome technical challenges like the need for exascale computing, addressing the “memory wall” that can slow down AI accelerators, increasing power efficiency, and other issues that are necessary to maintain the Moore’s Law-like advances we’ve seen in these chips, the state of AI would not be where it is today. In particular, organisations like Lam Research, which build extremely complex, sophisticated machines that help process the raw silicon wafers that eventually become today’s most powerful semiconductor chips, play a big, though little-understood, part in big tech advancements like AI.
Building Next-Generation AI Chips Through Heterogeneous Integration
Lam Research makes a wide array of equipment that performs multiple tasks in the highly precise, extremely complex, and long (often 30 days or more) process of creating a modern chip. But in the era of AI accelerators, it turns out even the most sophisticated individual chip isn’t enough.
Instead, the latest GPUs and other advanced processors are being assembled through a process called heterogeneous integration, which combines multiple independent elements, known as “chiplets,” into even more sophisticated pseudo-SOCs, or Systems on Chip (advanced multi-chip packages that mimic some characteristics of an SOC). Commonly referred to as advanced packaging, the technology that enables the creation of these pseudo-SOCs requires extremely sophisticated semiconductor manufacturing.
Extraordinarily precise component stacking, chip-to-chip connections, and other key technologies allow these chips to integrate multiple independent processing elements, separate connectivity elements, memory, and more. The ultimate goal is to create the most powerful and capable multi-chip package they can in the most effective and efficient space and power envelopes possible.
Advanced Packaging Techniques
As with individual wafer processing, there are often multiple steps and multiple technologies (and approaches) involved with chip packaging. Some entail direct side-by-side connections between various chiplets and other elements, while others use various forms of stacking technology where different pieces sit on top of one another. In all cases, a critical part of the packaging process involves creating the paths through which the connections between the various elements are made. Sometimes those paths are created through film layers that act as a type of “glue” between the elements, while in other situations, it may involve creating millions of tiny holes that are filled with a metal-like material that provides something akin to a physical bridge between the layers.
In the case of Lam Research, the company has developed machines for each of those core packaging technologies. For physical bridging types—which are called through silicon vias or TSVs—Lam offers products in their Syndion, Striker ALD, and SABRE 3D lines. Each performs different parts of the process, including etching for creating the holes, deposition and filling for both lining and then injecting the new material into the holes, and then various cleaning processes along the way.
Semiconductor Manufacturing Innovations Enable AI Progress
Though little understood, the advancements in AI acceleration that have been achieved to date are strongly tied back to the manufacturing technologies that enabled them to be built. Integrating things like High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) directly beside GPU cores, for example, has had a huge impact on the performance, scale and efficiency of the latest AI accelerators, and that, in turn, is driving the impressive advancements we’ve seen in Large Language Models (LLMs) and other AI applications.
Looking forward, it’s going to be continued advancements in 3D packaging—along the lines of what Lam Research is doing with their new VECTOR TEOS 3D tool—that allow those advancements to continue. They may not be easy to see, understand, or appreciate, but semiconductor manufacturing technologies play an enormously important role in moving the tech industry and society forward.
The post Manufacturing Breakthroughs in Chip Packaging Are Powering AI’s Future appeared first on ELE Times.
Powering the Future: How High-Voltage MLCCs Drive Efficiency in Modern Electronics
Courtesy: Murata Electronics
Power electronics is undergoing a profound transformation. Devices are now expected to operate faster, become smaller, and achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency.
To meet these demands, wide-bandgap (WBG) semiconductors, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), are increasingly adopted over silicon-based devices. These advanced materials enable significantly higher switching frequencies and increased voltage levels. This reduces system size and boosts power density.
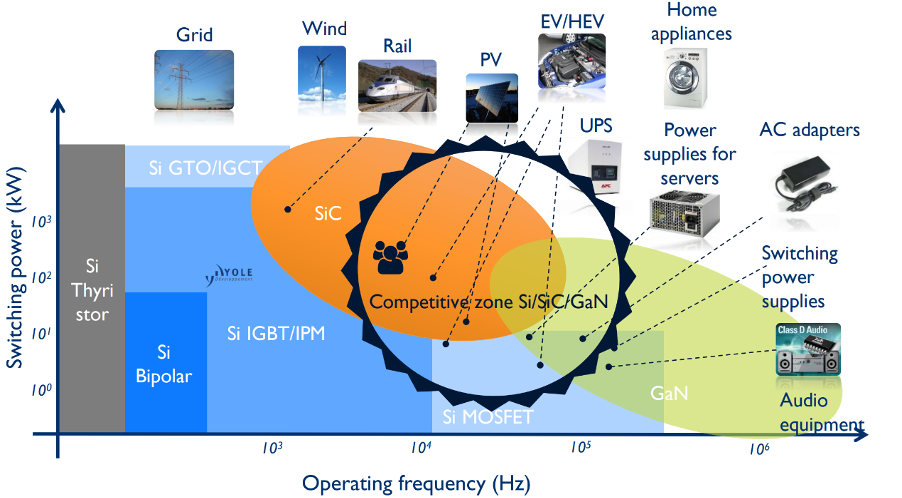 Figure 1: The typical operating frequency and switching power of various semiconductor materials (Source: Yole Group) [see MURA200 for original images]At the same time, the rapid electrification of transport, industry, and energy infrastructure is driving an unprecedented expansion in power conversion applications. This evolution exposes designers to a far wider spectrum of operating conditions.
Figure 1: The typical operating frequency and switching power of various semiconductor materials (Source: Yole Group) [see MURA200 for original images]At the same time, the rapid electrification of transport, industry, and energy infrastructure is driving an unprecedented expansion in power conversion applications. This evolution exposes designers to a far wider spectrum of operating conditions.
Critical Challenges in High-Voltage Systems
These evolving expectations place significant stress not only on active devices but also on the passive components integral to these systems. Higher switching speeds, for instance, lead to sharp voltage transients and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Increased voltages impose strict demands on insulation and overall reliability.
Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) play a vital role in suppressing high-frequency noise, absorbing transient spikes, and protecting semiconductor devices from overvoltage stress. Therefore, the advancement of MLCCs must align with the increased performance standards required by WBG devices, necessitating enhancements in dielectric compositions and creative packaging approaches.
Taming Transient Spikes
Snubber capacitors are essential in power electronics, especially where high-speed switching induces voltage overshoot and ringing. This is particularly critical during the turn-off transitions of MOSFETs or IGBTs. This issue is heightened in SiC and GaN power semiconductors, which exhibit greater surge voltages compared to traditional silicon IGBTs.
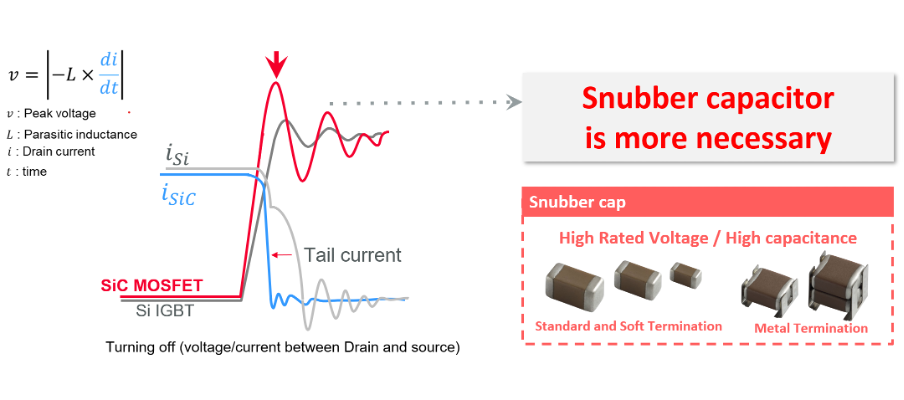 Figure 2: SiC MOSFETs exhibit a higher surge voltage than traditional Si IGBTs (Source: Murata) [see MURA200 for original images]A well-matched snubber capacitor effectively absorbs transient energy, suppresses peak voltages, and damps oscillations. Murata’s metal-termination MLCCs, such as the KC3 and KC9 series, are optimised for use in SiC-based circuits.
Figure 2: SiC MOSFETs exhibit a higher surge voltage than traditional Si IGBTs (Source: Murata) [see MURA200 for original images]A well-matched snubber capacitor effectively absorbs transient energy, suppresses peak voltages, and damps oscillations. Murata’s metal-termination MLCCs, such as the KC3 and KC9 series, are optimised for use in SiC-based circuits.
The post Powering the Future: How High-Voltage MLCCs Drive Efficiency in Modern Electronics appeared first on ELE Times.
Redefining the human experience with intelligent computing
Courtesy: Qualcomm
Enabling the devices, vehicles and machines that define tomorrow’s world.
What you should know:
- The next UI centres around you, with your AI agent seeing, hearing and acting on your behalf.
- We’re scaling AI to redefine the human experience—powering next-gen wearables and personal AI devices, and driving intelligence into robots, cars and smart homes.
- Our technologies enable extraordinary experiences that consumers and businesses depend on every day—bringing personal and physical AI everywhere.
Think of AI like coffee. You don’t walk into a café and ask for “a beverage brewed from roasted beans” — that’s assumed. You order the experience. Latte, half-pump vanilla, extra shot against a soundtrack of acoustic 90s alternative. The perfect mix to fuel your day, making you more productive, more creative, more you. AI works the same way. It’s a given, not a feature — the foundation of every experience, making each truly yours.
You are at the centre with your agent as your intelligent teammate. This is the next UI. Forget the seemingly endless scrolling and tedious tapping to complete one.single.thing only to do it again.and.again. Instead, your agent moves with you, learns from you and anticipates your needs. And thanks to AI processing on the device, it remains private, contextual and always-on. Like your favourite barista, who knows your order as soon as you walk in, including your (secret) treat every Friday.
We’re leading the charge toward the future of intelligent computing — reimagining possibilities for not only consumers, but also enterprises and industries worldwide. We’re scaling intelligence from edge to cloud, bringing AI everywhere. Our Snapdragon and Qualcomm Dragonwing platforms enable the devices, vehicles and machines that define tomorrow’s world — and redefine the human experience.
And again, I can’t say this enough, it’s all about you. Or more precisely, an “ecosystem of you” where your agent can see, hear and act on your behalf across an emerging category of AI-first intelligent wearables, along with smartphones and AI PCs.
The newest entrant in our Snapdragon X Series Compute Platforms, Snapdragon X2 Plus, delivers agentic AI experiences to aspiring creators, professionals and everyday users — broadening the already-growing Windows PC community.
Your home, too, is transforming into a responsive, intuitive environment. Understanding you and your family, your home adapts to your needs, routines and comforts. Lights, climate, security and entertainment are now intelligent with Dragonwing Q-7790 and Q-8750 processors. The backbone of these AI-enabled experiences and home automation? Connectivity, brought to you by Qualcomm, the leading wireless innovator.
But AI isn’t just personal. It’s also physical, acting alongside you.
Your car is transforming into an adaptive companion, driven by intelligence. Snapdragon is redefining automotive experiences, from enhancing safety and comfort to immersive entertainment. Private, contextual AI — sensing, processing, acting in real time — makes every drive smarter, more efficient and connected.
Advanced autonomous capabilities are also being used to power the next generation of personal service robots, all the way through to industrial full-size humanoids. Thanks to our full-stack robotics system, they will deliver intuitive and impactful assistance with precision, enhancing daily life and industry. And I’m sure they’ll learn how to make your coffee perfectly.
This is truly an exciting time in how technology is evolving around us and for us. Our innovations already power billions of devices, enabling the extraordinary experiences that consumers and businesses depend on every day. And we can’t wait to bring you more.
The post Redefining the human experience with intelligent computing appeared first on ELE Times.
The Forest Listener: Where edge AI meets the wild
Courtesy: Micron
Let’s first discuss the power of enabling. Enabling a wide electronic ecosystem is essential for fostering innovation, scalability and resilience across industries. By supporting diverse hardware, software and connectivity standards, organisations can accelerate product development, reduce costs and enhance user experiences. A broad ecosystem encourages collaboration among manufacturers, developers and service providers, helping to drive interoperability. Enabling an ecosystem for your customers is a huge value for your product in any market, but for a market that spans many applications, it’s paramount for allowing your customers to get to the market quickly. Micron has a diverse set of ecosystem partners for broad applications like microprocessors, including STMicroelectronics (STM). We have collaborated with STM for years, matching our memory solutions to their products. Ultimately, these partnerships empower our mutual businesses to deliver smarter, more connected solutions that meet the evolving needs of consumers and enterprises alike.
The platform and the kit
There’s something uniquely satisfying about peeling back the anti-static bag and revealing the STM32MP257F-DK dev board brimming with potential. As an embedded developer, I am excited when new silicon lands on my desk, especially when it promises to redefine what’s possible at the edge. The STM32MP257F-DK from STMicroelectronics is one of those launches that truly innovates. The STM32MP257F-DK Discovery Kit is a compact, developer-friendly platform designed to bring edge AI to life. And in my case, to the forest. It became the heart of one of my most exciting projects yet: the Forest Listener, a solar-powered, AI-enabled bird-watching companion that blends embedded engineering with natural exploration.
A new kind of birdwatcher
After a few weeks of development and testing, my daughter and I headed into the woods just after sunrise — as usual, binoculars around our necks, a thermos of tea in the backpack and a quiet excitement in the air. But this time, we brought along a new companion. The Forest Listener is a smart birdwatcher, an AI-powered system that sees and hears the forest just like we do. Using a lightweight model trained with STM32’s model zoo, it identifies bird species on the spot. No cloud, no latency, just real-time inference at the edge. My daughter has mounted the device on a tripod, connected the camera and powered it on. The screen lights up. It’s ready! Suddenly, a bird flutters into view. The camera captures the moment. Within milliseconds, the 1.35 TOPS neural processing unit (NPU) kicks in, optimised for object detection. The Cortex-A35 logs the sighting (image, species, timestamp), while the Cortex-M33 manages sensors and power. My daughter, watching on a connected tablet, lights up: “Look, Dad! It found another one!” A Eurasian jay, this time.
Built for the edge … and the outdoors
Later, at home, we scroll through the logs saved on the Memory cards. The system can also upload sightings via Ethernet. She’s now learning names, songs and patterns. It’s a beautiful bridge between nature and curiosity. At the core of this seamless experience is Micron LPDDR4 memory. It delivers the high bandwidth needed for AI inference and multimedia processing, while maintaining ultra-low power consumption, critical for our solar-powered setup. Performance is only part of the story: What truly sets Micron LPDDR4 apart is its long-term reliability and support. Validated by STM for use with the STM32MP257F-DK, this memory is manufactured at Micron’s dedicated longevity fab, ensuring a more stable, multiyear supply chain. That’s a game-changer for developers to build solutions that need to last — not just in home appliances, but in the harsh field environment. Whether you’re deploying an AI app in remote forests, industrial plants or smart homes, you need components that are not only fast and efficient but also built to endure. Micron LPDDR4 is engineered to meet the stringent requirements of embedded and industrial markets, with a commitment to support and availability that gives manufacturers peace of mind.
Beyond bird-watching
The Forest Listener is just one example of what the STM32MP257F-DK and Micron LPDDR4 can enable. In factories, the same edge-AI capabilities can monitor machines, detect anomalies, and reduce downtime. In smart homes, they can power face recognition, voice control and energy monitoring — making homes more intelligent, responsive and private, all without relying on the cloud.
The post The Forest Listener: Where edge AI meets the wild appeared first on ELE Times.
Solution Suite Concept: Software-Based Refrigerator
Courtesy: Renesas
Imagine a world without cold storage—medicines would spoil, food would perish, and supply chains would collapse. Refrigeration systems are vital to modern life, from pharmaceutical coolers to large-scale warehouses. These systems form the backbone of the cold chain, ensuring products meet strict storage requirements.
To achieve durability and sustainability in these operations, embracing AI is essential for maximum performance optimisation. Renesas has been continuously innovating in this space, delivering a range of AI-driven solutions tailored for the refrigeration industry—helping businesses enhance efficiency, reliability, and energy savings.
Renesas Enablement for AI-powered Refrigeration Solutions
Renesas’ solution concept introduces a suite of AI-driven applications designed to tackle everyday challenges in refrigeration systems. These proposals focus on enhancing operational efficiency and reliability in key areas such as predictive maintenance, energy optimisation, and asset management, among others.
Refrigerant gas is crucial for maintaining stable cold temperatures in cooling systems. Over time, however, leaks can develop due to wear and tear in pipes or refrigerant circuits. To address this challenge, Renesas AI leverages advanced AI algorithms to detect anomalies by analysing changes in electrical current and compressor vibrations. This proactive approach enables timely maintenance, prevents costly breakdowns, and ensures optimal cooling efficiency.
Compressor Overheat Detection
Compressor overheating can result from issues such as low refrigerant levels or clogged filters, leading to potential system damage. Renesas AI HVAC solutions go beyond leak detection by continuously monitoring filter conditions and measuring intake airflow in real time. By analysing this data, the system predicts risks before they escalate, ensuring the cooling system operates efficiently and reliably.
Cooling Capacity Monitoring
Renesas HVAC solutions integrate advanced AI features to predict fan imbalances that directly impact cooling efficiency. Using AI models trained with electrical current data, these anomalies can be detected, enabling seamless and sensorless monitoring. This proactive approach enhances system reliability and ensures optimal cooling performance.
Assets Monitoring: Availability and Expiry Tracking
AI-powered object detection and classification enable real-time monitoring of stock levels and refrigerated assets. The system can automatically suggest restocking needs and estimate lead times for each item. Reducing the need for manual inventory checks and minimising the frequency of opening cooling units, it reduces energy consumption and improves operational efficiency.
Person Identification
AI-powered person identification enhances security and user experience in refrigeration systems. Authorised access can be ensured through two approaches:
- Vision-based authentication using an object detection model combined with on-device learning for custom face recognition.
- Voice-based authentication using a speaker identification model with a microphone sensor.
These methods can be combined for two-step authentication, which is especially critical in medical or industrial refrigeration environments. For home appliances, person identification enables context-aware interactions, such as personalised dietary recommendations or recipe suggestions, creating a smarter and more intuitive user experience.
By integrating real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and intelligent object detection, these systems deliver optimal performance, energy efficiency, and operational reliability. From detecting refrigerant leaks and airflow issues to predicting fan imbalances and automating inventory management, the Renesas solution concept offers a comprehensive, end-to-end approach to cooling system optimisation.
This seamless and sensorless monitoring capability not only extends system longevity but also drives significant energy savings. As demand for smarter, more efficient refrigeration systems grows, Renesas is leading the way, pioneering the next generation of intelligent cooling solutions.
The post Solution Suite Concept: Software-Based Refrigerator appeared first on ELE Times.
The V2X Revolution: Satellite Integration, Quantum Security, and 5G RedCap Reshape Automotive Connectivity
Imagine your car negotiating traffic with satellites, quantum-encrypted handshakes, and roadside infrastructure—all while you sip your morning coffee. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the V2X revolution unfolding in production vehicles by 2027. As the Vehicle-to-Everything market hurtles from $6.53 billion in 2024 toward a staggering $70.94 billion by 2032, three converging technologies are rewriting the rules of automotive connectivity: satellite-integrated networks that promise coverage where cell towers fear to tread, post-quantum cryptography racing against the quantum computing threat, and cost-optimised 5G RedCap systems making autonomous driving infrastructure economically viable. The question isn’t whether your next vehicle will be connected—it’s whether the ecosystem will be ready when it rolls off the line.
The Convergence Catalyst: When Satellites, Quantum, and RedCap Collide
The automotive industry has weathered countless transformations, but the V2X revolution of 2025-2026 represents something unprecedented: three disparate technologies—satellite connectivity, quantum cryptography, and 5G RedCap, converging into a single automotive imperative as the market accelerates toward $70.94 billion by 2032.
The strategic calculus facing OEMs isn’t simply about adopting V2X; it’s about choosing which technological bet defines their competitive position. Some prioritise satellite-integrated Non-Terrestrial Networks, banking on 5GAA’s 2025 demonstrations proving vehicles can maintain emergency connectivity where terrestrial infrastructure fails. Their roadmaps target 2027 commercial deployments, envisioning truly ubiquitous vehicle connectivity from urban centres to remote highways.
“Connectivity is becoming more and more important for vehicles. No connection is not an option. Satellite came to our attention 3 to 5 years ago, and then it was costly and proprietary with large terminals,” said Olaf Eckart, Senior Expert, Cooperations R&D / Engineering Lead, NTN, BMW
Others race against the quantum threat timeline. With NIST finalising quantum-resistant standards including CRYSTALS-Kyber and CRYSTALS-Dilithium, these companies face an uncomfortable truth: today’s vehicle encryption could be obsolete within a decade. Their 18-24 month roadmaps aren’t about adding features; they’re about future-proofing against a cryptographic paradigm shift most consumers don’t yet understand.
The pragmatist camp focuses on 3GPP Release 17’s RedCap specifications entering mass production. These organisations see cost-effective 5G variants as critical enablers for vehicle-road-cloud integration architectures, making L2+ autonomous driving economically viable at scale.
What’s remarkable isn’t the diversity of approaches; it’s that all three are simultaneously correct. The V2X ecosystem emerging in 2026-2027 won’t be defined by a single winner but by seamless integration of all three domains. Vehicles rolling off 2027 production lines will need satellite backup for coverage gaps, quantum-resistant security for longevity, and RedCap efficiency for cost-effectiveness.
The question keeping executives awake isn’t which technology to choose; it’s whether their organisations can master all three fast enough to remain relevant.
Engineering Reality Check: Breaking Through the Technical Bottlenecks
Every breakthrough technology comes with footnotes written in engineering challenges, and V2X is no exception. The gap between demonstrations and production-ready systems is measured in thousands of testing hours and occasional failures that never reach press releases.
Consider satellite-integrated V2X’s deceptively simple promise: connectivity everywhere. Reality involves achieving seamless terrestrial-to-Non-Terrestrial Network handovers while maintaining sub-100ms latency that safety-critical applications demand. When vehicles at highway speeds switch from cellular towers to LEO satellite constellations, handovers must be invisible and instantaneous. Engineers are discovering that 3GPP Release 17/18 standards provide frameworks, but real-world implementation requires solving synchronisation challenges that textbooks barely address.
Post-quantum cryptography presents an even thornier dilemma. CRYSTALS-Kyber and CRYSTALS-Dilithium aren’t just longer keys—they’re fundamentally different mathematical operations consuming significantly more processing power than today’s RSA or ECC algorithms. Automotive-grade ECUs, designed with tight power budgets and cost constraints, weren’t built for quantum-resistant workloads. Development teams wrestle with a trilemma: maintain security standards, meet latency requirements, or stay within thermal envelopes. Pick two.
The integration paradox compounds complexity. Can existing vehicles receive V2X capabilities through OTA updates and modular hardware? Sometimes, a 2024 model with appropriate sensor suites might support RedCap upgrades via software. But satellite antenna arrays and quantum-capable security modules often require architectural changes that can’t be retrofitted; they need initial platform integration.
The coexistence problem adds another layer. Many vehicles must support multiple V2X standards simultaneously: legacy DSRC, C-V2X, and emerging satellite connectivity. Ensuring these systems don’t interfere while sharing antenna space and processing resources is creative problem-solving happening in testing facilities at 3 AM.
What separates vapourware from production-ready solutions isn’t the absence of challenges; it’s how engineering teams respond when elegant theory collides with messy reality.
NXP’s Post Quantum Cryptography chips use on-chip isolation so that “in the event of an identified attack, the technology doesn’t let the attack spread to other chips and controllers in the vehicle,” said the NXP Semiconductors, Engineering Team, Marius Rotaru (Software Architect) & Joppe Bos (Senior Principal Cryptographer).
Beyond the Vehicle: Infrastructure, Ecosystems, and the Path to Scale
The most sophisticated V2X technology becomes an expensive paperweight without supporting ecosystems. This truth is reshaping automotive development models, forcing OEMs beyond the vehicle into infrastructure challenges they’ve historically ignored.
The infrastructure gap is staggering. Satellite-integrated V2X requires ground stations for orbit tracking and handover coordination. Post-quantum security needs certificate authorities upgraded with quantum-resistant algorithms across entire PKI hierarchies. RedCap-enabled vehicle-road-cloud architectures demand roadside units at sufficient density, plus edge computing infrastructure processing terabytes of sensor data with minimal latency.
No single company can build this alone, spawning partnership models from traditional supplier relationships into complex consortia. Automotive OEMs partner with telecom operators on spectrum allocation, governments on roadside infrastructure and regulatory frameworks, and satellite operators, cloud providers, and cybersecurity firms; often simultaneously, sometimes competitively.
Regulatory landscapes add complexity. V2X touches spectrum allocation, data privacy, cybersecurity standards, and safety certification, each governed by different agencies with different timelines. Europe swung toward C-V2X after years of DSRC mandates. China receives state-backed vehicle-road-cloud infrastructure investment. United States approaches vary by state, creating fragmented deployment landscapes complicating nationwide rollouts.
When does this reach mainstream production? RedCap systems enter vehicles now, in 2025-2026, leveraging existing cellular infrastructure. Satellite integration likely reaches commercial deployment by 2027-2028 for premium vehicles and emergency services. Post-quantum security faces longer timelines; threats aren’t imminent enough to justify computational overhead across fleets.
Three factors will accelerate or delay timelines: infrastructure deployment speed, regulatory harmonisation, and killer applications making V2X tangible to consumers. V2X reaches mainstream adoption when it solves problems people actually have.
Looking toward 2027-2030, the competitive landscape splits between integrated mobility providers mastering the full vehicle-infrastructure-cloud stack and specialised component suppliers. Winners will be organisations that built ecosystems delivering end-to-end experiences. In the V2X era, the vehicle is just the beginning.
by: Shreya Bansal, Sub-Editor
The post The V2X Revolution: Satellite Integration, Quantum Security, and 5G RedCap Reshape Automotive Connectivity appeared first on ELE Times.
20 Years of EEPROM: Why It Matters, Needed, and Its Future
ST has been the leading manufacturer of EEPROM for the 20th consecutive year. As we celebrate this milestone, we wanted to reflect on why the electrically erasable programmable read-only memory market remains strong, the problems it solves, why it still plays a critical role in many designs, and where we go from here. Indeed, despite the rise in popularity of Flash, SRAM, and other new memory types, EEPROM continues to meet the needs of engineers seeking a compact, reliable memory. In fact, over the last 20 years, we have seen ST customers try to migrate away from EEPROM only to return to it with even greater fervour.
Why companies choose EEPROM today? Granularity Understanding EEPROM
Understanding EEPROM
One of the main advantages of electrically erasable programmable read-only memory is its byte-level granularity. Whereas writing to other memory types, like flash, means erasing an entire sector, which can range from many bytes to hundreds of kilobytes, depending on the model, an EEPROM is writable byte by byte. This is tremendously beneficial when writing logs, sensor data, settings, and more, as it saves time, energy, and reduces complexity, since the writing operation requires fewer steps and no buffer. For instance, using an EEPROM can save significant resources and speed up manufacturing when updating a calibration table on the assembly line.
PerformanceThe very nature of EEPROM also gives it a significant endurance advantage. Whereas flash can only support read/write cycles in the hundreds of thousands, an EEPROM supports millions, and its data retention is in the hundreds of years, which is crucial when dealing with systems with a long lifespan. Similarly, its low peak current of a few milliamps and its fast boot time of 30 µs mean it can meet the most stringent low-power requirements. Additionally, it enables engineers to store and retrieve data outside the main storage. Hence, if teams are experiencing an issue with the microcontroller, they can extract information from the EEPROM, which provides additional layers of safety.
ConvenienceThese unique abilities explain why automotive, industrial, and many other applications just can’t give up EEPROM. For many, giving it up could break software implementation or require a significant redesign. Indeed, one of the main advantages of EEPROM is that they fit into a small 8-pin package regardless of memory density (from 1 Kbit to 32 Mbit). Additionally, they tolerate high operating temperatures of up to 145 °C for serial EEPROM, making them easy to use in a wide range of environments. The middleware governing their operations is also significantly more straightforward to write and maintain, given their operation.
ResilienceSince ST controls the entire manufacturing process, we can provide greater guarantees to customers facing supply chain uncertainties. Concretely, ST offers EEPROM customers a guarantee of supply availability through our longevity commitment program (10 years for industrial-grade products, 15 years for automotive-grade). This explains why, 40 years after EEPROM development began in 1985 and after two decades of leadership, some sectors continue to rely heavily on our EEPROMs. And why new customers seeking a stable long-term data storage solution are adopting it, bolstered by ST’s continuous innovations, enabling new use cases.
Why will the industry need EEPROM tomorrow? More storage EEPROM vs. Page EEPROM
EEPROM vs. Page EEPROM
Since its inception in the late 70s, EEPROM’s storage has always been relatively minimal. In many instances, it is a positive feature for engineers who want to reserve their EEPROM for small, specific operations and segregate it from the rest of their storage pool. However, as serial EEPROM reached 4 Mbit and 110 nm, the industry wondered whether the memory could continue to grow in capacity while shrinking process nodes. A paper published in 2004 initially concluded that traditional EEPROMs “scale poorly with technology”. Yet, ST recently released a Page EEPROM capable of storing 32 Mbit that fits inside a tiny 8-pin package.
The Page EEPROM adopts a hybrid architecture, meaning it uses 16-byte words and 512-byte pages while retaining the ability to write at the byte level. This offers customers the flexibility and robustness of traditional EEPROM but bypasses some of the physical limitations of serial EEPROM, thus increasing storage and continuing to serve designs that rely on this type of memory while still improving endurance. Indeed, a Page EEPROM supports a cumulative one billion cycles across its entire memory capacity. For many, Page EEPROMs represent a technological breakthrough by significantly expanding data storage without changing the 8-pin package size. That’s why we’ve seen them in asset tracking applications and other IoT applications that run on batteries.
New featuresST also recently released a Unique ID serial EEPROM, which uses the inherent capabilities of electrically erasable programmable read-only memory to store a unique ID or serial number to trace a product throughout its assembly and life cycle. Usually, this would require additional components to ensure that the serial number cannot be changed or erased. However, thanks to its byte-level granularity and read-only approach, the new Unique ID EEPROM can store this serial number while preventing any changes, thus offering the benefits of a secure element while significantly reducing the bill of materials. Put simply, the future of EEPROM takes the shape of growing storage and new features.
The post 20 Years of EEPROM: Why It Matters, Needed, and Its Future appeared first on ELE Times.
Modern Cars Will Contain 600 Million Lines of Code by 2027
Courtesy: Synopsys
The 1977 Oldsmobile Toronado was ahead of its time.
Featuring an electronic spark timing system that improved fuel economy, it was the first vehicle equipped with a microprocessor and embedded software. But it certainly wasn’t the last.
While the Toronado had a single electronic control unit (ECU) and thousands of lines of code (LOC), modern vehicles have many ECUs and 300 million LOC. What’s more, the pace and scale of innovation continue to accelerate at an exponential, almost unfathomable rate.
It took half a century for cars to reach 300 million LOC.
We predict the amount of software in vehicles will double in the next 12 months alone, reaching 600 million LOC or more by 2027.
The fusion of automotive hardware and software
Automotive design has historically been focused on structural and mechanical platforms — the chassis and engine. Discrete electronic and software components were introduced over time, first to replace existing functions (like manual window cranks) and later to add new features (like GPS navigation).
For decades, these electronics and the software that define them were designed and developed separately from the core vehicle architecture — standalone components added in the latter stages of manufacturing and assembly.
This approach is no longer viable.
Not with the increasing complexity and interdependence of automotive electronics. Not with the criticality of those electronics for vehicle operation, as well as driver and passenger safety. And not with a growing set of software-defined platforms — from advanced driver assistance (ADAS) and surround view camera systems to self-driving capabilities and even onboard agentic AI — poised to double the amount of LOC in vehicles over the next year.
From the chassis down to the code, tomorrow’s vehicles must be designed, developed, and tested as a single, tightly integrated, highly sophisticated system.
Shifting automotive business models
The rapid expansion of vehicular software isn’t just a technology trend — it’s rewriting the economics of the automotive industry. For more than a century, automakers competed on horsepower, handling, and mechanical innovation. Now, the battleground is shifting to software features, connectivity, and continuous improvement.
Instead of selling a static product, OEMs are adopting new, more dynamic business models where vehicles evolve long after they leave the showroom. Over-the-air updates can deliver new capabilities, performance enhancements, and safety improvements without a single trip to the dealer. And features that used to be locked behind trim levels can be offered as on-demand upgrades or subscription services.
This transition is already underway.
Some automakers are experimenting with monthly fees for heated seats or performance boosts. Others are building proprietary operating systems to replace third-party platforms, giving them control over the user experience — as well as the revenue stream. By the end of the decade, software subscriptions will become as common as extended warranties, generating billions in recurring revenue and fundamentally changing how consumers think about car ownership.
The engineering challenge behind OEM transformation
Delivering on the promise of software-defined vehicles (SDVs) that continuously evolve isn’t as simple as adding more code. It requires a fundamental rethinking of how cars are designed, engineered, and validated.
Hundreds of millions of lines of code must push data seamlessly across a variety of electronic components and systems. And those systems — responsible for sensing, safety, communication, and other functions — must work in concert with millisecond precision.
For years, vehicle architectures relied on dozens of discrete ECUs, each dedicated to a specific function. But as software complexity grows, automakers are shifting toward fewer, more powerful centralised compute platforms that can handle much larger workloads. This means more code is running on less hardware, with more functionality consolidated onto a handful of high-performance processors. As a result, the development challenge is shifting from traditional ECU integration — where each supplier delivered a boxed solution — to true software integration across a unified compute platform.
As such, hardware and software development practices can no longer be separate tracks that converge late in the process. They must be designed together and tailored for one another — well before any physical platform exists.
This is where electronics digital twins (eDTs) are becoming indispensable. By creating functionally accurate virtual models of vehicle electronics and systems, design teams can shift from late-stage integration to a model where software and hardware are co-developed from day one.
eDTs and virtual prototypes do more than enable earlier software development at the component level — they allow engineers to simulate, validate, and optimise the entire vehicle electronics. This means teams can see how data flows across subsystems, how critical components interact under real-world scenarios, and how emerging features might impact overall safety and performance. With eDTs, automakers can test billions — even trillions — of operating conditions and edge cases, many of which would be too costly, too time-consuming, or otherwise infeasible with physical prototypes.
By embracing eDTs, the industry is not just keeping pace with escalating complexity — it is re-engineering longstanding engineering processes, accelerating innovation, and improving the quality and safety of tomorrow’s vehicles.
The road ahead
Our prediction of cars containing 600 million lines of code by 2027 isn’t just a number. It signals a turning point for an industry that has operated in largely the same manner for more than a century.
Many automakers are reimagining their identity.
No longer just manufacturers, they’re becoming technology companies with business models that resemble those of cloud providers and app developers. They’re adopting agile, iterative practices, where updates roll out continuously rather than in multi-year product refreshes. And they’re learning how to design, develop, test, and evolve their products as a unified system — from chassis and engine to silicon and software — rather than a collection of pieces that are assembled on a production line.
Unlike the 1977 Oldsmobile Toronado, the car you buy in 2027 won’t be the same car you drive in 2030 — and that’s by design.
The post Modern Cars Will Contain 600 Million Lines of Code by 2027 appeared first on ELE Times.
Advancement in waveguides to progress XR displays, not GPUs
Across emerging technology domains, a familiar narrative keeps repeating itself. In Extended Reality (XR), progress is often framed as a race toward ever more powerful GPUs. In wireless research, especially around 6G, attention gravitates toward faster transistors and higher carrier frequencies in the terahertz (THz) regime. In both cases, this framing is misleading. The real constraint is no longer raw compute or device-level performance. It is system integration. This is not a subtle distinction. It is the difference between impressive laboratory demonstrations and deployable, scalable products.
XR Has Outgrown the GPU BottleneckIn XR, GPU capability has reached a point of diminishing returns as the primary limiter. Modern graphics pipelines, combined with foveated rendering, gaze prediction, reprojection, and cloud or edge offloading, can already deliver high-quality visual content within reasonable power envelopes. Compute efficiency continues to improve generation after generation. Yet XR has failed to transition from bulky headsets to lightweight, all-day wearable glasses. The reason lies elsewhere: optics, specifically waveguide-based near-eye displays.
Waveguides must inject, guide, and extract light with high efficiency while remaining thin, transparent, and manufacturable. They must preserve colour uniformity across wide fields of view, provide a sufficiently large eye-box, suppress stray light and ghosting, and operate at power levels compatible with eyewear-sized batteries. Today, no waveguide architecture geometric (reflective), diffractive, holographic, or hybrid solves all these constraints simultaneously. This reality leads to a clear conclusion: XR adoption will be determined by breakthroughs in waveguides, not GPUs. Rendering silicon is no longer the pacing factor; optical system maturity is.
The Same Structural Problem Appears in THz and 6GA strikingly similar pattern is emerging in terahertz communication research for 6G. On paper, THz promises extreme bandwidths, ultra-high data rates, and the ability to merge communication and sensing on a single platform. Laboratory demonstrations routinely showcase impressive performance metrics. But translating these demonstrations into real-world systems has proven far harder than anticipated. The question is no longer whether transistors can operate at THz frequencies; they can, but whether entire systems can function reliably, efficiently, and repeatably at those frequencies.
According to Vijay Muktamath, Founder of Sensesemi Technologies, the fundamental bottleneck holding THz radios back from commercialisation is system integration. Thermal management becomes fragile, clock and local oscillator integration grows complex, interconnect losses escalate, and packaging parasitics dominate performance. Each individual block may work well in isolation, but assembling them into a stable system is disproportionately difficult. This mirrors the XR waveguide challenge almost exactly.
When Integration Becomes Harder Than InnovationAt THz frequencies, integration challenges overwhelm traditional design assumptions. Power amplifiers generate heat that cannot be dissipated easily at such small scales. Clock distribution becomes sensitive to layout and material choices. Even millimetre-scale interconnects behave as lossy electromagnetic structures rather than simple wires.
As a result, the question of what truly limits THz systems shifts away from transistor speed or raw output power. Instead, the constraint becomes whether designers can co-optimise devices, interconnects, packaging, antennas, and thermal paths as a single electromagnetic system. In many cases, packaging and interconnect losses now degrade performance more severely than the active devices themselves. This marks a broader transition in engineering philosophy. Both XR optics and THz radios have crossed into a regime where system-level failures dominate component-level excellence.
Materials Are Necessary, But Not SufficientThis raises a critical issue for 6G hardware strategy: whether III–V semiconductor technologies such as InP and GaAs will remain mandatory for THz front ends. Today, their superior electron mobility and high-frequency performance make them indispensable for cutting-edge demonstrations.
However, relying exclusively on III–V technologies introduces challenges in cost, yield, and large-scale integration. CMOS and SiGe platforms, while inferior in peak device performance, offer advantages in integration density, manufacturability, and system-level scaling. Through architectural innovation, distributed amplification, and advanced packaging, these platforms are steadily pushing into higher frequency regimes. The most realistic future is not a single winner, but a heterogeneous architecture. III–V devices will remain essential where absolute performance is non-negotiable, while CMOS and SiGe handle integration-heavy functions such as beamforming, control, and signal processing. This mirrors how XR systems offload rendering, sensing, and perception tasks across specialised hardware blocks rather than relying on a single dominant processor.
Why THz Favours Point-to-Point, Not Cellular CoverageAnother misconception often attached to THz communication is its suitability for wide-area cellular access. While technically intriguing, this vision underestimates the physics involved. THz frequencies suffer from severe path loss, atmospheric absorption, and extreme sensitivity to blockage. Beam alignment overhead becomes significant, especially in mobile scenarios. As Mr Muktamath puts it, “THz is fundamentally happier in controlled environments. Point-to-point links, fixed geometries, short distances, that’s where it shines.”
THz excels in short-range, P2P links where geometry is controlled and alignment can be maintained. Fixed wireless backhauls; intra-data-centre communication, chip-to-chip links, and high-resolution sensing are far more realistic early applications. These use cases resemble the constrained environments where XR has found initial traction in enterprise, defence, and industrial deployments— rather than mass consumer adoption.
Packaging: The Silent DominatorPerhaps the clearest parallel between XR waveguides and THz radios lies in packaging. In XR, the waveguide itself is the package: it dictates efficiency, form factor, and user comfort. In THz systems, packaging and interconnects increasingly dictate whether the system works at all. Losses introduced by packaging can erase transistor-level gains. Thermal resistance can limit continuous operation. Antenna integration becomes inseparable from the RF front-end. This has forced a shift from chip- centric design to electromagnetic system design, where silicon, package, antenna, and enclosure are co-designed from the outset.
Communication and Sensing: Convergence with ConstraintsTHz also revives the idea of joint communication and sensing on shared hardware. In theory, high frequencies offer exceptional spatial resolution, making simultaneous data transmission and environmental sensing attractive. In practice, coexistence introduces non-trivial trade-offs.
Waveform design, dynamic range, calibration, and interference management all become more complex when reliability and throughput must be preserved. The most viable path is not full hardware unification, but carefully partitioned coexistence, with shared elements where feasible and isolation where necessary. This echoes XR architectures, where sensing and rendering share infrastructure but remain logically separated to maintain performance.
A Single Lesson Across Two DomainsXR waveguides and THz radios operate in different markets, but they are constrained by the same fundamental truth: the era of component-led innovation is giving way to system-led engineering. Faster GPUs do not solve optical inefficiencies. Faster transistors do not solve packaging losses, thermal bottlenecks, or integration fragility.
As Mr. Muktamath aptly concludes, “The future belongs to teams that can make complex systems behave simply, not to those who build the most impressive individual blocks.” The next generation of technology leadership will belong to organisations that master cross-domain co-design across devices, packaging, optics, and software. Manufacturability and yield as first-order design constraints, Thermal and power integrity as architectural drivers and Integration discipline over isolated optimisation. In both XR and THz, success will not come from building the fastest block, but from making the entire system work reliably, repeatedly, and at scale. That is the real frontier now.
The post Advancement in waveguides to progress XR displays, not GPUs appeared first on ELE Times.
AI-Enabled Failure Prediction in Power Electronics: EV Chargers, Inverters, and SMPS
Reliability is now a defining parameter for modern power electronic systems. As the world pushes harder toward electric mobility, renewable energy adoption, and high-efficiency digital infrastructure, key converters like EV chargers, solar inverters, and SMPS are running in incredibly demanding environments. High switching frequencies, aggressive power densities, wide bandgap materials (like SiC/GaN), and really stringent uptime expectations have all squeezed those reliability margins down to almost nothing. Clearly, traditional threshold-based alarms or basic periodic maintenance are no longer enough to guarantee stable operation.
This is exactly where AI-enabled failure prediction emerges as a breakthrough. By integrating real-time sensing, historical stress patterns, physics-based models, and deep learning, AI unlocks the ability to spot early degradation. This gives us the power to accurately estimate remaining useful life (RUL) and prevent catastrophic breakdowns long before they ever occur.
Jean‑Marc Chéry, CEO of STMicroelectronics, has emphasised that the practical value of AI in power electronics emerges at fleet and lifecycle scale rather than at individual-unit prediction level, particularly for SiC- and GaN-based SMPS.
Aggregated field data across large deployments is used to refine derating guidelines, validate device-level reliability models, and harden next-generation power technologies, instead of attempting deterministic failure prediction on a per-unit basis.
Limitations of Traditional Monitoring in Power Electronics
Conventional condition monitoring methods, things like simple temperature alarms, current protection limits, or basic event logs, operate reactively. They only catch failures after components have already drifted past the acceptable redline. Yet, converter failures actually start much earlier from subtle, long-term changes. Think about:
- Gradual ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) increase in electrolytic capacitors
- Bond wire fatigue and solder joint cracking inside IGBT/MOSFET modules
- Gate oxide degradation in newer SiC devices
- Magnetic core saturation and insulation ageing
- Switching waveform distortions caused by gate driver drift
AI Techniques Powering Predictive Failure Intelligence
AI-based diagnostics in power electronics rest on three complementary pillars:
- Deep Learning for Real-Time Telemetry
AI-based diagnostics in power electronics rely on three complementary pillars:
Deep Learning for Real Time Telemetry Converters pump out rich telemetry data: temperatures, currents, switching waveforms, harmonics, soft switching behaviour, and acoustic profiles. Deep learning models find patterns here that are absolutely impossible for a human to spot manually.
- CNNs (Convolutional Neural Networks): These analyse switching waveforms, spot irregularities in turn-on/turn-off cycles, identify diode recovery anomalies, and classify abnormal transient events instantly.
- LSTMs (Long Short Term Memory Networks): These track the long-term drift in junction temperature, capacitor ESR, cooling efficiency, and load cycle behaviour over months.
- Autoencoders: learn the “healthy signature” of a converter and identify deviations that signal emerging faults.
- Physics-Informed ML
Pure machine learning struggles with operating points it has not seen; physics-informed machine learning offers better generalisation. It integrates:
- Power cycle fatigue equations
- MOSFET/IGBT thermal models
- Magnetics core loss equations
- Capacitor degradation curves
- SiC/GaN stress lifetime relationships
Peter Herweck, former CEO of Schneider Electric, has underscored that long-life power conversion systems cannot rely on data-driven models alone.
In solar and industrial inverters, Schneider Electric’s analytics explicitly anchor AI models to thermal behaviour, power-cycling limits, and component ageing physics, enabling explainable and stable Remaining Useful Life estimation across wide operating conditions.
- Digital Twins & Edge AI
Digital twins act as virtual replicas of converters, simulating electrical, thermal, and switching behaviour in real time. AI continuously updates the twin using field data, enabling:
- Dynamic stress tracking
- Load-cycle-based lifetime modelling
- Real-time deviation analysis
- Autonomous derating or protective responses
Edge-AI processors integrated into chargers, inverters, or SMPS enable on-device inference even without cloud connectivity.
AI-Driven Failure Prediction in EV Chargers
EV fast chargers (50 kW–350 kW+) operate under harsh conditions with high thermal and electrical stress. Uptime dictates consumer satisfaction, making predictive maintenance critical.
Key components under AI surveillance
- SiC/Si MOSFETs and diodes
- Gate drivers and isolation circuitry
- DC-link electrolytic and film capacitors
- Liquid/air-cooling systems
- EMI filters, contactors, and magnetic components
Roland Busch, CEO of Siemens, has emphasised that reliability in power-electronic infrastructure depends on predictive condition insight rather than reactive protection.
In high-power EV chargers and grid-connected converters, Siemens’ AI-assisted monitoring focuses on detecting long-term degradation trends—thermal cycling stress, semiconductor wear-out, and DC-link capacitor ageing—well before protection thresholds are reached.
AI-enabled predictive insights
- Waveform analytics: CNNs detect micro-oscillations in switching transitions, indicating gate driver degradation.
- Thermal drift modelling: LSTMs predict MOSFET junction temperature rise under high-power cycling.
- Cooling system performance: Autoencoders identify airflow degradation, pump wear, or radiator clogging.
- Power-module stress estimation: Digital twins estimate cumulative thermal fatigue and RUL.
Charging network operators report a 20–40% reduction in unexpected downtime by implementing AI-enabled diagnostics.
Solar & Industrial Inverters: Long-Life Systems Under Environmental Stress
Solar inverters operate for 10–20 years in harsh outdoor conditions—dust, high humidity, temperature cycling, and fluctuating PV generation.
Common failure patterns identified by AI
- Bond-wire lift-off in IGBT modules due to repetitive thermal stress
- Capacitor ESR drift affecting DC-link stability
- Transformer insulation degradation
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) anomalies due to sensor faults
- Resonance shifts in LCL filters
AI-powered diagnostic improvements
- Digital twin comparisons highlight deviations in thermal behaviour or DC-link ripple.
- LSTM RUL estimation predicts when capacitors or IGBTs are nearing end-of-life.
- Anomaly detection identifies non-obvious behavior such as partial shading impacts or harmonic anomalies.
SMPS: High-Volume Applications Where Reliability Drives Cost Savings
SMPS units power everything from telecom towers to consumer electronics. With millions of units deployed, even a fractional improvement in reliability creates massive financial savings.
AI monitors key SMPS symptoms
- Switching frequency drift due to ageing components
- Hotspot formation on magnetics
- Acoustic signatures of transformer failures
- Leakage or gate-charge changes in GaN devices
- Capacitor health degradation trends
Manufacturers use aggregated fleet data to continuously refine design parameters, enhancing long-term reliability.
Cross-Industry Benefits of AI-Enabled Failure Prediction
Industries implementing AI-based diagnostics report:
- 30–50% reduction in catastrophic failures
- 25–35% longer equipment lifespan
- 20–30% decline in maintenance expenditure
- Higher uptime and service availability
Challenges and Research Directions
Even with significant progress, several challenges persist:
- Scarcity of real-world failure data: Failures occur infrequently; synthetic data and stress testing are used to enrich datasets.
- Model transferability limits: Variations in topology, gate drivers, and cooling systems hinder direct model reuse.
- Edge compute constraints: Deep models often require compression and pruning for deployment.
- Explainability requirements: Engineers need interpretable insights, not just anomaly flags.
Research in XAI, transfer learning, and physics-guided datasets is rapidly addressing these concerns.
The Future: Power Electronics Designed with Built-In Intelligence
In the coming decade, AI will not merely monitor power electronic systems—it will actively participate in their operation:
- AI-adaptive gate drivers adjusting switching profiles in real time
- Autonomous derating strategies extending lifespan during high-stress events
- Self-healing converters recalibrating to minimise thermal hotspots
- Cloud-connected fleet dashboards providing RUL estimates for entire EV charging or inverter networks
- WBG-specific failure prediction models tailored for SiC/GaN devices
Conclusion
AI-enabled failure prediction is completely transforming the reliability of EV chargers, solar inverters, and SMPS systems. Engineers are now integrating sensor intelligence, deep learning, physics-based models, and digital twin technology. This allows them to spot early degradation, accurately forecast future failures, and effectively stretch the lifespan of the equipment.
This whole predictive ecosystem doesn’t just cut your operational cost; it significantly boosts system safety, availability, and overall performance. As electrification accelerates, AI-driven reliability will become the core foundation of next-generation power electronic design. It makes systems smarter, more resilient, and truly future-ready.
The post AI-Enabled Failure Prediction in Power Electronics: EV Chargers, Inverters, and SMPS appeared first on ELE Times.



