ELE Times
Infineon introduces XENSIV TLE4802SC16-S0000 with inductive sensing for higher accuracy and performance
Infineon Technologies AG is launching the XENSIV TLE4802SC16-S0000, an inductive sensor designed to enhance performance in automotive chassis applications. The sensor enables high-precision torque and angle measurements with robust stray field robustness, supporting digital output via SENT or SPC protocols. It achieves highly accurate sensing without needing additional shielding. Tailored for use in electric power steering systems, including torque and steering angle sensors, as well as pedal and suspension applications, the sensor offers both flexibility and reliability.
The XENSIV TLE4802SC16-S0000 combines a coil system driver, signal conditioning circuits, and a digital signal processor (DSP) in a single package. The sensor includes overvoltage and reverse polarity protection and comes in a RoHS-compliant and halogen-free surface-mounted TSSOP-16 package. It is qualified to AECQ100, Grade 0, for operation across a wide temperature range from -40°C to 150°C. Furthermore, the sensor is fully compliant with ISO 26262, making it ideal for safety-critical systems. A built-in cybersecurity function protects the system communications against man-in-the-middle attacks. The TLE4802SC16-S0000 is the first in a new family of inductive sensors, with further variants planned for release.
The post Infineon introduces XENSIV TLE4802SC16-S0000 with inductive sensing for higher accuracy and performance appeared first on ELE Times.
Anritsu to Showcase Groundbreaking PCI-Express 6.0 and 7.0 Demonstrations at PCI-SIG Developers Conference 2025
Anritsu Company will exhibit cutting-edge high-speed signal integrity solutions at the PCI-SIG Developers Conference from June 11-12 in Santa Clara, CA. Anritsu will present PCI-Express 6.0 and 7.0 live demonstrations of the industry-leading MP1900A BERT in collaboration with Synopsys, Teledyne LeCroy, CIG, and Tektronix.
Live Demonstrations
World’s First PCI-Express 6.0 Link Training over Optics
Anritsu is joining forces with Synopsys, Tektronix, and CIG to demonstrate the world’s first PCIe 6.0 optical connection link training using the Anritsu MP1900A BERT, Synopsys PCIe 6.x PHY and Controller IP, Tektronix DPO70000 Real Time Oscilloscope, and CIG OSFP LPO optical module.
PCIe over optical links provides higher bandwidth, covers longer distances, and is more energy-efficient, effectively addressing key bottlenecks for AI workloads in data centers.
This joint demonstration highlights Anritsu’s leadership in next-generation optical PCIe.
PCI-Express 7.0 Differential Skew Evaluation
In collaboration with Teledyne LeCroy, Anritsu will present a solution for evaluating the effect of differential skew in PCIe 7.0.
PCIe 7.0 uses PAM4 signaling, which reduces eye height by more than three times compared to NRZ. Combined with the speed increase from 32.0 Gbaud in PCIe 6.0 to 64.0 Gbaud, this results in a smaller unit interval (UI) that is significantly more sensitive to skew.
In high-speed environments, signals traversing an ISI channel may exhibit a dip in the fundamental frequency due to skew. While most BERTs lack built-in skew evaluation functions, Anritsu addresses this by using two MP1900A MU196020A PAM4 PPG units with the Channel Sync function to inject P-N skew and Teledyne LeCroy’s WaveMaster 8650HD 65 GHz oscilloscope for advanced analysis.
The post Anritsu to Showcase Groundbreaking PCI-Express 6.0 and 7.0 Demonstrations at PCI-SIG Developers Conference 2025 appeared first on ELE Times.
Infineon collaborates with Typhoon HIL to accelerate development of xEV power electronic systems using real-time hardware-in-the-loop platform
Infineon Technologies AG announced a collaboration with Typhoon HIL, a leading provider of Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) simulation solutions, to provide automotive engineering teams with a fully-integrated, real-time development and test environment for key elements of xEV powertrain systems. Customers working with Infineon’s AURIX TC3x/TC4x automotive microcontrollers (MCUs) can now use a complete HIL simulation and test solution using Typhoon’s HIL simulator for ultra-high-fidelity motor drive, on-board charger, BMS, and power electronics emulation, which provides a plug-and-play interface via the Infineon TriBoard Interface Card.
“Developers of xEV components including motor drives, battery management systems, on-board chargers, and DC-DC converters increasingly rely on Controller Hardware-in-the-Loop (C-HIL), on top of Software-in-the-Loop (SIL) and simulation-based approaches, to quickly achieve results and more rapidly iterate in both prototyping and test cycles,” said Christopher Thibeault, Director of Partner & Ecosystem Management Automotive Americas, Infineon Technologies. “With Typhoon’s proven real-time HIL platform, our AURIX customers can access a design and test environment that will help bring their automotive solutions based on dependable electronics to market faster.”
The solution offered by Infineon and Typhoon HIL includes any of several Typhoon HIL Simulators for real-time digital testing, a suite of testbed hardware and software tools, and the Infineon TriBoard Interface Card, which supports Infineon AURIX TC3xx and TC4xx evaluation boards and plugs directly into a single row of DIN41612 connectors on the front panel of the HIL Simulator. The solution streamlines validation workflows, expedites design and testing processes, and reduces development costs and complexity for customers. Typhoon HIL also offers an “Automotive Communication Extender” product for its HIL Simulator solution based on an AURIX TC3xx processor, which will provide an enhanced communication interface that allows customers to connect to a larger number of heterogenous ECUs under test via CAN, CAN FD, LIN, and SPI protocols.
“We are excited to partner with a leader in the automotive integrated circuits market, to provide MCU developers with a platform for development and testing of AURIX-based controllers before hardware design is completed,” said Petar Gartner, Director of HIL Solutions, Typhoon HIL. “Our joint customers gain a competitive edge by accelerating their design and test operations while reducing costs, which ultimately translates to market advantage. We look forward to this ongoing collaboration with Infineon.”
The post Infineon collaborates with Typhoon HIL to accelerate development of xEV power electronic systems using real-time hardware-in-the-loop platform appeared first on ELE Times.
Vishay Intertechnology Introduces New High-Reliability Isolation Amplifiers With Industry-Leading CMTI for Precision Applications
Devices Offer Industry-Leading 150 kV/μs CMTI, 400 kHz Bandwidth, and Low Minimum Gain Error of ± 0.3 %
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. announced the release of its latest isolation amplifiers, the VIA0050DD, VIA0250DD, and VIA2000SD. These new devices offer enhanced performance for a wide range of industrial, automotive, and medical applications, where high precision, reliability, and compact size are critical.
The VIA series of isolation amplifiers are designed to deliver exceptional thermal stability and precise measurement capabilities. With a typical common-mode transient immunity (CMTI) of 150 kV/μs, these amplifiers provide robust performance even in harsh environments, such as heavy-duty motor applications. The low typical gain error of ± 0.05 % and minimal gain drift of 15 ppm/°C typical ensure calibration-free, precise measurements over time and temperature. Additionally, these devices offer a high bandwidth of 400 kHz, enabling faster measurements compared to traditional opto-based isolation amplifiers.
Each amplifier in this series also features low offset error and drift, reinforced isolation, and inbuilt diagnostics for simplified precision current and voltage measurements. The inbuilt common mode voltage detection prevents failures in current and voltage measurement applications, making these amplifiers particularly suited for demanding applications where reliability is paramount. This series is designed to be compatible with Vishay’s WSBE low TCR, high power shunts, ensuring superior performance across a wide temperature range from -40°C to +125°C.
The VIA0050DD is a capacitive isolation amplifier optimized for environments where space is at a premium and low power consumption is essential. It features a high common-mode transient immunity (CMTI) of 100 kV/μs minimum, ensuring reliable performance even in noisy environments. Its low differential input voltage of ± 50 mV makes it ideal for precision isolated current measurements in space-constrained applications, such as power inverters, battery energy storage systems, motor phase current sensing, and industrial motor controls. Similarly, with its wide differential input voltage of ± 250 mV, the VIA0250DD allows for isolated current as well as voltage measurements.
The VIA2000SD offers the highest signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and bandwidth among the three models, making it the best choice for high-fidelity signal transmission in complex environments. Its linear differential input voltage in the range of 0.02 V to 2 V allows for precise isolated voltage measurements for applications such as bus voltage monitoring and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
The VIA series isolation amplifiers are designed to provide reliable, accurate performance across a variety of applications, including bus voltage monitoring, AC motor controls, power and solar inverters, and UPS. These amplifiers ensure accurate measurements across high voltage potential dividers and precision shunts, provide ease in monitoring of industrial motor drives, deliver robust performance in renewable energy systems, and maintain signal integrity in critical power systems.
The post Vishay Intertechnology Introduces New High-Reliability Isolation Amplifiers With Industry-Leading CMTI for Precision Applications appeared first on ELE Times.
Mouser Electronics Named 2024 Distributor of the Year by Bulgin
Mouser Electronics, Inc. announced that it has been named 2024 Distributor of the Year by Bulgin, a leading manufacturer of environmentally sealed connectors and components for various industries, including automotive, industrial, medical and more. Representatives for Bulgin cited Mouser’s strategic support of new product launches and customer growth in 2024.
“Mouser is a valued partner, and we congratulate the Mouser team on this well-deserved award, which celebrates Mouser’s customer service, effective communication, and commitment to meeting our business needs and goals,” said Eric Smith, Vice President of Global Distribution Channel with Bulgin. “Mouser played a key role in contributing to our overall success in 2024, and we look forward to continuing the momentum in 2025 and beyond.”
“We’d like to thank Bulgin for this great honor. This award recognizes our continued efforts to be the industry’s New Product Introduction (NPI) leader, with the latest products from forward-thinking companies like Bulgin,” said Krystal Jackson, Vice President of Supplier Management at Mouser. “We have an outstanding business relationship with Bulgin and anticipate great success together in the future.”
The post Mouser Electronics Named 2024 Distributor of the Year by Bulgin appeared first on ELE Times.
5G-Powered V2X: Using Intelligent Connectivity to Revolutionize Mobility
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication systems and lightning-fast 5G networks are merging to usher in a new era of global mobility. We are getting closer to the promise of safer roads, autonomous driving, and intelligent traffic ecosystems as a result of this convergence, which is changing how cars interact with their surroundings. Tech pioneers like Jio, Alepo, and Keysight Technologies are at the forefront of this change, facilitating V2X implementation across many infrastructures and regions.
V2X: What Is It?The term “vehicle-to-everything” (V2X) refers to a broad category of technologies that allow automobiles to interact with their surroundings. Networks (V2N), pedestrians (V2P), infrastructure (V2I), other vehicles (V2V), and connected devices (V2D) are all included in this. Every mode has special features that improve driver ease, traffic efficiency, and road safety.
Thanks to vehicle-to-vehicle (v2v) communication, cars can exchange vital information, including direction, speed, and braking condition. This makes collision avoidance systems and early alerts easier, especially in low-visibility situations. Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) enables automobiles to communicate with traffic lights, smart city systems, and road signs. By alerting drivers about impending risks or real-time signal changes, it facilitates traffic planning.
A proactive, as opposed to reactive, transportation system is made possible by the network of intelligent contacts created by this variety of communication channels. An environment where traffic flows are optimized, accidents are reduced, and cars can operate with more autonomy is the end outcome.
The Impact of Jio on India’s V2X Market DependencyOne of India’s top telecom companies, Jio, is actively constructing a strong 5G infrastructure to support V2X in the nation going forward. Jio’s V2X platform aims to create a digital transportation environment in which cars are intelligent, networked machines that can make decisions in real time.
Jio claims that their 5G-based V2X solutions are designed to make important applications like smart traffic control, cooperative collision avoidance, and autonomous driving possible. These uses make extensive use of 5G’s ultra-low latency and high bandwidth characteristics, which enable almost immediate device-to-device communication.
Road safety is still a major concern in India, where Jio’s effort has the potential to be revolutionary. Roadside unit (RSU) deployment and network slicing for V2X services allow the platform to serve latency-sensitive applications, such as danger detection and emergency vehicle prioritising. Additionally, Jio’s efforts are in line with India’s larger goal of developing intelligent transportation systems under the framework of Digital India.
Alepo’s 5G Core: An Expandable C-V2X BackboneAlepo’s 5G Converged Core platform introduces software-defined intelligence to the V2X space, while Jio’s focus is on connectivity and infrastructure. Alepo’s basic product is capable of managing V2X-specific subscriptions, Quality of Service (QoS) policies, and session orchestration. It also supports the cellular V2X (C-V2X) standard.
Alepo’s platform stands out by enabling two distinct C-V2X communication pathways—PC5 for direct communication and Uu for network-assisted transmission. Direct communication, which allows peer-to-peer transmission between vehicles without requiring a cellular network, usually operates in the 5.9 GHz ITS frequency. In scenarios where milliseconds count, such as platooning or high-speed highway synchronisation, this is crucial.
On the other hand, network-based communication links cars to cloud services and other organisations by leveraging the cellular infrastructure that is already in place. Alepo’s 5G core skillfully strikes a balance between these modes to guarantee uninterrupted connection in any setting.
Alepo’s system’s user equipment (UE) classification is another essential component. Vehicles and pedestrians are distinguished by the system as distinct UE kinds, each with its own QoS characteristics. This makes it possible to handle data requirements and mobility patterns in a tailored way, guaranteeing that a pedestrian warning is handled differently from a vehicle coordination signal. For a sophisticated V2X ecosystem to be supported at scale, this degree of granularity is essential.
The Testing and Validation Ecosystem of KeysightThorough validation is essential to the efficacy of V2X systems, and Keysight Technologies is essential in this regard. Testing for compliance and interoperability must change to keep up with the complexity of V2X devices. This need is met by Keysight’s SA8700A C-V2X Test Solution, which supports both protocol and RF testing according to 3GPP Release 14 guidelines.
Manufacturers and developers may validate their V2X devices in controlled laboratory settings thanks to this service. End-to-end simulation of real-world situations, including lane-change assistance, junction collision warnings, and emergency braking alerts, is supported. Keysight’s technologies guarantee that devices not only function but also function under stress, thanks to their comprehensive diagnostic feedback and latency measurements.
Furthermore, Keysight provides the WaveBee V2X Test and Emulation package, which is intended to replicate actual driving situations on test roads and tracks. From early development to field testing after deployment, these solutions provide ongoing validation across the product lifecycle. These testing platforms guarantee user safety, performance, and compliance as international laws tighten and safety-critical applications gain traction.
Obstacles in the Way of V2X MaturityWhile the promise of V2X is vast, its full-scale deployment is hindered by several critical hurdles. Standardisation is a significant obstacle. The global automotive landscape is fragmented, with regional preferences varying between technologies like DSRC and C-V2X. To guarantee smooth communication between automobiles made by various manufacturers, these standards must be harmonised.
Privacy and security are important issues to consider. As cars are becoming data nodes, it is important to ensure private data is protected from abuse or leakage. V2X networks need to implement secure authentication methods, end-to-end encryption, and anomaly detection methods to maintain resilience and trust.
Investment in infrastructure is another issue. It is critical to densify roadside units, edge servers, and network slicing in order for V2X systems to provide the best experience. Governments and municipalities need to engage in making smart mobility infrastructure happen and, while telecom has its role through networks and infrastructure developments, the effort must come from all parties.
Conclusion: It’s Closer Than You ThinkRight now, in the transportation space, parts of the ecosystem are finally being redesigned through the fusion of 5G and a new V2X communication standard. At the junction of connectivity with safer cars, smarter roads, and seamless transportation, companies like Jio, Alepo, and Keysight have already begun shaping that future.
As infrastructure continues to grow, and standardization becomes more advanced, V2X will go from a specialized innovation to an essential part of urban mobility. This technology could change everything from increasing safety by lowering traffic deaths to building networks of autonomous vehicles. The time has come for urban planners, politicians, telecom, and automotive industry players to partner up and together invest in V2X.
The post 5G-Powered V2X: Using Intelligent Connectivity to Revolutionize Mobility appeared first on ELE Times.
Infineon OptiMOS 80 V and 100 V, and MOTIX enable high-performing motor control solutions for Reflex Drive’s UAVs
Reflex Drive, a deep tech startup from India has selected power devices from Infineon Technologies AG for its next-generation motor control solutions for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). By integrating Infineon’s OptiMOS 80 V and 100 V, Reflex Drive’s electric speed controllers (ESCs) achieve improved thermal management and higher efficiency, enabling high power density in a compact footprint. Additionally, the use of Infineon’s MOTIX IMD701 controller solution which combines the XMC1404 microcontroller with the MOTIX 6EDL7141 3-phase gate driver IC delivers compact, precise, and reliable motor control. This enables improved performance, greater reliability, and longer flight times for UAVs.
“Our partnership with Reflex Drive is an important contribution to our market launch strategy and presence in India,” says Nenad Belancic, Global Application Manager Robotics and Drones at Infineon. “Our partner has proven its expertise with numerous customers who have obtained aviation certifications. In addition, the company has presented its innovative technologies enabled by Infineon systems at important international industry events.”
“Our collaboration with Infineon has led to significant advances in UAV electronics,” says Amrit Singh, Founder of Reflex Drive. “We believe drones have the potential to transform industries, from agriculture to logistics, and with Infineon’s devices, we can help drive this transformation at the forefront.”
Reflex Drives’s ESCs with field-oriented control (FOC) offer improved motor efficiency and precise control, while its high-performance BLDC motors are designed for optimized flight control and enable predictive maintenance of drive systems. Weighing only 180 g and with a compact volume of 120 cm³, the ESCs can deliver continuous power output of 3.8 kW (12S/48 V, 80 A continuous). Due to their lightweight design, robust power output, and consistent FOC control – even under demanding weather conditions – make them ideal for motors in the thrust range from 15 to 20 kg. Therefore, they are particularly suitable for drone applications in the fields of agricultural spraying technology, seed dispersal, small-scale logistics, and goods transport.
The post Infineon OptiMOS 80 V and 100 V, and MOTIX enable high-performing motor control solutions for Reflex Drive’s UAVs appeared first on ELE Times.
Network Traffic Analysis of NoFilter GPT: Real-Time AI for Unfiltered Conversations
NoFilter GPT is a cutting-edge conversational AI built to deliver unfiltered, bold, and authentic interactions. It offers different modes for different tasks: Raw Mode delivers candid, no-nonsense dialogue; Insight Mode explores complex topics with sharp analysis; and Reality Check Mode debunks misinformation with brutally honest takes. NoFilter GPT is designed for users who value clarity, directness and intellectual integrity in real-time conversations.
Network Traffic AnalysisThe ATI team in Keysight has analyzed the network traffic of NoFilter GPT and found some interesting insights that can help researchers optimize performance and enhance security. This analysis was conducted using HAR captures from a web session. NoFilter GPT operates with standard web protocols and relies on secure TLS encryption for communication.
Overall AnalysisWe have performed extensive user interactions with the NoFilter GPT web application. The captured traffic was completely TLS encrypted. We have further analyzed the traffic based on host names.
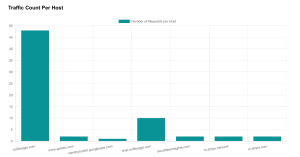
Figure 1: Request-Response count per host
In the figure above we can observe the majority of request-response interactions were observed with nofiltergpt.com, handling core AI functions like chat and image generation. Additionally, NoFilterGPT related host, chat.nofiltergpt.com manage AI chat, image generation, and token-based request authentication, while other external hosts primarily serve static assets and analytics.
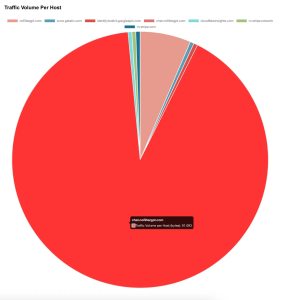
Figure 2: Cumulative payload per host
The diagram above shows that the host chat.nofiltergpt.com has the maximum cumulative payload followed by nofiltergpt.com. The rest of the hosts are creating smaller network footprints.
Analyzing EndpointsBy examining the HAR file, we gain a detailed view of the HTTP requests and responses between the client and NoFilter GPT’s servers. This analysis focuses on critical endpoints and their roles in the platform’s functionality.
Chat CompletionEndpoint: https://chat.nofiltergpt.com/run/nofilterai/controller5?identifier…
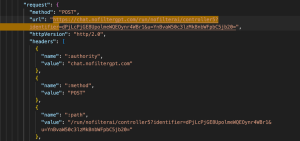
- Method: POST
- Purpose: This is the actual request that sends user input to the chat model and receives a response.
- Request Headers:
- Content-Type: application/json
- Accept: */* (Accepts any response type, indicating a flexible API for logging events.)
- Origin: https://nofiltergpt.com (Ensures requests originate from NoFilterGPT’s platform)
- Request Payload: Base64-encoded JSON containing user message, system prompt, temperature, etc.
- Response Status: 200 OK (successful session creation)
This triggers a response from the model.
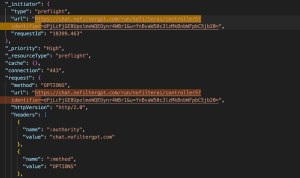
- Method: OPTIONS
- Purpose: This is a CORS ( Cross-Origin Resource Sharing ) preflight request automatically sent by the browser before the POST request.
- Request Payload: None
The server responds with headers indicating what methods and origins are allowed, enabling the browser to safely send the POST.
Image Generation- Endpoint: https://chat.nofiltergpt.com/media/generate2.php
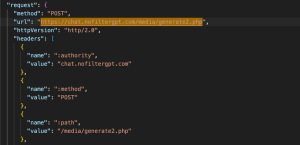
- Method: POST
- Purpose: Sends an image generation prompt to the server.
- Request Headers:
- Content-Type: application/json
- Accept: */* (Accepts any response type, indicating a flexible API for logging events.)
- Request Payload: JSON with token, prompt, width, height, steps, sampler, etc.
- Response Status: 200 OK (successful session creation)
This generates and returns an image based on the prompt and settings.
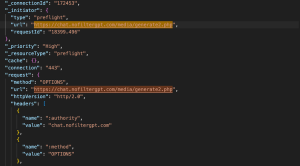
- Method: OPTIONS
- Purpose: Browser-initiated CORS preflight checks to see if the server will accept the POST request
- Request Payload: None
Gets permission from the server to proceed with the actual POST request.
NOTE: While NoFilterGPT can be useful it is a prohibited tool by many companies and government entities. Policy and technical systems must be in place to prevent usage, and it is vital to confirm this via test using BreakingPoint. These tests help validate the security measures and help organizations prevent accidental or malicious use of the platform.
NoFilterGPT Traffic Simulation in Keysight ATIAt Keysight Technologies Application and Threat Intelligence (ATI), since we always try to deliver the hot trending application, we have published the NoFilter GPT application in ATI-2025-05 which simulates the HAR collected from the NoFilter GPT web application as of March 2025 including different user actions like performing text-based queries, uploading multimedia files, using the generate image feature to create custom visuals and refining search results. Here all the HTTP transactions are replayed in HTTP/2 over TLS1.3.
Figure 3: NoFilterGPT Mar25 HAR Replay HTTP/2 over TLS1.3 Superflow in BPS
The NoFilterGPT application and its 4 new Superflows as shown below:
Figure 4: NoFilterGPT App and its Superflows in BPS
Leverage Subscription Service to Stay Ahead of AttacksKeysight’s Application and Threat Intelligence subscription provides daily malware and bi-weekly updates of the latest application protocols and vulnerabilities for use with Keysight test platforms. The ATI Research Centre continuously monitors threats as they appear in the wild. Customers of BreakingPoint now have access to attack campaigns for different advanced persistent threats, allowing BreakingPoint Customers to test their currently deployed security control’s ability to detect or block such attacks.
The post Network Traffic Analysis of NoFilter GPT: Real-Time AI for Unfiltered Conversations appeared first on ELE Times.
A Balanced Bag of Tricks for Efficient Gaussian Splatting
3D reconstruction is a long-standing problem in computer vision, with applications in robotics, VR and multimedia. It is a notorious problem since it requires lifting 2D images to 3D space in a dense, accurate manner.
Gaussian splatting (GS) [1] represents 3D scenes using volumetric splats, which can capture detailed geometry and appearance information. It has become quite popular due to their relatively fast training, inference speeds and high quality reconstruction.
GS-based reconstructions generally consist of millions of Gaussians, which makes them hard to use on computationally constrained devices such as smartphones. Our goal is to improve storage and computational inefficiency of GS methods. Hence, we propose Trick-GS, a set of optimizations that enhance the efficiency of Gaussian Splatting without significantly compromising rendering quality.
BackgroundGS is a method for representing 3D scenes using volumetric splats, which can capture detailed geometry and appearance information. It has become quite popular due to their relatively fast training, inference speeds and high quality reconstruction.
GS reconstructs a scene by fitting a collection of 3D Gaussian primitives, which can be efficiently rendered in a differentiable volume splatting rasterizer by extending EWA volume splatting [2]. A scene represented with 3DGS typically consists of hundreds of thousands to millions of Gaussians, where each 3D Gaussian primitive consists of 59 parameters. The technique includes rasterizing Gaussians from 3D to 2D and optimizing the Gaussian parameters where a 3D covariance matrix of Gaussians are later parameterized using a scaling matrix and a rotation matrix. Each Gaussian primitive also has an opacity (α ∈ [0, 1]), a diffused color and a set of spherical harmonics (SH) coefficients, typically consisting of 3-bands, to represent view-dependent colors. Color C of each pixel in the image plane is later determined by Gaussians contributing to that pixel with blending the colors in a sorted order.
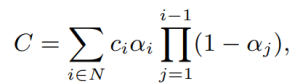
GS initializes the scene and its Gaussians with point clouds from SfM based methods such as Colmap. Later Gaussians are optimized and the scene structure is changed by removing, keeping or adding Gaussians to the scene based on gradients of Gaussians in the optimization stage. GS greedily adds Gaussians to the scene and this makes the approach in efficient in terms of storage and computation time during training.
Tricks for Learning Efficient 3DGS RepresentationsWe adopt several strategies that can overcome the inefficiency of representing the scenes with millions of Gaussians. Our adopted strategies mutually work in harmony and improve the efficiency in different aspects. We mainly categorize our adopted strategies in four groups:
a) Pruning Gaussians; tackling the number of Gaussians by pruning.
b) SH masking; learning to mask less useful Gaussian parameters with SH masking to lower the storage requirements.
c) Progressive training strategies; changing the input representation by progressive training strategies.
d) Accelerated implementation; the optimization in terms of implementation.
a) Pruning Gaussians:a.1) Volume Masking
Gaussians with low scale tend to have minimal impact on the overall quality, therefore we adopt a strategy that learns to mask and remove such Gaussians. N binary masks, M ∈ {0, 1}N , are learned for N Gaussians and applied on its opacity, α ∈ [0, 1]N , and non-negative scale attributes, s by introducing a mask parameter, m ∈ RN. The learned masks are then thresholded to generate hard masks M;
![]()
These Gaussians are pruned at densification stage using these masks and are also pruned at every km iteration after densification stage.
a.2) Significance of Gaussians
Significance score calculation aims to find Gaussians that have no impact or little overall impact. We adopt a strategy where the impact of a Gaussian is determined by considering how often it is hit by a ray. More concretely, the so called significance score GSj is calculated with 1(G(Xj ), ri) where 1(·) is the indicator function, ri is ray i for every ray in the training set and Xj is the times Gaussian j hit ri.
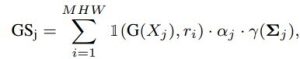
where j is the Gaussian index, i is the pixel, γ(Σj ) is the Gaussian’s volume, M, H, and W represents the number of training views, image height, and width, respectively. Since it is a costly operation, we apply this pruning ksg times during training with a decay factor considering the percentile removed in the previous round.
b) Spherical Harmonic (SH) MaskingSHs are used to represent view dependent color for a Gaussian, however, one can appreciate that not all Gaussians will have the same levels of varying colors depending on the scene, which provides a further pruning opportunity. We adopt a strategy where SH bands are pruned based on a mask learned during training, and unnecessary bands are removed after the training is complete. Specifically, each Gaussian learns a mask per SH band. SH masks are calculated as in the following equation and SH values for the ith Gaussian for the corresponding SH band, l, is set to zero if its hard mask, Mshi(l), value is zero and unchanged otherwise.
![]()
where mli ∈ (0, 1), Mlsh ∈ {0, 1}. Finally, each masked view dependent color is defined as ĉi(l) = Mshi(l)ci(l) where ci(l) ∈ R(2l+1)×3. Masking loss for each degree of SH is weighted by its number of coefficients, since the number of SH coefficients vary per SH band.
c) Progressive training strategiesProgressive training of Gaussians refers to starting from a coarser, less detailed image representation and gradually changing the representation back to the original image. These strategies work as a regularization scheme.
c.1) By blurring
Gaussian blurring is used to change the level of details in an image similar. Kernel size is progressively lowered at every kb iteration based on a decay factor. This strategy helps to remove floating artifacts from the sub-optimal initialization of Gaussians and serves as a regularization to converge to a better local minima. It also significantly impacts the training time since a coarser scene representation requires less number of Gaussians to represent the scene.
c.2) By resolution
Progressive training by resolution. Another strategy to mitigate the over-fitting on training data is to start with smaller images and progressively increase the image resolution during training to help learning a broader global information. This approach specifically helps to learn finer grained details for pixels behind the foreground objects.
c.3) By scales of Gaussians
Another strategy is to focus on low-frequency details during the early stages of the training by controlling the low-pass filter in the rasterization stage. Some Gaussians might become smaller than a single pixel if each 3D Gaussian is projected into 2D, which results in artefacts. Therefore, the covariance matrix of each Gaussian is added by a small value to the diagonal element to constraint the scale of each Gaussian. We progressively change scale for each Gaussian during the optimization similar to ensure the minimum area that each Gaussian covers in the screen space. Using a larger scale in the beginning of the optimization enables Gaussians receive gradients from a wider area and therefore the coarse structure of the scene is learned efficiently.
We adopt a strategy that is more focused on the training time efficiency. We follow on separating higher SH bands from the 0th band within the rasterization, thus lower the number of updates for the higher SH bands than the diffused colors. SH bands (45 dims) cover a large proportion of these updates, where they are only used to represent view-dependent color variations. By modifying the rasterizer to split SH bands from the diffused color, we update higher SH bands every 16 iterations whereas diffused colors are updated at every iteration.
GS uses photometric and structural losses for optimization where structural loss calculation is costly. SSIM loss calculation with optimized CUDA kernels. SSIM is configured to use 11×11 Gaussian kernel convolutions by standard, where as an optimized version is obtained by replacing the larger 2D kernel with two smaller 1D Gaussian kernels. Applying less number of updates for higher SH bands and optimizing the SSIM loss calculation have a negligible impact on the accuracy, while it significantly helps to speed-up the training time as shown by our experiments.
Experimental ResultsWe follow the setup on real-world scenes. 15 scenes from bounded and unbounded indoor/outdoor scenarios; nine from Mip-NeRF 360, two (truck and train) from Tanks&Temples and two (DrJohnson and Playroom) from Deep Blending datasets are used. SfM points and camera poses are used as provided by the authors [1] and every 8th image in each dataset is used for testing. Models are trained for 30K iterations and PSNR, SSIM and LPIPS are used for evaluation. We save the Gaussian parameters in 16-bit precision to save extra disk space as we do not observe any accuracy drop compared to 32-bit precision.
Performance EvaluationOur most efficient model Trick-GS-small improves over the vanilla 3DGS by compressing the model size drastically, 23×, improving the training time and FPS by 1.7× and 2×, respectively on three datasets. However, this results in slight loss of accuracy, and therefore we use late densification and progressive scale-based training with our most accurate model Trick-GS, which is still more efficient than others while not sacrificing on the accuracy.
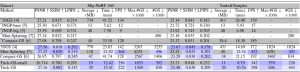
Table 1. Quantitative evaluation on MipNeRF 360 and Tanks&Temples datasets. Results with marked ’∗’ method names are taken from the corresponding papers. Results between the double horizontal lines are from retraining the models on our system. We color the results with 1st, 2nd and 3rd rankings in the order of solid to transparent colored cells for each column. Trick-GS can reconstruct scenes with much lower training time and disk space requirements while not sacrificing on the accuracy.
Trick-GS improves PSNR by 0.2dB on average while losing 50% on the storage space and 15% on the training time compared to Trick-GS-small. The reduction on the efficiency with Trick-GS is because of the use of progressive scale-based training and late densification that compensates for the loss from pruning of false positive Gaussians. We tested an existing post-processing step, which helps to further reduce model size as low as 6MB and 12MB respectively for Trick-GS-small and Trick-GS over MipNeRF 360 dataset. The post-processing does not heavily impact the training time but the accuracy drop on PSNR metric is 0.33dB which is undesirable for our method. Thanks to our trick choices, Trick-GS learns models as low as 10MB for some outdoor scenes while keeping the training time around 10mins for most scenes.
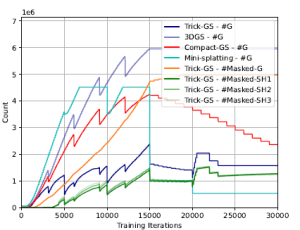
Figure 1. Number of Gaussians (#G) during training (on MipNeRF 360 – bicycle scene) for all methods, number of masked Gaussians (#Masked-G) and number of Gaussians with a masked SH band for our method. Our method performs a balanced reconstruction in terms of training efficiency by not letting the number of Gaussians increase drastically as other methods during training, which is a desirable property for end devices with low memory.
Learning to mask SH bands helps our approach to lower the storage space requirements. Trick-GS lowers the storage requirements for each scene over three datasets even though it might result in more Gaussians than Mini-Splatting for some scenes. Our method improves some accuracy metrics over 3DGS while the accuracy changes are negligible. Advantage of our method is the requirement of 23× less storage and 1.7× less training time compared to 3DGS. Our approach achieves this performance without increasing the maximum number of Gaussians as high as the compared methods. Fig. 1 shows the change in number of Gaussians during training and an analysis on the number of pruned Gaussians based on the learned masks. Trick-GS achieves comparable accuracy level while using 4.5× less Gaussians compared to Mini-Splatting and 2× less Gaussians compared to Compact-GS, which is important for the maximum GPU consumption on end devices. Fig. 2 shows the qualitative impact of our progressive training strategies. Trick-GS obtains structurally more consistent reconstructions of tree branches thanks to the progressive training.

Figure 2. Impact of progressive training strategies on challenging background reconstructions. We empirically found that progressive training strategies as downsampling, adding Gaussian noise and changing the scale of learned Gaussians have a significant impact on the background objects with holes such as tree branches.
Ablation StudyWe evaluate the contribution of tricks in Tab. 2 on MipNeRF360 – bicycle scene. Our tricks mutually benefits from each other to enable on-device learning. While Gaussian blurring helps to prune almost half of the Gaussians compared to 3DGS with a negligible accuracy loss, downsampling the image resolution helps to focus on the details by the progressive training and hence their mixture model lowers the training time and the Gaussian count by half. Significance score based pruning strategy improves the storage space the most among other tricks while masking Gaussians strategy results in lower number of Gaussians at its peak and at the end of learning. Enabling progressive Gaussian scale based training also helps to improve the accuracy thanks to having higher number of Gaussians with the introduced split strategy.
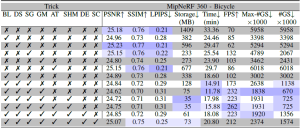
Table 2. Ablation study on tricks adopted by our approach using‘bicycle’ scene. Our tricks are abbreviated as BL: progressive Gaussian blurring, DS: progressive downsampling, SG: significance pruning, GM: Gaussian masking, SHM: SH masking, AT: accelerated training, DE: late densification, SC: progressive scaling. Our full model Trick-GS uses all the tricks while Trick-GS-small uses all but DE and SC.
Summary and Future DirectionsWe have proposed a mixture of strategies adopted from the literature to obtain compact 3DGS representations. We have carefully designed and chosen strategies from the literature and showed competitive experimental results. Our approach reduces the training time for 3DGS by 1.7×, the storage requirement by 23×, increases the FPS by 2× while keeping the quality competitive with the baselines. The advantage of our method is being easily tunable w.r.t. the application/device needs and it further can be improved with a post-processing stage from the literature e.g. codebook learning, huffman encoding. We believe a dynamic and compact learning system is needed based on device requirements and therefore leave automatizing such systems for future work.
The post A Balanced Bag of Tricks for Efficient Gaussian Splatting appeared first on ELE Times.
Synopsys Interconnect IPs Enabling Scalable Compute Clusters
Courtesy: Synopsys
Recent advancements in machine learning have resulted in improvements in artificial intelligence (AI), including image recognition, autonomous driving, and generative AI. These advances are primarily due to the ability to train large models on increasingly complex datasets, enabling better learning and generalization as well as the creation of larger models. As datasets and model sizes grow, there is a requirement for more powerful and optimized computing clusters to support the next generation of AI.
With more than 25 years of experience in delivering field-proven silicon IP solutions, we are thrilled to partner with NVIDIA and the NVIDIA NVLink ecosystem to enable and accelerate the creation of custom AI silicon. This strategic collaboration will leverage Synopsys’ expertise in silicon IPs to assist in the development of bespoke AI silicon, forming the foundation for advanced compute clusters aimed at delivering the next generation of transformative AI experiences.
Compute challenges with larger datasets and increasingly large AI modelsTraining trillion-parameter-plus models on large datasets necessitates substantial computational resources, including specialized accelerators such as Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) and Tensor Processing Units (TPUs). AI computing clusters incorporate three essential functions:
- Compute — implemented using processors and dedicated accelerators.
- Memory — implemented as High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) or Double Data Rate (DDR) with virtual memory across the cluster for memory semantics.
- Storage — implemented as Solid State Drives (SSDs) that efficiently transfer data from storage to processors and accelerators via Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)-based Network Interface Cards (NICs).
Retimers and switches constitute the fabric that connects accelerators and processors. To enhance the computational capabilities of the cluster, it is necessary to increase capacity and bandwidth across all functions and interconnects.
Developing increasingly sophisticated, multi-trillion-parameter models requires the entire cluster to be connected over a scale-up and scale-out network so it can function as a unified computer.

Figure 1: A representative compute cluster with scale-up and scale-out network.
Standards-based IPs for truly interoperable compute clustersThe successful deployment of next-generation computing clusters relies on silicon-verified interconnects that utilize advanced process node technology and guarantee interoperability. Standardized interconnects enable an interoperable, multi-vendor implementation of a cluster.
PCIe is an established standard for processor-to-accelerator interfaces, ensuring interoperability among processors, NICs, retimers, and switches. Since 1992, the PCI-SIG has been defining Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) solutions, with PCIe now in its seventh generation. The extensive history and widespread deployment of PCIe ensure that IP solutions benefit from the silicon learning of previous generations. Furthermore, the entire ecosystem developing processors, retimers, switches, NICs, and SSDs possesses significant deployment experience with PCIe technology. Our complete IP solution for PCIe 7.0 is built upon our experience with more than 3,000 PCIe designs, launched in June 2024 with endorsements from ecosystem partners such as Intel, Rivos, Xconn, Microchip, Enfabrica, and Kandou.
When deploying trained models in the cloud, hyperscalers aim to continue utilizing their software on custom processors that interface with various types of accelerators. For NVIDIA AI factories, NVLink Fusion provides another method for connecting processors to GPUs.
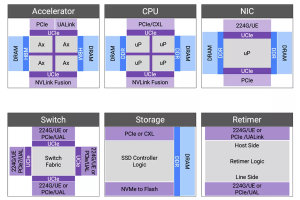
Figure 2: Components and interconnects of a next-generation compute cluster.
Accelerators can be connected in various configurations, affecting the efficiency of compute clusters. Scale-up requires memory semantics for a virtual memory pool across the cluster, while scale-out involves connecting tens-of-thousands to hundreds-of-thousands of GPUs with layers of switching and congestion management. Unlike scale-up, scale-out is more latency-tolerant and designed for bandwidth oversubscription to suit AI model data parallelism. In December 2024, we launched our Ultra Accelerator Link (UALink) and Ultra Ethernet solution to connect accelerators efficiently. The solution, which was publicly supported with quotes from AMD, Juniper and Tenstorrent, is based on silicon-proven 224G PHY and more than 2,000 Ethernet designs.
Trillion-parameter models demand extensive memory storage and high data rates for low latency access, necessitating increased memory bandwidth and total capacity. HBM provides both substantial capacity and high bandwidth. Our HBM4 IP represents the sixth generation of HBM technology, offering pin bandwidths up to 12 Gbps, which results in an overall interface bandwidth exceeding 3 TBps.
Co-packaged multi-die aggregation not only enhances compute throughput by overcoming the limitations of advanced fabrication processes but also facilitates the integration of optical interconnects through emerging Co-Packaged Optical (CPO) technologies. Since 2022, we have been developing linear electro-optical (EO) interfaces to create energy-efficient EO links. The Universal Chiplet Interconnect Express (UCIe) standard has provided a well-defined path for multi-vendor interoperability. In collaboration with Intel in 2023, we successfully demonstrated the first UCIe-connected, chiplet-based test chip.
Multi-die integration poses challenges for heat dissipation, potentially impacting temperature-sensitive photonic components or causing thermal runaway. Our comprehensive multi-die solution, including Die-to-Die IP, HBM IP, and 3DIC Compiler for system-in-package integration, provides a reliable and robust multi-die implementation.
Adopting well-established and extensively validated IP solutions across critical interconnects – from processor-accelerator interfaces to advanced multi-die architectures and HBM – mitigates the risks associated with custom design and integration. Pre-verified IPs streamline the design and verification process, accelerate timelines, and ultimately pave the way for successful first-pass silicon, enabling the rapid deployment of innovative and interoperable compute clusters.
The post Synopsys Interconnect IPs Enabling Scalable Compute Clusters appeared first on ELE Times.
Redefining Robotics: High-Precision Autonomous Mobile Robots
Courtesy: Lattice Semiconductors
Imagine a robot navigating a crowded factory floor, rerouting itself in real-time around equipment, humans, and unexpected obstacles — all while maintaining motion control and system stability. This isn’t a distant vision; this is the reality engineered by Agiliad in partnership with Lattice Semiconductor.
In a market full of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) that rely on generic control stacks and prebuilt kits, this AMR stands out as a deep-tech system, purpose-built for intelligent indoor mobility. Unlike conventional AMRs that often trade performance for modularity or ease of deployment, this robot integrates a custom motion control framework based on Lattice’s Certus-NX FPGA, along with a ROS2-based advanced SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), sensor fusion, and navigation stack running on NVIDIA Jetson Orin— all tightly orchestrated for low-latency, high-reliability operation.
This next-generation AMR is more than just mobile — it’s aware, adaptable, and engineered for deterministic control in real-world conditions. Designed for use in industrial settings, research labs, and beyond, the robot brings together embedded intelligence, energy efficiency, and full-stack integration to set a new benchmark for autonomous systems.
Key Features of the Robot: The Intelligence Behind the Robot
Advanced Localization & Mapping: RTAB-Map SLAM, a robust loop-closure-enabled algorithm, leverages both 3D lidar and camera feeds for consistent mapping even in environments with visual and spatial ambiguities.
- 3D Obstacle Detection & Avoidance: Using a combination of 3D voxel layers and spatio-temporal layers, the robot dynamically detects and navigates around static and moving objects — maintaining safe clearance while recalculating routes on the fly.
- Path Planning: The navigation stack uses the SMAC (Search-Based Motion Planning) planner for global routing and MPPI (Model Predictive Path Integral) for locally optimized trajectories, allowing real-time adaptation to dynamic environmental changes.
- Precision Motion Control via FPGA: BLDC motors are governed by Lattice Certus-NX FPGAs executing custom PI (proportional integral) control loops in hardware, ensuring smooth acceleration, braking, and turning — critical for safety in confined spaces.
Sensor Fusion for Environmental Awareness :
Lidar and stereo camera data is processed on the Lattice Avant-E FPGA and fused with point cloud information to detect and differentiate humans and objects, providing real-time environmental awareness for safe and adaptive navigation.

System Architecture Breakdown Diagram
The AMR’s architecture is a layered, modular system built for reliability, scalability, and low power consumption. Jetson handles ROS2 algorithms, while the Lattice FPGAs manage motion control.
- Robot Geometry and Integration with ROS2 : The robot’s geometry and joints are defined in a URDF model derived from mechanical CAD files. The Robot State Publisher node in ROS2 uses this URDF to publish robot structure and transform data across the ROS2 network.
- Lattice Avant-E FPGA Based Sensor Fusion : Sensor data from lidar and stereo vision cameras is transmitted to the Avant-E FPGA over UDP. Avant-E employs OpenCV for real-time image identification and classification, fusing visual data with point cloud information to accurately detect and differentiate humans from other objects in the environment. This fused data — including human-specific classification and distance metrics — is then transmitted to the ROS2 framework running on NVIDIA Jetson. This high-fidelity sensor fusion layer ensures enhanced situational awareness, enabling the robot to make informed navigation decisions in complex, dynamic settings.
- SLAM & Localization: Lidar provides a 3D point cloud of the environment, while the camera supplies raw image data. An RTAB-Map (Real-Time Appearance-Based Mapping) processes this information to create a 3D occupancy grid. Odometry is derived using an iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm, with loop closure performed using image data. This enables continuous optimization of the robot’s position, even in repetitive or cluttered spaces.
- Navigation: Navigation generates cost maps by inflating areas around obstacles. These cost gradients guide planners to generate low-risk paths. SMAC provides long-range planning, while MPPI evaluates multiple trajectory options and selects the safest path.
- ROS2 Control and Differential Drive Kinematics: ROS2 computes a command velocity (linear and angular) which is translated into individual wheel velocities using differential drive kinematics.
- Hardware Interface: This layer ensures integration between ROS2 and the robot’s hardware. Serial communication (UART) between Jetson and Certus-NX transmits motor velocity commands in real-time.
- Lattice Certus-NX FPGA-Based Motion Control: Lattice’s Certus-NX FPGA executes real-time motor control algorithms with high reliability and minimal latency, enabling deterministic performance, efficient power use, and improved safety under industrial loads:
PI Control Loops for velocity and torque regulation, using encoder feedback to ensure performance regardless of frictional surface conditions.
Commutation Sequencer that uses hall sensor feedback to control 3-phase BLDC motor excitation.
How It All Works Together: A Decision-Making Snapshot

The robot’s intelligence simulates a real-time decision-making loop:
Where am I?
The robot localizes using RTAB-Map SLAM with loop closure, updating its position based on visual and spatial cues.
Where should I go?
A user-defined goal (set via touchscreen or remote interface) is passed to the global planner, which calculates a safe, efficient route using SMAC.
How do I get there?
The MPPI planner simulates and evaluates dozens of trajectories in real-time, using critic-based scoring to dynamically adapt to the robot’s surroundings.
What if something blocks the path?
Sensor data updates the obstacle map, triggering real-time replanning. If no safe path is found, recovery behaviors are activated via behavior servers.
| Component / Design Element | Rationale |
| Differential Drive | Simpler control logic and reduced energy usage compared to omni-wheels |
| Lidar Placement (Center) | Avoids blind spots; improves loop closure and mapping accuracy |
| Maxon BLDC Motors | High torque (>4.5 Nm) for payload handling and smooth mobility |
| Certus-NX FPGA Motion Control | Enables deterministic control with low CPU overhead |
| Camera Integration | Improves visual SLAM and scene understanding |
| Convex Caster Wheels | Reduces ground friction, enhances turning in confined areas |
| Cooling Architecture | Fans and vents maintain safe operating temperatures |
| Jetson as CPU | Provides headroom for future GPU-based algorithm integration |
Lattice FPGA Technology
Lattice’s Certus-NX and Avant-E FPGAs deliver complementary capabilities that are critical for autonomous robotic systems:
- Low Power Consumption : Extends battery life in mobile systems
- Real-Time Performance: Delivers responsive control loops and fast data handling
- Flexible Architecture : Supports custom control logic and sensor interfaces
Combined with NVIDIA Jetson Orin and embedded vision tools, the result is a scalable and adaptable robotic platform.
Looking Ahead: Enabling the Future of Robotics
Agiliad’s engineering model emphasizes deep system-level thinking, rapid prototyping, and cross-domain integration, delivering a fully operational system within a compressed development timeline by leveraging low power Lattice FPGAs. This reflects Agiliad’s deep expertise in full-stack design and multidisciplinary integration across mechanical, electrical, embedded, and software.
The post Redefining Robotics: High-Precision Autonomous Mobile Robots appeared first on ELE Times.
Made-in-India Chips Coming in 2025, Says Ashwini Vaishnaw
India is going to make their very first indigenous chip by the end of 2025, making a very important step towards technological advancements for this nation. Announcing this, Union Minister of Electronics and IT, Ashwini Vaishnaw, said that the chip employing 28-90nm technology is slated for rollout this year. This is envisaged as part of a larger plan for India to promote semiconductor manufacturing in the country and cut down on import dependency.
The first chip would be manufactured at Tata Electronics’ unit at Jagiroad in Assam, with an investment of 27,000 crore. The facility, coming up under the aegis of the India Semiconductor Mission, is a huge investment into the northeast and shall create many job opportunities. The government has also approved setting up the sixth fab in Uttar Pradesh through a JV of HCL and Foxconn, further deepening the semiconductor ecosystem in the country.
Minister Vaishnaw stated that the 28-90nm chips are used in various sectors such as automotive, telecommunications, power and railways. India, therefore, intends to focus on this segment that accounts for roughly 60 percent of the global semiconductor market so that it can position itself as a major market player.
Apart from manufacturing, the government is putting a greater emphasis on developing indigenous IP and design skills. Work is progressing towards the development of 25 chips with indigenous IP-aimed at improving cyber security. 13 projects are being pursued under the aegis of the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Bengaluru, thereby giving concrete expression to self-reliance and innovation.
Building an indigenous fab aligns with the objectives laid down in India’s “Digital India” concept, which works towards prompting India as a global nucleus for electronics manufacturing. India’s entry into the semiconductor industry is anticipated to have a significant impact on the economy both domestically and globally, given the continuous disruptions in the supply chain and in the rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Conclusion:
This initiative is directly in keeping with the “Digital India” vision to transform the country into a gobal hub for electronics manufacturing. With supply chain issues and technological shifts currently gripping the world, practically entering semiconductor production would certainly having far-reaching implications for the Indian economy as well as on the global level.
The post Made-in-India Chips Coming in 2025, Says Ashwini Vaishnaw appeared first on ELE Times.
India will become the world’s electronics factory : We have the policy, the talent, and now the infrastructure to make it happen
India is making significant efforts to boost its electronics manufacturing industry with the goal of establishing itself as a prominent player in the global market. The electronics industry is witnessing remarkable growth and advancement, with a special emphasis on expanding manufacturing operations in India, particularly in the realm of semiconductor chips and electronics components. Noteworthy developments include the production of India’s first locally developed semiconductor chip in Gujarat, the initiation of state-level electronics component manufacturing programs in Tamil Nadu, and the implementation
of various PLI (Production Linked Incentive) schemes aimed at promoting local production. Furthermore, efforts are underway to establish a repairability index for electronics to tackle e-waste, and the government is actively promoting research and development as well as innovation within the sector.
India is currently enacting a series of strategic measures to enhance its electronics manufacturing sector with the aim of positioning itself as a key player on the global stage in the field of electronics production.
The “Make in India” initiative, launched to transform India into a global manufacturing hub, focuses on enhancing industrial capabilities, fostering innovation, and creating world-class infrastructure. This initiative aims to position India as a key player in the global economy by attracting investments, promoting skill development, and encouraging domestic manufacturing.
The Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP) was introduced by the government to boost the domestic value addition in the manufacturing of mobile phones as well as their sub-assemblies and parts. The primary objective of this scheme is to stimulate high-volume production and establish a robust local manufacturing framework for mobile devices.
To enhance the growth of domestic manufacturing and foster investment in the mobile phone value chain, including electronic components and semiconductor packaging, the government introduced the Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI) for Large Scale Electronics Manufacturing. This initiative offers incentives ranging from 3% to 6% on incremental sales of products manufactured in India within target segments such as Mobile Phones and Specified Electronic Components.
Another initiative is the PLI scheme for passive electronic components, with a budget of INR 229.19 billion. This scheme aims to promote the domestic manufacturing of passive electronic components such as resistors and capacitors. These components are integral to various industries such as telecom, consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices.
The Semicon India Program, initiated in 2021 with a considerable budget of ₹76,000 crore, aims to bolster the domestic semiconductor sector through a mix of incentives and strategic alliances. The comprehensive initiative not only focuses on the development of fabrication facilities (fabs) but also emphasizes on enhancing packaging, display wires, Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Testing (OSATs), sensors, and other vital components crucial for a thriving semiconductor ecosystem.
The Indian government is promoting research and development, along with fostering innovation, within the electronics industry. India is actively engaging in collaborations with international firms, with a specific focus on high-tech manufacturing and chip design.
India’s progress in establishing itself as a prominent destination for electronic manufacturing on the global stage has been characterized by a series of deliberate policy decisions, significant advancements in infrastructure, and a growing interconnectedness with the international community. Through careful leveraging of present circumstances and the diligent resolution of pertinent obstacles, India continues to make substantial strides towards the realization of its ambitious vision.
Devendra Kumar
Editor
The post India will become the world’s electronics factory : We have the policy, the talent, and now the infrastructure to make it happen appeared first on ELE Times.
Silicon Photonics Raises New Test Challenges
Semiconductor devices continuously experience advancements leading to technology and innovation leaps, such as we see today for applications in AI high-performance computing for data centers, edge AI devices, electrical vehicles, autonomous driving, mobile phones, and others. Recent technology innovations include Angstrom-scale semiconductor processing nodes, high-bandwidth memory, advanced 2.5D/3D heterogeneous integrated packages, chiplets, and die-to-die-interconnects to name a few. In addition, silicon photonics in a co-packaged optics (CPO) form factor promises to be a key enabling technology in the field of high-speed data communications for high-performance computing applications.
What is CPO?
CPO is a packaging innovation that integrates silicon photonics chips with data center switches or GPU computing devices onto a single substrate (see Figure 1). It addresses the growing demand for interconnects with higher bandwidth and speed, low latency, lower power consumption, and improved efficiency in data transfer for AI data center applications.

Figure 1 Co-packaged Optics (Source: Broadcom)
To understand CPO we need to first understand its constituent technologies. One such critical technology for CPO is silicon photonics. Silicon photonics provides the foundational technology for integrating high-speed optical functions directly into silicon chips. CMOS foundries have developed advanced processes based on silicon semiconductor technology to enable photonic functionality on silicon wafers. CPO uses heterogeneous integrated packaging (HIP) that integrates these silicon photonics chips directly with electronic chips, such as AI accelerator chips or a switch ASIC, on a single substrate or package. Together, silicon photonics and HIP deliver CPO products. Thus, CPO is the convergence of silicon photonics, ASICs and advanced heterogeneous packaging capability supply chains.
As mentioned earlier, CPO brings high-speed, high bandwidth, low latency, low-power photonic interconnects to the computation beachfront. In addition, photonics devices are almost loss-less for large distances enabling one such AI accelerator to share workloads with another AI accelerator hundreds of meters away, while acting as one compute resource. This high-speed and long-distance interconnect CPO fabric promises to re-architect the data center, a key innovation to unlock future AI applications.
Early CPO prototypes are being developed as of 2025 which integrate photonics “engines” with the switch or GPU ASICs on a single substrate, rather than using advanced heterogeneous packages for integration. The optical “engine” in this context refers to the packaging of the silicon photonics chips with other discrete components plus the optical fiber connector; and CPO in this context refers to the assembly of several optical engines with the switch or GPU ASICs on a common substrate.
How to Shorten CPO Time to Market?
The datacom market for CPO presents an opportunity size of about two orders of magnitude higher than what silicon photonics manufacturing supply chains have been historically accustomed to handling, such as the high-mix, low-volume products and applications in telecom and biotech. To successfully achieve CPO at this higher volume, three elements need to advance:
- The silicon photonics supply chain needs to scale up capacity and achieve high yields at wafer and at the optical engine level.
- New heterogeneous integrated packaging concepts need to be proven with the OSATs and contract manufacturers for co-packaged optics.
- New, high-volume test techniques need to be developed and proven, as the current silicon photonics testing processes are highly manual and not scalable for high volume manufacturing.
CPO technology is not mature or at high volume yet, but test equipment providers and device suppliers need to be ready for its arrival as it has a direct impact on automated test equipment test requirements, whether at the wafer, package, or system level. Investments in photonics testing capabilities are critical for developing hybrid testing systems that can keep pace with rapid advancements in photonics, and can handle both electrical and optical signals simultaneously. CPO testing requires active thermal management, high power, large package handling, custom photonic handling and alignment, high-speed digital signaling, wide-band photonic signaling, and high frequency RF signal testing.
Additionally, there are multiple test insertions from wafer to final package test that need to be optimized for test coverage, test time, and cost (see Figure 2). Expertise and experience are required to optimize the test coverage at each insertion to avoid incurring significant product manufacturing cost in both operational expense and capital equipment.

Figure 2: Silicon Photonics Wafer-to-CPO Test Insertions
CPO Test Challenges
Testing CPO devices presents unique challenges due to the diverse processes and materials involved, both electrical and photonics. A unique challenge lies in the inherent complexity of aligning optical components with the precision needed to ensure reliable test results. Optical signals are highly sensitive to minute deviations in alignment, unlike traditional electrical signals, where connection tolerances are more forgiving. The intricacies of CPO, which integrate photonics with high-digital content computing devices, demand precise positioning of lasers, waveguides, and photodetectors. Even the smallest misalignment can result in signal degradation, power loss, or inaccurate measurements, complicating test processes. As this technology advances, automated test equipment needs to evolve to accommodate the precise requirements posed by photonics and optical-electrical integration.
In addition to the precision required, the materials and processes involved in CPO introduce variability. When multiple optical chiplets from different suppliers, each using possibly different materials or designs, are packaged into a single substrate, maintaining alignment across these disparate elements becomes exponentially more difficult. Each optical chiplet may have its own unique optical properties, meaning that test equipment must handle a range of optical alignments without compromising the accuracy of signal transmission or reception. This increases the demand for automated test equipment to adapt and provide consistently reliable measurements across various types of materials and optical designs.
The time-consuming nature of achieving precise alignment also creates a significant bottleneck in high-volume semiconductor testing environments. Aligning optical components, often manually or through semi-automated processes, adds time to test cycles, which can negatively impact throughput and efficiency in production environments. To mitigate these delays, automated test equipment suppliers must invest in advanced photonics testing capabilities, such as hybrid systems that can handle both electrical and optical signals simultaneously and efficiently. These systems must also incorporate faster, more reliable alignment techniques, potentially leveraging AI-driven calibration and adaptive algorithms that can adjust in real-time.
Test meets the high-stakes needs of CPO
With the push for faster data interconnects supporting the latest industry protocols—such as PCIe 5.0/6.0/7.0 and 400G/800G/1.6T b/s Ethernet, and beyond—the stakes are high for data center reliability and performance. Any failure or suboptimal performance in data interconnects can lead to significant downtimes and performance bottlenecks. Consequently, there is a greater emphasis on enhanced test coverage to identify and address potential issues before the components are deployed in data centers. As a result, the semiconductor test industry must provide comprehensive test solutions that cover all aspects of component performance, including signal integrity, thermal behavior, and power consumption under a range of operating conditions.
Ultimately, the industry’s shift toward CPO will demand a transformation in test methodologies and equipment, with special emphasis on accurate optical alignment at all test insertions, from wafer to CPO packages. Semiconductor test leaders who invest in advanced photonics testing systems will be better positioned to handle the complexities of this emerging technology, ensuring that they can keep pace with both rapid advancements and growing market demands.
Teradyne is at the forefront of these innovations anticipating new technologies and taking a proactive approach to developing flexible and effective automated test equipment capabilities for the latest advancements in semiconductor packaging and materials.

Dr. Jeorge S. Hurtarte
Senior Director, SoC Product Strategy Semiconductor Test group
Teradyne
The post Silicon Photonics Raises New Test Challenges appeared first on ELE Times.
Enhance HMI User Experience with Built-in Large Memory MPU
Courtesy: Renesas
The HMI market continues to drive growth in better user experience and increased automation with the expansion of HMI applications. This results in a strong demand for improved functionality and performance in display-based applications, such as real-time plotting, smooth animation, and USB camera image capture, in affordable systems. Microprocessors (MPUs) with high-speed, large-capacity built-in memory that can be used like microcontrollers (MCUs) are gaining attention in the market. Renesas’ RZ/A3M MPU with a built-in 128MB DDR3L SDRAM and a compatible package for a two-layer PCB design is the ideal solution for realizing smooth animation and high-quality HMI at a reasonable system cost.
High-Performance HMI and Real-Time GraphicsIntegrating high-speed, large-capacity memory directly into the MPU package offers several advantages, including mitigating concerns about high-speed signal noise on the PCB and simplifying PCB design for the users. The large-capacity memory needed for high-performance HMIs is externally connected to the MPU in the conventional way. Additionally, PCBs equipped with DDR memory and high-speed signal interfaces require multi-layer PCB designs to account for signal noise, making it challenging to reduce PCB costs. Also, the common capacity of on-chip SRAM is typically between 1MB and 10MB, which is too small for high-performance HMIs that need to include a reasonable number of tasks in the near future. To overcome these issues, Renesas released an industry-leading RZ/A3M MPU with a large built-in 128MB DDR3L memory to support high-performance HMI and real-time graphics performance to enhance better and faster user experiences. Most importantly, the board does not require a high-speed signal interface and supports two-layer PCB design to reduce board noise and simplify system development for users.

Figure 1. Strengths of Built-in DDR Memory
Designing High-Performance PCBs at a Reasonable System CostThe number of PCB layers and the ease of design significantly impact the cost of system implementation and maintenance in user applications. As shown in Figure 2, using a wide pin pitch of 0.8mm allows for the layout of signal lines and placement of VIAs between the balls. Additionally, placing the balls handling the main signals in the outer rows of the 244-pin 17mm x 17mm LFBGA package and positioning the GND and power pins as inner balls allows for efficient routing of the necessary signal lines for the system (Figure 3). The RZ/A3M MPU is designed to build cost-effective systems with two-layer PCBs through its innovative packaging and pin assignments.

Figure 2. Signal Wiring and Ball Layout

Figure 3. Optimized Ball Arrangement for a Two-Layer Board Layout
User-Friendly Interface Enabling Smooth GUI DisplayThe high-resolution graphic LCD controller integrated into the RZ/A3M supports both parallel RGB and 4-lane MIPI-DSI interfaces, accommodating displays up to 1280×800. Additionally, the 2D graphics engine, high-speed 16-bit 1.6Gbps DDR3L memory, and 1GHz Arm Cortex-A55 CPU enable high-performance GUI displays, including smooth animations and real-time plotting that increase the possibility of automation in HMI applications. Connecting a USB camera to the USB 2.0 interface enables smooth capture of camera images, making it easy to check inside of an apparatus, for example, the doneness of the food in the oven or the condition in the refrigerator.
The EK-RZ/A3M is an evaluation kit for the RZ/A3M. It includes an LCD panel with a MIPI-DSI interface. With this kit, users can immediately start evaluation. Renesas also has several graphics ecosystem partners – LVGL, SquareLine Studio, Envox, Crank, RTOSX – who deliver GUI solutions utilizing the EK-RZ/A3M to further accelerate your development cycle.

Figure 4. High-Definition HMI Example with the EK-RZ/A3M
The RZ/A3M MPU, equipped with high-speed 128MB DDR3L memory and a 1GHz Arm Cortex-A55, excels in developing cost-effective HMI applications with real-time plot UIs, smooth animations, and USB camera capture. The integrated memory simplifies PCB design by removing the need for high-speed signal interface design.
The post Enhance HMI User Experience with Built-in Large Memory MPU appeared first on ELE Times.
Zonal Architecture 101: Reducing Vehicle System Development Complexity
Courtesy: Onsemi
Thirty years ago, cars were marvels of mechanical engineering, but they were remarkably simple by today’s standards. The only electronics in an entry-level car would have been a radio and electronic ignition. The window winders were manual. The dashboard had an electromechanical speedometer and some warning lights. Power flowed directly from the battery to the headlights via a switch on the dashboard. There was no ABS, no airbags, and no centralized computer. Everything was analog and isolated.
Fast forward to today, vehicles are packed with hundreds of features, many mandated by regulation or demanded by consumers. To implement these features, automakers bolted on electronic control units (ECUs) one after another. Each system (braking, lighting, infotainment, and more) gained its own ECU, software and wiring. Over time, this created an ever-more-complex web of over 100 to 150 ECUs in a single vehicle.
To break through this complexity, automakers are embracing software-defined vehicle (SDV) architectures. SDVs aim to centralize software control, making it easier to update, manage, and extend features. But even with this shift, the underlying wiring and distributed hardware can remain a bottleneck unless automakers also rethink the vehicle’s physical architecture.
Enter zonal architecture: a modern, location-based design strategy that complements SDV principles and dramatically simplifies vehicle systems.
What Is Zonal Architecture?Zonal architecture is a paradigm shift, organizing vehicle electronics by location instead of by function. Instead of assigning each subsystem its own dedicated ECU, zone controllers are installed in each region of the vehicle, such as the front-left corner, rear-right corner, or cabin. These controllers manage local devices like lights, switches, and sensors within their respective zones. Rather than each component running its own software, the zone controller acts as a hub, handling power distribution and data communications.
These zone controllers connect to a central computer, which houses the core software that defines how the vehicle behaves. So instead of having separate ECUs for central locking, lighting, or climate control, the central compute unit makes decisions, while zone controllers carry them out.
This shift replaces hundreds of point-to-point wires with a simpler, more manageable zonal layout. By doing so, it dramatically improves design clarity and system efficiency.
Real-World Challenges of Implementing Zonal ArchitectureWhile the benefits are compelling, implementing zonal architecture isn’t without its challenges. For one, not all edge modules can be completely stripped of intelligence. Some components, such as advanced lighting systems, still require local processing for performance, safety, or proprietary functionality. Tier 1 suppliers deliver these modules with built-in software because they possess specialized knowledge of how to program and control them.
This raises a core challenge for SDVs using zonal designs: balancing centralized control with localized flexibility. In many cases, carmakers handle the central compute software, while Tier 1s manage the embedded software for the modules they manufacture. A pure, software-only central brain is a goal, but compromises are often necessary.
The Role of Ethernet in Zonal DesignsTraditional ECUs used legacy communication protocols like CAN and LIN, which were adequate for isolated modules but became unwieldy when scaled across a zonal architecture. That’s where automotive Ethernet, specifically 10BASE-T1S, comes into play.
10BASE-T1S is a low-speed (10 Mbps), multi-drop Ethernet standard designed specifically for automotive use. It enables multiple nodes (think headlights, turn signals, and door locks) to share a single twisted pair of wires, reducing the need for expensive point-to-point connections.

Figure 1. Example of 10BASE-T1S multi-drop connections
This approach simplifies cabling, lowers cost, and leverages Ethernet’s mature ecosystem, including time synchronization and error recovery, without the overhead of higher-speed Ethernet like 100BASE-T1 or gigabit Ethernet, which are unnecessary for low-bandwidth devices.
Smart Switches in Power DistributionZonal controllers not only relay data, but also distribute electrical power to the components in their zone. This means they play a critical role in system safety and diagnostics. onsemi’s smart switches go far beyond basic circuit protection. These intelligent devices offer:
- Voltage and current monitoring for each channel
- Support for automotive safety standards such as ASIL B and ASIL D
- Fail-safe and fail-operational modes, ensuring continuity of function even when faults are detected
For example, in the event of a malfunction, a smart switch can reduce power, isolate the fault, or enter a safe fallback mode rather than shutting down critical systems like headlights entirely. This level of insight and control is critical and mandatory for higher levels of automated driving.

Figure 2. Typical zonal power distribution architecture
Benefits of Zonal ArchitectureZonal architecture delivers five major advantages across vehicle development, production and operation:
- Reduced wiring harness complexity and weight: Fewer wires and connectors reduce both vehicle weight and build time.
- Lower cost of materials and assembly: Simplified wiring means reduced manufacturing cost and easier maintenance.
- Improved scalability: New features can be added or changed via software, without reengineering hardware layouts.
- Centralized software control: Streamlines development and enables over-the-air (OTA) updates, a key enabler of SDVs.
- Smarter feature coordination: Take lighting as an example. In legacy vehicles, flashing the headlights upon unlock required integrating multiple ECUs. In zonal designs, the central computer sends a single command, and the appropriate zone controller executes it—no redundant wiring or separate lighting logic required.
Zonal architecture represents a paradigm shift in how vehicles are designed and built. By grouping functions by physical location and leveraging Ethernet-based communications, automakers significantly reduce system complexity, wiring costs and maintenance challenges.
When combined with software-defined vehicle principles, zonal designs pave the way for faster innovation, greater customization, and smarter diagnostics.
With enabling technologies like 10BASE-T1S, Remote Control Protocol ICs, and intelligent power distribution, onsemi is helping carmakers bring this vision to life, delivering scalable, safe, and efficient zonal solutions that meet the evolving demands of modern mobility.
The post Zonal Architecture 101: Reducing Vehicle System Development Complexity appeared first on ELE Times.
Foxconn Taps NVIDIA to Accelerate Physical and Digital Robotics for Global Healthcare Industry
Courtesy: Nvidia
The world’s largest electronics manufacturer is building smart hospital solutions using NVIDIA technologies from the data center to the edge.
The global healthcare system is expected to face a shortage of 4.5 million nurses by 2030— and one of the main causes is high burnout. Manufacturing giant Foxconn is helping ease the burden with NVIDIA-accelerated solutions like Nurabot, a collaborative nursing robot that offloads time-consuming, fatiguing tasks such as transporting medication and samples across the hospital.
Nurabot is just one of Foxconn’s smart hospital applications developed using NVIDIA technologies and deployed by Taiwan’s leading medical centers. Its other tools include AI models to support patient health monitoring and digital twins of hospital facilities to help management teams with design and planning.
Together, these applications can transform medical centers into smart hospitals powered by NVIDIA physical AI and its three-computer solution. First, massive AI models are trained and fine-tuned on supercomputers. Next, in simulation, digital twins are used for planning, testing and robotics training — and third, edge computing systems enable rapid AI inference on robots and sensors.
Taichung Veterans General Hospital (TCVGH), Baishatun Tung Hospital – Mazu Hospital, and Cardinal Tien Hospital are among the Taiwan-based healthcare institutions adopting Foxconn’s smart hospital solutions to support clinicians and advance patient care.
“Taiwan has a highly developed healthcare infrastructure with a strong push toward digital health transformation, creating the ideal environment for robotic integration,” said Shu-Fang Liu, deputy director of the nursing department at TCVGH, which is currently conducting a field trial with Nurabot. “Robots are augmenting our capabilities so we can provide more focused, meaningful care.”
Recognized as one of the world’s top 100 smart hospitals, TCVGH is developing multiple solutions to address the severe shortage of nursing personnel in Taiwan. In addition to implementing welfare policies to retain talent, the hospital is harnessing AI technology to ease the burden on frontline staff, noted Dr. Yun-Ching Fu, the hospital’s superintendent.
The hospital began working with Foxconn last year to codevelop the Nurabot collaborative nursing robots as part of its smart healthcare initiative led by Dr. Shih-An Chen, honorary superintendent at TCVGH.
Supporting Smart Hospitals From the Data Center to the EdgeFoxconn’s smart hospital solution begins in the data center, where high-performance compute is applied to develop large AI foundation models — like FoxBrain, a large language model (LLM) developed using the NVIDIA NeMO framework. Trained on NVIDIA Hopper GPUs, FoxBrain is capable of text-to-speech, automatic speech recognition and natural language processing.
The company is also using its Honhai Super AI Computing Center 1, which features NVIDIA DGX systems, to develop healthcare-specific AI models. Offered through Foxconn’s CoDoctor AI platform, powered by NVIDIA AI, these models improve diagnostic accuracy and optimize clinical workflows for tasks including retinal imaging, vital sign monitoring, arrhythmia screening and cancer screening.

Clinicians in the radiology department at Tungs’ Taichung MetroHarbor Hospital use Foxconn’s CoDoctor AI platform for medical imaging workflows. Credit: Foxconn
Foxconn is also working with medical centers to integrate the NVIDIA AI Blueprint for video search and summarization, which can analyze real-time video data to alert healthcare workers of medical events and generate visual summaries for hospital management teams.
It will contribute CoroSegmentater, its AI model for coronary artery segmentation, to the MONAI open-source medical imaging platform pioneered by NVIDIA and leading academic medical centers. The model, powered by MONAI’s Auto3DSeg framework for 3D medical image segmentation, can be used to support diagnostics, preoperative planning and patient education.
Clinical teams can use FoxConn’s CoroSegmentater model with NVIDIA Omniverse platform to visualize the heart in 3D. Credit: Foxconn

Clinical teams can visualize these segmentations on 3D visualizations of the heart and vascular system running on NVIDIA OVX servers with NVIDIA Isaac for Healthcare, built on the NVIDIA Omniverse platform. Foxconn has also used Omniverse to develop a tool that can simulate the effects of drug treatments on the tumors of breast cancer patients.
Beyond simulating biology, Foxconn is working with TCVGH, Baishatun Tung Hospital – Mazu Hospital, and Cardinal Tien Hospital to simulate healthcare facilities using NVIDIA Omniverse. With these physically accurate simulations, the hospitals are planning out the design of new facilities, making data-driven decisions to optimize operations and building simulations to train robots.
Digital twins of TCVGH, Baishatun Tung Hospital – Mazu Hospital, and Cardinal Tien Hospital facilities. Credit: Foxconn

TCVGH, for instance, built a digital twin of one of its nursing stations and wards as a training ground for Nurabot — enabling the robotic system to practice navigating through virtual hallways before testing in the real world.
Taichung Veterans General Hospital Pilots Collaborative Nursing RobotNurabot — built by Foxconn and Japanese multinational company Kawasaki Heavy Industries — uses the FoxBrain LLM, virtual training with Isaac for Healthcare and onboard compute powered by the NVIDIA Holoscan sensor processing platform running on an NVIDIA Jetson Orin device.
Foxconn estimates that when deployed in clinical applications for delivering medication, transporting specimens and patrolling wards, Nurabot can reduce the workload of nurses by up to 30%.
“In one of our wards, we are using Nurabot to deliver wound care kits and health education materials to patient bedsides,” said Liu. “For nurses, having a robot assistant reduces physical fatigue, saving them multiple trips to supply rooms and allowing them to focus more on patients.”
TCVGH is conducting a field trial with Nurabot. Credit: TCVGH, Foxconn, Kawasaki Heavy Industries
During visiting hours, Nurabot helps guide patients and visitors through the ward, reducing the administrative workload for frontline staff. And during night shifts, where hospitals operate with fewer staff, it can help pick up the slack.
Liu hopes the nursing robots will also be able to soon converse with patients in multiple languages, recognize individuals to enable personalized interactions, and help nurses move patients.
Someone with a lung condition, for example, may need the help of two nurses to get up from their hospital bed and move to a chair to perform breathing exercises. With the help of an assistant like Nurabot, the task might be accomplished with a single nurse, allowing the other to focus on caring for the rest of the ward.
The post Foxconn Taps NVIDIA to Accelerate Physical and Digital Robotics for Global Healthcare Industry appeared first on ELE Times.
How to get great results with an infrared thermometer
Courtesy: Fluke
Temperature, Fundamentals
Infrared (IR) thermometers enable you to measure temperature quickly, at a distance, and without touching the object you’re measuring. They are so useful, easy, and even fun to use that they have become as common in kitchens as they have on factory floors. Infrared thermometers are often used to find overheated equipment and electrical circuits, but they have hundreds of other uses.

Measurement spot diameters of a Fluke 63 Infrared Thermometer at three distances.
However, there are a few “gotchas” when using an infrared thermometer that can generate readings that are misleading or just plain wrong. Fortunately, these sources of error are easy to avoid or work around.
Common uses for infrared thermometers in industry
- Finding faulty terminations in high power electrical circuits
- Locating overloaded circuit breakers
- Identifying fuses at or near their current rated capacity
- Identifying problems in electrical switch gear
- Monitoring and measuring bearing temperatures in large motors or other rotating equipment
- Identifying “hot spots” in electronic equipment
- Identifying leaks in sealed vessels
- Troubleshooting steam traps
- Finding faulty insulation in process pipes or other insulated processes
- Capturing process temperature readings
Every infrared thermometer has a “distance-to-spot” (D:S) ratio that tells you the diameter of the area being measured compared to the distance from the target. For example, if your thermometer has a distance-to-spot ratio of 12:1, it measures an approximately one-inch-diameter spot when it’s 12 inches from the target (about 2.5 cm at 30 cm). If you try to use that thermometer to measure a two-inch (5-cm) area from even just a few feet (1 m) away, you’re not going to get an accurate result because the thermometer will also be measuring the temperature outside the area you want to measure.
Distance-to-spot ratios vary a lot (from about 1:1 on the least expensive thermometers to about 60:1 on top-of-the-line models) and vary slightly with distance, so be sure to check the label on your thermometer or in the manual.
2. Lead Astray by the Laser?Most handheld infrared thermometers have laser pointers that show the approximate center of the measurement area. It’s important to know that the laser is only a pointer and not used for the actual temperature measurement. Another common misconception is that the thermometer is measuring the area illuminated by the laser beam. The measurement spot is always wider.
3. Confused by Bright Shiny Objects?Infrared thermometers have good accuracy when measuring most objects, but shiny, reflective surfaces can be a challenge. You should be especially wary when measuring the temperature of shiny metal objects, but even reflections off of glossy paint can affect accuracy. Putting a piece of non-reflective tape (such as electrical tape) over the shiny surface or applying some flat paint gives you a target from which you can get a better measurement.

Taking measurements on non-reflective tape or flat paint helps avoid errors caused by shiny surfaces.
The reason for this is that not all materials emit the same amount of infrared energy when they are at the same temperature. In general, most materials emit more infrared energy than shiny metals do – they have higher “emissivity.” (Emissivity is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, with 0 being non-emissive and 1 being perfectly emissive). Reflective surfaces are less emissive than dull surfaces. Weathered or oxidized metals are more emissive than polished, shiny metals.
If you need to take temperature readings on low emissivity objects regularly, consider an IR thermometer that enables you to compensate for variations in emissivity. For example, the Fluke 561 Infrared Thermometer enables you to set emissivity to “High” (for measuring most surfaces, such as wood, paint, rubber, plaster, or concrete), “Medium” (for oxidized metals or granite, for example), or “Low” (for shiny metals).
4. Obscured Optics?Where you use your infrared thermometer can also affect its accuracy. For example, if there is steam or dust in the between the target and the thermometer, some of the IR energy may be deflected before reaching the thermometer. Similarly, a dirty or scratched lens on your IR thermometer may impair its ability to “see” the IR energy that it needs to make a measurement. A lens that has fogged when the thermometer is brought into a warm room from a colder environment can also affect accuracy.
5. Temperature Shocked?Finally, for highest accuracy, it’s best to allow some time (about 20 minutes is usually enough) for your IR thermometer to come to the temperature of its surroundings when bringing the thermometer into surroundings that are significantly warmer or colder than where it has been stored.
Noncontact infrared thermometers offer a great combination of speed, convenience, and accuracy, but only when they’re used correctly.
To get the best results possible, remember to:- Know your IR thermometer’s distance-to-spot ratio, and get close enough to the target so your thermometer reads only the area that you want it to measure.
- Watch out for (and compensate for) shiny, “low emissivity” objects.
- Remember that steam or dust can affect the accuracy of IR thermometers.
- Keep the lens of your thermometer clean and free of scratches.
- To get the most accurate results, allow some time for the thermometer to come to the temperature of its surroundings.
The post How to get great results with an infrared thermometer appeared first on ELE Times.
Simulations à la Carte: Infusing SPICE Models for a Tasty Design Experience
Courtesy: Infineon
Have you ever noticed how the simplest dishes become unforgettable with just the right seasoning? As an Ecuadorian, I’ve learned this firsthand. A touch of “ají”—a traditional chili sauce—can transform any meal into something extraordinary. The tamarillo-based hot sauce is my personal favorite. It’s not just a condiment; it’s an experience. And when it comes to power electronics, I’ve come to see SPICE models in the same way. They’re the secret ingredient that can take your circuit simulations from bland to brilliant.
Let me show you how adding a bit of SPICE to your simulations can make all the difference.
The foundation for a flavorful design: Compact modelsThink of a compact model as your base recipe. It’s the essential framework that captures the behavior of a semiconductor device. As shown in Fig.1, a good compact model blends all the critical elements: electrical characteristics, parasitic effects, and even thermal dynamics.
For example, a compact model typically includes three layers:
– Chip model: The core of the device, accounting for its on-state and off-state characteristics, capacitances, and thermal behavior.
– Parasitic model: This layer considers resistive, inductive, and capacitive effects from the package—factors that can influence performance.
– Thermal model: It simulates how heat flows through the device, giving you insight into self-heating effects during operation.

Fig.1. A simplified structure of a compact model is shown for a SiC MOSFET in a TO247-4 package.
When these models come together, they provide a detailed picture of how a semiconductor behaves in real-world conditions. But, as with any recipe, the quality of the outcome depends on the precision and care put into each ingredient.
In the land of flavors, spicy is the king: Spice modelsIn the world of circuit simulations, SPICE models are the trusted seasoning. They’re incredibly detailed and flexible, making them perfect for analyzing switching behavior under various conditions. But just like too much chili in a dish, there’s a tradeoff: SPICE simulations can be time-consuming, especially for long-term scenarios, like a solar inverter operating over a full day.
To speed things up, designers sometimes use simplified thermal-loss models based on datasheet data. These are faster to work with but come with limitations. They often represent how a device performs on a specific test bench rather than in real-life applications, which can lead to less accurate results. A brief comparison between both abstraction levels is depicted on Fig.2.

Fig.2. Comparison of spice model and thermal-loss description models
It’s a bit like cooking with pre-made sauces—quick and convenient, but not quite as satisfying as making everything from scratch.
When life gives you chilies, make it hot: Infineon’s approachSo, how do you get the best of both worlds? How do you achieve simulations that are both fast and accurate? At Infineon, we asked these same questions, and we’ve worked hard to deliver the answers.
Our SPICE SiC MOSFET models are like your fresh, high-quality ingredients. Designed for accuracy, they provide detailed insights into dynamic response and performance. And here’s the best part: we’ve built an automated workflow that takes these models to the next level.
Using our SPICE simulator, we’ve created a system that extracts switching waveforms under various conditions, calculates energy losses, and translates them into a thermal-loss format (XML files), a simplified flow scheme is shown in the Fig. 3. This makes it easy to incorporate high-quality data into system-level simulations without sacrificing speed. Imagine having a perfectly balanced sauce ready to enhance any dish—that’s what we’re offering for your circuit designs.

Fig.3. Flow diagram to design custom thermal models using spice simulations
The finishing touchLike a great meal, a successful power converter design is all about balance. You need the right ingredients, careful preparation, and attention to detail. At Infineon, we’re passionate about helping you get it just right.
With our SPICE models and simulation tools, you’ll gain deeper insights into how our products perform in your specific applications. You’ll save time, reduce costs, and open the door to faster innovations—all while improving system performance and reliability. And let’s not forget the big win: a reduced carbon footprint, thanks to more efficient designs.
So, the next time you’re working on a simulation, remember this: a little SPICE can go a long way. Explore our tools, try our models, and see how they can transform your designs. After all, every great creation—whether it’s a dish or a circuit—deserves the perfect touch.
The post Simulations à la Carte: Infusing SPICE Models for a Tasty Design Experience appeared first on ELE Times.
Protect Your Critical Timing Applications with TimeProvider XT Extension Shelf
Courtesy: Microchip
Communications network operators who are struggling to support legacy SSU and BITS systems can now migrate to a newer platform that supports E1/T1/CC critical timing services as well as next-generation network-based timing services using PTP, NTP and Synchronous Ethernet.
The Importance of Timing ConnectionsIn today’s rapidly evolving telecommunications landscape, maintaining precise and reliable timing is crucial for the seamless operation of central office environments. Timing connections that support synchronization, timing or timestamps related to signaling information are critical. Even something as simple as NTP timing services for credit card transactions is vital.
Transitioning to Modern PlatformsNow is the time to migrate from legacy Synchronization Supply Units (SSU) and Building Integrated Timing Supply (BITS) technologies to newer platforms. These modern platforms support next-generation network-based timing services using PTP, NTP and Synchronous Ethernet as well as legacy SONET/SDH TDM synchronization.
Traditional SSU and BITS timing equipment is becoming outdated and reaching end-of-life, posing significant challenges for maintaining reliable timing services. The TimeProvider 4×00 and TimeProvider XT Extension System addresses these challenges by providing advanced timing capabilities and supporting next-generation network-based timing services. Below are several use cases outlining the value of migrating legacy synchronization to a modern platform.
Use Cases Use Case 1: Enhancing Holdover CapabilitiesIn this use case, the TimeProvider 4×00 system with dual time provider oscillators serves as the holdover oscillators for the SSU or BITS clock application. We remove the oscillators in the SSU/BITS shelf and we drive the outputs directly from the inputs. This approach is cost-effective and ensures resiliency, as many older oscillators are expensive to repair and often no longer available. The holdover hierarchy, supported by Rubidium atomic clock oscillators, meets Stratum one and G.811 requirements for synchronous Ethernet use cases. This adds holdover capability as well as next generation packet-based timing services to your offices with a very low cost and a way to ensure resiliency moving into the future. (see figure 1)
Figure 1

The Model 2 + 2 use case demonstrates the use of PTP timing services with APTS flow between two locations (e.g., central offices or mobile switching offices) A and B. This setup allows for a PTP APTS flow from location A to B and vice versa. With only one antenna per location, if a GNSS antenna fails, location A can back up location B and vice versa. By implementing this model, customers can build confidence in PTP/APTS technology and prepare for future PTP use cases. (see Figure 2)
Figure 2

The TimeProvider 4×00 and TimeProvider XT Expansion Shelf can be used to overlay legacy SSU and BITS platforms. Many of our customers have extremely old DCD or SSU and BITS platforms in place that are no longer reliable and near end of life. So, it is in the best interest of our customers to migrate the critical timing services in an office that supports signaling, transmission or high volumes of network services over to a more modern reliable platform like the Time Provider 4×00 and XT extension. (see Figure 3)
Figure 3

The final use case involves completely replacing legacy SSU BITS equipment with a TimeProvider grandmaster and XT Extension shelves that support legacy outputs. This approach is beneficial for several reasons:
- Older products are often at the end of their lifecycle.
- Customers may not need the high number of outputs provided by older platforms.
- Modern platforms consume less power, reducing overall power consumption.
- High replacement and repair costs for end-of-life SSU and BITS platforms can be avoided.
Moving to a more modern, reliable platform can actually save money in the long term related to repairs and end of life scenarios. Additionally, replacing legacy systems can help clean up office wiring issues, providing a more organized and efficient setup. (see Figure 4)
Figure 4

The good news is that it is very easy to replace a legacy office SSU/BITS with a new TimeProvider 4×00 grandmaster and XT extension. Each XT shelf has 40 individually configurable E1/T1/CC outputs, and up to five shelves can be connected, providing 200 outputs per system. This solution is backwards compatible; legacy wirewrap and patch output panels can be left in place. During a service window, simply disconnect the cable from the SSU/BITS equipment and attach it to TimeProvider XT shelf (see Figure 5).
Figure 5


Below is a simplified five-step process to replace a legacy SSU/BITS with a new TimeProvider 4×00 grandmaster and TimeProvider XT shelf fan-out.
- Install and configure the TimeProvider 4×00 grandmaster clock and XT shelve(s) in the rack near the legacy SSU/BITS.
- Install and connect the new rooftop antenna for the TimeProvider 4×00 system. Note: that the TimeProvider 4×00 system is not compatible with the legacy SSU antenna electronics.
- Confirm that the TimeProvider 4×00 system with XT shelves are fully locked to GNSS and alarm free.
- Schedule maintenance window time to disconnect output panels from the legacy BITS/SSU and reconnect them to the TimeProvider XT shelves. Or, network elements can be moved individually from the SSU/BITs equipment to the XT shelves.
- The BITS/SSU systems will switch to backup references or enter holdover with associated alarms when the legacy SSU/BITS is disconnected. Confirm that the XT shelves E1/T1/CC outputs are functioning, and all alarms have cleared.
Microchip has developed detailed procedures for exact equipment replacement scenarios. Please contact your Microchip representative for examples of detailed procedures.
TimeProvider 4×00 Grandmaster Overview and Comparison to a Legacy SSU/BITSTable 1 provides a full side by side comparison of the TimeProvider 4×00 grandmaster with XT Expansion Shelf to a legacy SSU 2000/2000e. Figure 6 is an overview of the TimeProvider XT Extension Shelf.
Table 1. Legacy SSU/BITS vs. TimeProvider 4×00 with XT extension shelf
| Functionality | DCD, SSU 2000/2000e, TP1x00, TSG-3800, TimeHub | TimeProvider 4×00 Grandmaster and XT shelf |
| Node clocks in synchronization networks ITU-T G.812 | Yes | Yes |
| Composite clock ITU G.703 | Yes | Yes |
| Input filtering of wander and jitter ITU-T G.824 | Yes | Yes |
| PRTC ITU-T G.8272 | Yes (PRTC-A and PRTC-B) | |
| ePRTC ITU-T G.8272.1 | Yes (when deployed with a collocated cesium standard ePRC clock) | |
| GNSS | GPS only | Full GNSS (GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, Beidou, QZSS, NaviC user selectable) and multi-band L1/L2/E5B/L5 support |
| BlueSky GNSS spoofing and jamming protection | Yes | |
| T1/E1/CC outputs | Yes | Yes |
| NTPr v4 and v6 with MD5 security | Yes | |
| IEEE 1588 PTP | Yes (input and output) | |
| SyncE ITU-T G.8261 | Yes |
Figure 6

The TimeProvider 4×00 and TimeProvider XT Expansion Shelf is a powerful solution for protecting and enhancing critical timing applications in central office environments. By migrating from outdated SSU and BITS technologies to modern platforms that support PTP, NTP and synchronous Ethernet, organizations can ensure the accuracy and reliability of their timing infrastructure. The use cases presented here demonstrate the versatility and benefits of the TimeProvider XT Extension Shelf, making it an essential component for any central office looking to future-proof its timing services.
Migrate your critical services timing needs to a new modern platform that can serve your existing and future requirements as you evolve your timing and network infrastructure.
The post Protect Your Critical Timing Applications with TimeProvider XT Extension Shelf appeared first on ELE Times.



