Feed aggregator
I made a glowing version of gretz bridge
 | submitted by /u/Mistrzunio21 [link] [comments] |
Weekly discussion, complaint, and rant thread
Open to anything, including discussions, complaints, and rants.
Sub rules do not apply, so don't bother reporting incivility, off-topic, or spam.
Reddit-wide rules do apply.
To see the newest posts, sort the comments by "new" (instead of "best" or "top").
[link] [comments]
Happy 50th Birthday to Intel 8080, the Microprocessor That Started It All - News
 | submitted by /u/Crazy_Circuit_201 [link] [comments] |
EEVblog 1659 - Quick 861 Pro Hot Air Station REVIEW
Cute 20kv low efford bridge
 | Made during challenge "12hours to 200kv". It's not safe, it's not wise but looks kind of cool. [link] [comments] |
Clapp versus Colpitts

Edwin Henry Colpitts (January 19, 1872 – March 6, 1949)
James Kilton Clapp (December 03, 1897 – 1965)
The two persons above are the geniuses who gave us two classic oscillator circuits as shown in Figure 1.
 Figure 1 The two classic oscillators circuits: Colpitts (left) and Clapp (right).
Figure 1 The two classic oscillators circuits: Colpitts (left) and Clapp (right).
We’ve looked at these two oscillators individually before in “The Colpitts oscillator” and “Clapp oscillator”.
However, a side-by-side examination of the two oscillators is additional time well spent.
The Clapp oscillator was devised as an improvement over the Colpitts oscillator by virtue of adding one capacitor, C3, in the above image.
The amplifier “A” is nominally at a gain value of unity, but as a matter of practicality, the gain value is slightly lower than that because the amplifier is really a “follower”. If made with a vacuum tube, then “A” is a cathode follower. If made with a bipolar transistor, then “A” is an emitter follower. If made with a field effect transistor, then “A” is a source follower. The concept itself remains the same.
Each oscillator works because the RLC network develops a voltage step-up at the frequency of oscillation. The “R” is not an incorporated component though. The “R” (R1 or R2) simply represents an output impedance of the follower. The 10 ohms that we see here is purely an arbitrary value guess on my part. The other components are also of arbitrary value choices, but they are convenient values for illustrating just how these little beasties work.
We use SPICE simulations to examine the transfer functions of the two RLC networks as shown in Figure 2.
 Figure 2 Colpitts versus Clapp spice simulations using the transfer functions of the two RLC networks.
Figure 2 Colpitts versus Clapp spice simulations using the transfer functions of the two RLC networks.
Each RLC network has a peak in its frequency response which will result in oscillation at that peak frequency. However, the peak of the Clapp circuit is much sharper and narrower than that of the Colpitts circuit. This narrowing has the beneficial effect of suppressing spectral noise centered around the oscillation frequency.
Note in the examples above that the oscillation peaks differ by 0.16% and that the reactance of the L1 inductor and the reactance of the L2 C3 pair differ by 1.12%. That’s just a matter of my having chosen some convenient numbers with the intent of having the two curves match in that regard at the same peak frequency. (I almost succeeded.)
The Clapp oscillator has several advantages over the Colpitts oscillator. The transfer function peak of the Clapp circuit is narrower than that of the Colpitts which tends to yield an oscillator output with less spurious off-frequency energy meaning a “cleaner” signal.
Another advantage of the Clapp circuit is that capacitors C4 and C5 can be made very large as the L2 C3 combination is made to look like a very small inductance value at the oscillation frequency. The larger C4 and C5 values mean that any variations of those capacitance values brought about by variations of the input capacitance of the “A” stage have a minimal effect on the oscillation frequency.
That’s because frequency control of the Clapp circuit is primarily set by the series resonance of the L2 C3 pair rather than the parallel resonance of L1 versus the C1 C2 pair in the Colpitts circuit. If the “A” input capacitance tends to vary for this reason or that, the Clapp circuit is far less prone to an unwanted frequency shift as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 A Clapp versus Colpitts frequency shift comparison showing how the Clapp circuit (right) is far less prone to this unwanted shift in frequency.
John Dunn is an electronics consultant, and a graduate of The Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn (BSEE) and of New York University (MSEE).
Related Content
- The Colpitts oscillator
- Clapp oscillator
- Emitter followers as Colpitts oscillators
- Oscillator has voltage-controlled duty cycle
The post Clapp versus Colpitts appeared first on EDN.
Polar Light achieves 625nm-wavelength red pyramidal micro-LED
Passive Q filter using a mini 1:1 audio transformer with its primary and secondary coils wired in series as an inductor, in conjunction with a cap and resistors to target mid frequencies.
 | submitted by /u/Probablyawerewolf [link] [comments] |
DigiKey Sponsors Eleckart Competition at Shaastra 2025 Annual Technical Festival
DigiKey, a leading global commerce distributor offering the largest selection of technical components and automation products in stock for immediate shipment, is proud to sponsor the Eleckart competition during the 2025 Shaastra Technical Festival in Chennai, India, from Jan. 3-7, 2025.
The Eleckart event will test students’ understanding of digital electronics and their problem-solving capabilities using a minimal set of resources. The event consists of two rounds. The first round will test participants’ knowledge of creating electronic circuit diagrams using DigiKey’s Scheme-it platform. The final round will be on circuit building using actual components while managing the points that are deducted through components taken. Winners will receive prizes up to ₹50,000.
The festival is hosted by the Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM) and showcases engineering, science and technology with competitions, lectures, exhibitions, demonstrations and workshops. Students can register for technology-related workshops focusing on the Internet of Things (IoT), rocket propulsion, Arduino, CAD for industrial designs, AI and machine learning, and quantum computing.
“DigiKey is excited to sponsor the Eleckart competition during IITM’s Shaastra Technical Festival and have a chance to connect with the 60,000 attendees that will visit the summit,” said Y.C. Wang, director of global academic programs at DigiKey. “India is one of DigiKey’s top markets and this opportunity allows us to interact with students, engineers and designers who will foster future innovations in India and around the world.”
On Jan. 4, DigiKey representatives will showcase Sparkfun’s Experiential Robotics Platform (XRP) at the Eleckart event. Students can visit the DigiKey table to learn about the organization’s largest selection of technical components and about DigiKey’s tech resources such as online conversion calculators, PCB builders and design tools. Students can also receive free DigiKey PCB rulers.
The post DigiKey Sponsors Eleckart Competition at Shaastra 2025 Annual Technical Festival appeared first on ELE Times.
Industrial MCU packs EtherCAT controller

GigaDevice has introduced the GD32H75E 32-bit MCU, featuring an integrated GDSCN832 EtherCAT subdevice controller, which is also available as a standalone device. Both components target industrial automation applications, including servo control, variable frequency drives, industrial PLCs, and communication modules.

Powered by an Arm Cortex-M7 core running at up to 600 MHz, the GD32H75E microcontroller includes a DSP hardware accelerator, double-precision floating-point unit, hardware trigonometric accelerator, and filter algorithm accelerator. It also comes with 1024 KB of SRAM, up to 3840 KB of flash memory with security protection, and a 64-KB cache to enhance CPU efficiency and real-time performance.
The MCU’s integrated EtherCAT subdevice controller, licensed from Beckhoff Automation, manages EtherCAT communication, acting as an interface between the EtherCAT fieldbus and the sub-application. It includes two internal PHY ports and an external MII. With 64-bit distributed clock support, it enables synchronization with other EtherCAT devices, achieving DC synchronization accuracy to within 1 µs.
The GD32H75E MCU is available in two variants: one with two internal Ethernet PHYs and another that supports bypass mode, both housed in BGA240 packages. Samples and development boards are available now, with mass production planned for Q2 2025.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Industrial MCU packs EtherCAT controller appeared first on EDN.
Wireless audio SoC integrates AI processing

Airoha Technology’s AB1595 Bluetooth audio chip features a 6-core architecture and a built-in AI hardware accelerator. It consolidates functions typically spread across multiple chips into a single SoC and achieves Microsoft Teams Open Office certification.

The AB1595 uses AI algorithms and input from up to 10 microphones to improve speech clarity by reducing background noise. This collaboration allows it to accurately distinguish between the user’s voice and environmental sounds, achieving professional-grade speech quality. In noisy environments like offices and cafes, it enhances voice noise suppression from 10 dB up to 40 dB, optimizing speech quality and elevating consumer headsets to professional teleconference standards.
Real-time adaptive active noise cancellation (ANC) in the AB1595 boosts environmental noise attenuation across a wide frequency range. It detects the user’s wearing condition (e.g., fit or leakage) and adjusts compensation accordingly. Internal filters automatically adapt to both the fit and surrounding noise, balancing effective noise cancellation with comfort for a superior wearing and listening experience.
Airoha reports that the AB1595 has been adopted by customers, with products expected to be available in Q1 2025. A datasheet was not available at the time of this announcement. Contact Airoha Technology here.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post Wireless audio SoC integrates AI processing appeared first on EDN.
85-V LED driver handles multiple topologies

Designed for automotive LED lighting systems, Diodes’ AL8866Q driver supports buck, boost, buck-boost, and single-ended primary-inductance converter (SEPIC) topologies. This DC-switching LED driver-controller operates over an input voltage range of 4.7 V to 85 V, accommodating 12-V, 24-V, and 48-V battery power rails. It is suitable for applications such as daytime running lights, high/low beams, fog lights, turn signals, and brake lights.

The AL8866Q employs a 400-kHz fixed-frequency peak current-mode control architecture. Spread spectrum frequency modulation enhances EMI performance and aids compliance with the CISPR 25 Class 5 standard.
The device enables analog or PWM dimming via its DIM pin. A 1% reference tolerance ensures better brightness control and matching between lamps. With an analog dimming range of 1% to 100%, the AL8866Q maintains ±12% output current accuracy at 20% dimming. Alternatively, PWM dimming, ranging from 0.1 kHz to 1 kHz, provides a 100:1 dynamic range.
An integrated soft-start function gradually increases the inductor and switch current, minimizing potential overvoltage and overcurrent at the output. The driver also includes an open-drain fault output to signal various fault conditions.
Prices for the AEC-Q100 Grade 1 qualified AL8866Q driver start at $0.48 each in lots of 1000 units.
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post 85-V LED driver handles multiple topologies appeared first on EDN.
PCIe Gen4 SSD delivers 6200 MB/s

The P400 V4 from Patriot Memory is a PCIe Gen 4 x4 M.2 SSD, offering read speeds up to 6200 MB/s and write speeds up to 5200 MB/s. Optimized for PC and PS5 compatibility, it provides gamers and content creators with high-speed performance and enhanced thermal management. Its compact M.2 2280 form factor makes it well-suited for space-constrained systems, including thin laptops and small form-factor PCs.

With a read speed of 6200 MB/s, the P400 V4 achieves a total bytes written (TBW) rating of 1280 TB. Available in storage capacities ranging from 500 GB to 4 TB, the drive features SmartECC technology for improved reliability. To maintain consistent peak performance during intensive operations, the P400 V4 incorporates a graphene heatshield that helps prevent thermal throttling and efficiently manages thermal output.
The P400 V4’s PCIe Gen 4 x4 controller is NVMe 2.0 compliant, offering improved performance and support for the latest features. The SSD comes with a 5-year warranty and supports Windows 7, 8.0, 8.1, 10, and 11 (drivers may be required for older versions).
Find more datasheets on products like this one at Datasheets.com, searchable by category, part #, description, manufacturer, and more.
The post PCIe Gen4 SSD delivers 6200 MB/s appeared first on EDN.
Porotech advances partnership with Foxconn from R&D to mass production of AR and micro-LED technology
2nd Year Electrical Engineering Student - Final Project for Solid State Electronics Class - 3 Bit Binary Sequence to Decimal Value Converter
 | submitted by /u/Accomplished_Pace860 [link] [comments] |
Neo completes sale of Rare Metals facility in Quapaw, Oklahoma
The advent of co-packaged optics (CPO) in 2025

Co-packaged optics (CPO)—the silicon photonics technology promising to transform modern data centers and high-performance networks by addressing critical challenges like bandwidth density, energy efficiency, and scalability—is finally entering the commercial arena in 2025.
According to a report published in Economic Daily News, TSMC has successfully integrated CPO with advanced semiconductor packaging technologies, and sample deliveries are expected in early 2025. Next, TSMC is projected to enter mass production in the second half of 2025 with 1.6T optical transmission offerings.

Figure 1 CPO facilitates a shift from electrical to optical transmission to address the interconnect limitations such as signal interference and overheating. Source: TrendForce
The report reveals that TSMC has successfully trialled a key CPO technology—micro ring modulator (MRM)—at its 3-nm process node in close collaboration with Broadcom. That’s a significant leap from electrical to optical signal transmission for computing tasks.
The report also indicates that Nvidia plans to adopt CPO technology, starting with its GB300 chips, which are set for release in the second half of 2025. Moreover, Nvidia plans to incorporate CPO in its subsequent Rubin architecture to address the limitations of NVLink, the company’s in-house high-speed interconnect technology.
What’s CPO
CPO is a crucial technology for artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) applications. It enhances a chip’s interconnect bandwidth and energy efficiency by integrating optics and electronics within a single package, which significantly shortens electrical link lengths.
Here, optical links offer multiple advantages over traditional electrical transmission; they lower signal degradation over distance, reduce susceptibility to crosstalk, and offer significantly higher bandwidth. That makes CPO an ideal fit for data-intensive AI and HPC applications.
Furthermore, CPO offers significant power savings compared to traditional pluggable optics, which struggle with power efficiency at higher data rates. The early implementations show 30% to 50% reductions in power consumption, claims an IDTechEx study titled “Co-Packaged Optics (CPO): Evaluating Different Packaging Technologies.”
This integration of optics with silicon—enabled by advancements in chiplet-based technology and 3D-IC packaging—also reduces signal degradation and power loss and pushes data rates to 1.6T and beyond.

Figure 2 Optical interconnect technology has been gaining traction due to the growing need for higher data throughput and improved power efficiency. Source: IDTechEx
Heterogeneous integration, a key ingredient in CPO, enables the fusion of optical engine (OE) with switch ASICs or XPUs on a single package substrate. Here, the optical engine includes both photonic ICs and electronic ICs. The packaging in CPO generally employs two approaches. The first one involves the packaging of optical engine itself and the second one focuses on the system-level integration of the optical engine with ICs like ASICs or XPUs.
A new optical computing era
TSMC’s approach involves integrating CPO modules with advanced packaging technologies such as chip-on-wafer-on-substrate (CoWoS) or small outline integrated circuit (SOIC). It eliminates traditional copper interconnects’ speed limitations and puts TSMC at the forefront of a new optical computing era.
However, challenges such as low yield rates in CPO module production might lead TSMC to outsource some optical-engine packaging orders to other advanced packaging companies. This shows that the complex packaging process encompassing CPO fabric will inevitably require a lot of fine-tuning before commercial realization.
Still, it’s a breakthrough that highlights a tipping point for AI and HPC performance, wrote Jeffrey Cooper in his LinkedIn post. Cooper, a former sourcing lead for ASML, also sees a growing need for cross-discipline expertise in photonics and semiconductor packaging.
Related Content
- Optical interconnects draw skepticism, scorn
- TSMC crunch heralds good days for advanced packaging
- Intel and FMD’s Roadmap for 3D Heterogeneous Integration
- Heterogeneous Integration and the Evolution of IC Packaging
- CEA-Leti Develops Active Optical Interposers to Connect Chiplets
- Road to Commercialization for Optical Chip-to-Chip Interconnects
The post The advent of co-packaged optics (CPO) in 2025 appeared first on EDN.
Tech Data and Dell Technologies Sign MoU to Drive AI Adoption through Dell AI Factory
Collaboration delivers comprehensive AI solutions portfolio, backed by partner support through Tech Data’s Destination AI program
Tech Data, a TD SYNNEX Company, and Dell Technologies have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to enable the Dell AI Factory in India, a one-stop platform that offers products, solutions and services to accelerate AI adoption across industries.
With this agreement, Tech Data and Dell will establish a Center of Excellence for Dell to showcase use cases and product demonstrations. They will also collaborate with leading Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) to deliver pre-validated, end-to-end AI solutions. These offerings seamlessly combine Dell’s advanced hardware with specialized software, simplifying AI deployments for partners and empowering them to engage customers confidently and address evolving market needs.
Tech Data’s Destination AI program will further support partners with training, technical guidance, and pre- and post-sales services, accelerating their AI readiness and driving sustainable business growth.
“We are excited to strengthen our partnership with Dell Technologies and introduce the Dell AI Factory to Channel Partners,” said Sundaresan K., Vice President and Country General Manager, Tech Data Advanced (India) Private Limited. “India’s AI market is expanding rapidly, and Partners are eager to capitalize on the immense opportunities it presents. The Dell AI Factory, combined with our Destination AI program, is designed to equip them with the advanced tools and capabilities they need to meet this growing demand and deliver cutting-edge AI solutions to their customers.”
program, is designed to equip them with the advanced tools and capabilities they need to meet this growing demand and deliver cutting-edge AI solutions to their customers.”
To further strengthen the AI ecosystem, Tech Data will onboard additional ISVs, enhancing the Dell AI Factory with specialized software solutions that complement Dell’s technology. This will ensure greater adaptability to the unique needs of various industries.
“At Dell Technologies, we are committed to driving innovation that simplifies and accelerates technology adoption,” said Vivek Malhotra, Senior Director & General Manager, India Channels, Dell Technologies. “Our collaboration with Tech Data to launch the Center of Excellence in India underscores this commitment, offering channel partners a robust platform to deliver tailored AI solutions seamlessly. By combining our expertise through Dell AI Factory and advanced hardware solutions, we are equipping our partners with the tools and expertise necessary to address diverse industry challenges and unlock new growth opportunities in the AI era.”
The post Tech Data and Dell Technologies Sign MoU to Drive AI Adoption through Dell AI Factory appeared first on ELE Times.
Amazon Sidewalk: The first STM32-qualified devices are already making a difference. Check out this customer testimonial!
For the first time, Nucleo boards housing an STM32WBA5 and an STM32WLx5 received the Amazon Sidewalk certification, thus guaranteeing these STM32 MCUs will offer robust integration, high efficiency, and trusted security when deployed on an Amazon Sidewalk network. We are even showing how Subeca, an end-to-end water management platform in the United States, leveraged these STM32 devices to obtain its Amazon Sidewalk qualification, thus ensuring its customers can benefit from this vast and secure network to create a cost-effective and scalable solution for water metering and pressure management IoT systems.
What is Amazon Sidewalk?The idea behind Amazon Sidewalk is elegantly simple: using Internet-connected devices like Amazon Echos or some Ring Floodlight and Spotlight Cams, which serve as Amazon Sidewalk Bridges, to create a low-bandwidth and low-powered wireless network by piggybacking on a tiny amount of the Bridges’ bandwidth (80 Kbps). An Amazon Sidewalk device can thus connect to a Sidewalk Bridge using Bluetooth, securely connecting to its network and benefiting from the Internet. Moreover, once an Amazon Sidewalk end device is provisioned to the network via Bluetooth LE, it can rely on the long-range connectivity of the STM32WL5 to extend the network coverage over vast distances.
Amazon Sidewalk is free to use and simplifies operations. If a Sidewalk Bridge loses its Wi-Fi connection, Amazon’s technology can initiate a reconnection to the router without the user’s intervention. Bandwidth is also very low, and data usage is minimal and capped at 500 MB a month, meaning that even customers with a constrained Internet connection won’t feel its impact. Moreover, Amazon has numerous encryption and secure mechanisms to keep data private and safe. Hence, it’s possible to use Amazon Sidewalk for logistic, personal, or pet tracking, beyond-the-fence asset monitoring, smart irrigation systems, healthcare monitoring, or, as Subeca demonstrates, for more demanding applications like utilities monitoring on a national scale, as the Sidewalk coverage map suggests.
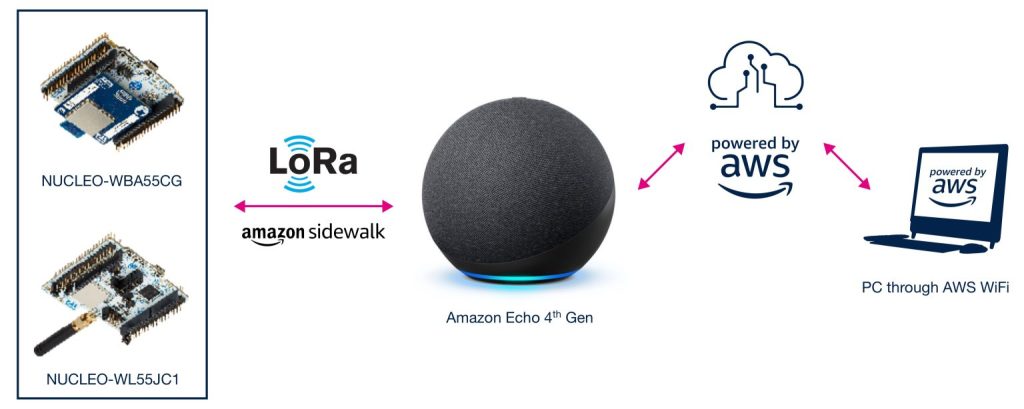 Amazon Sidewalk in one image
What the Amazon Sidewalk qualification means for STM32 developers
The hardware
Amazon Sidewalk in one image
What the Amazon Sidewalk qualification means for STM32 developers
The hardware
As of today, boards featuring the STM32WBA5, STM32WL5, and STM32WLE5 have received the Amazon Sidewalk qualification. The STM32WBA5 offers a Cortex-M33, a Bluetooth LE 5.4 transceiver, and can target a SESIP Level 3 certification, while the STM32WLx5 devices use a Cortex-M4 and a sub-GHz radio. Engineers might choose an STM32WBA55 and an STM32WLE5 to optimize memory usage or an STM32WBA55 and an STM32WL55 for the greater flexibility this configuration affords.
Concretely, the STM32WBA5 talks directly to the Amazon Sidewalk Bridge using a Bluetooth LE connection. And in some instances, that’s all the system needs. However, when networking multiple end nodes over large distances, like in the case of Subeca, it’s necessary to use the STM32WL5 to talk to devices using CSS (Chirp Spread Spectrum, such as LoRa) or an FSK modulation, depending on the distance and frequency range engineers wish to target.
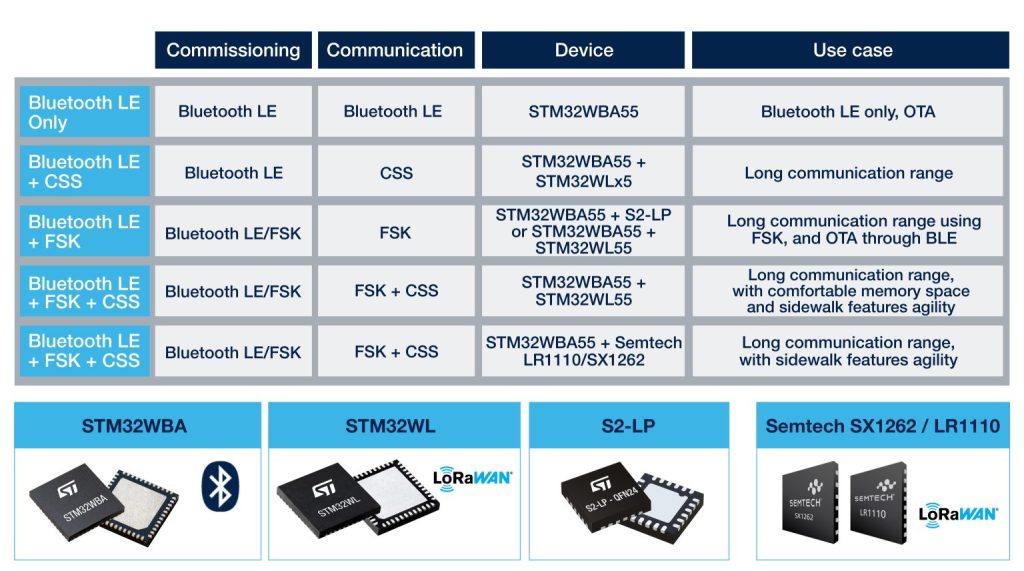 Amazon Sidewalk qualified hardware configurations
The software
Amazon Sidewalk qualified hardware configurations
The software
 An STM32WBA55 development board
An STM32WBA55 development board
To help developers jumpstart their projects, ST is offering software packages that help implement a network stack that easily interacts with Amazon Sidewalk. This dramatically simplifies the connection to the network, the integration of security features into the application, and the onboarding process. Put simply, while an Amazon Sidewalk guarantees that ST devices will provide the reliability and safety required, it is also a testament to our partnership with Amazon and our desire to help engineers take advantage of this technology.
Real-world applicationsThe qualification and partnership between Amazon and ST means that partners like Subeca can focus on showcasing their expertise and distinguishing their products from the competition instead of spending resources solving networking challenges. As Patrick Keaney, CEO of Subeca, explained,
“Our focus is on innovating and simplifying solutions that solve real-world challenges in the water market. We believe technology like advanced metering, leak detection, and pressure monitoring should be available to all water utilities everywhere, regardless of size. That means wireless connectivity is a must. ST’s STM32WBA5 and STM32WL5/STM32WLE5 wireless microcontrollers enabled us to bring our first Amazon sidewalk-qualified products to the market with great architectural flexibility, performance, low-power consumption in a cost-effective manner with meaningful device longevity and robust and resilient supply chain. Leveraging ST’s expansive device portfolio and ecosystem coupled with great technical support, ST offered us quality technical ingredients, ease-of-use, and portability required to transform our vision into reality.”
 A NUCLEO-WL55JC1
A NUCLEO-WL55JC1
Avnet also showcased an Amazon Sidewalk demo at AWS Re:Invent 2024 featuring an STM32WBA5, an STM32WL55, and Avnet’s IoTConnect platform to handle the onboarding, device management, and data integration with AWS. AVnet’s solution is often a darling at ST Technology Tours because it vastly simplifies the creation of IoT systems by handling some of the most complex development operations. Put simply, the demo is one of the best examples of how ST, Amazon Sidewalk, and a member of the ST Partner Program can come together to make a difference in the operations of a company trying to take part in the IoT revolution.
Why it matters?Interconnecting a myriad of small devices to each other and the Internet has always been the IoT dream. The challenge is that building a new infrastructure from scratch is expensive, and without massive adoption, it will never reach critical mass. Amazon Sidewalk solves this issue by utilizing existing Echo devices and other Bridges connected to a router. By simply leveraging existing installations, the network is already in place. And by enabling product makers and customers to use it for free, it significantly lowers the barrier to entry.
Additionally, Amazon Sidewalk handles a lot of the complexities associated with such a network, from security to over-the-air updates. That’s why Amazon instituted a qualification program. To protect all participants in this ecosystem, Amazon authorizes devices to connect to its network. It also explains the company’s certification program. By qualifying STM32 microcontrollers, Amazon ensures that its partners use trusted devices that will run the network stack reliably and implement security features according to strict standards.
The post Amazon Sidewalk: The first STM32-qualified devices are already making a difference. Check out this customer testimonial! appeared first on ELE Times.
let my intrusive thoughts get a little carried away with a dead computer
 | submitted by /u/Piggy_Royale [link] [comments] |




