Microelectronics world news
I love my teacher
 | submitted by /u/RequiemOfLigh [link] [comments] |
USB Hub made entirely of TH components
 | Didnt think it was a thing! Would have expected some mandatory SMT ICs [link] [comments] |
Wolfspeed adds VP of sales for EMEA
Passive RC circuit produces gain

Could a simple passive RC network without any transformers, inductors, switches, or non-linear components produce a voltage gain?
Wow the engineering world with your unique design: Design Ideas Submission Guide
Well, it’s not “free energy,” however, yes, and can even use the same value resistor and capacitor in a ladder network shown in Figure 1, although differing values also can be utilized.
 Figure 1 Passive RC circuit using resistors and capacitors of the same value in a ladder network.
Figure 1 Passive RC circuit using resistors and capacitors of the same value in a ladder network.
Of course, this isn’t of much use other than a curiosity, but it’s a fun circuit to build and play around with!
I built one with seven sections (Figure 2) using an R of 10 kΩ and a C of 0.1 µF, then plotted the results.

Figure 2 A seven-section RC ladder network with an R of 10 kΩ and C of 0.1 µF.
The Bode plot can be seen in Figure 3. As you can see, the gain remains around 0 dBv and behaves as a low-pass filter, then slowly rises to a peak of 1.07 dBv at 1 kHz before falling off.

Figure 3 Bode plot of the passive RC circuit showing low-pass filter behavior until a slow rise to a peak of 1.07 dBv at 1 kHz.
This agrees well with the simulation shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4 Circuit simulation of a passive RC circuit that closely matches the Bode plot shown in Figure 3.
If you swap the resistors and capacitors, the circuit behaves like a high-pass filter and produces a higher gain of 1.13 dBv at 26 Hz, as shown in Figure 5, and a simulation in Figure 6.

Figure 5 Bode plot of the passive RC circuit showing high-pass filter behavior.

Figure 6 Circuit simulation of a passive RC circuit that closely matches the Bode plot shown in Figure 5.
As noted by someone, this technique can be employed with an emitter-follower, which has a voltage gain less than unity to create an oscillator. However, that’s for another upcoming Design Idea (DI), which will also include a note on how a single unbiased JFET can produce a +dBv voltage gain!
Anyway, hopefully some folks find this interesting and have some fun!
Michael A Wyatt is a life member with IEEE and has continued to enjoy electronics ever since his childhood. Mike has a long career spanning Honeywell, Northrop Grumman, Insyte/ITT/Exelis/Harris, ViaSat, and retiring (semi) with Wyatt Labs. During his career, he accumulated 32 US Patents and, in the past, published a few EDN Articles, including Best Idea of the Year in 1989.
Related Content
- RC networks
- SPICE Course, Part 2: Time Constant Simulation
- Designing RC active filters with standard-component values
- A simple software lowpass filter suits embedded-system applications
The post Passive RC circuit produces gain appeared first on EDN.
Tower and Scintil announce availability of first heterogeneously integrated DWDM lasers for AI infrastructure
Build a practical 400 mA linear Li-ion charger with visible CC-CV behavior

Single-cell lithium-ion (Li-ion) chargers are widely used, yet many practical designs rely on highly integrated ICs that conceal their internal operation. The type of Li-ion charger outlined in this design is, somewhat surprisingly, not readily found in a general review of available internet and YouTube resources.
Wow the engineering world with your unique design: Design Ideas Submission Guide
The present circuit is practical, deployable, and firmly grounded in established circuit theory, and may offer a complementary perspective to prevailing practice, particularly for designers who value analytical transparency and first-principles reasoning. It operates from a 5 V supply, commonly found in 5 V/1 A smartphone chargers, delivers 400 mA of constant current (CC), then transitions to 4.217 V constant-voltage (CV) regulation, and has been built and tested using half of an LM324 quad operational amplifier.
The circuit, shown in Figure 1, performs reliably and is well-suited for bench chargers, embedded products, and instructional laboratories. This design emphasizes simplicity, component availability, and safe charging behavior while remaining easy to analyze and adapt.

Figure 1 Schematic of the dual-loop linear Li ion charger. The schematic shows the key nodes that are referenced and plotted in the LTSpice simulation. In practice, a 1N4007 diode for D2 also worked well.
The charger uses two independent control loops acting on a PNP pass transistor. An inner loop regulates charge current, while an outer loop regulates battery voltage. The voltage loop output also provides a convenient indicator of charging status.
CC loop operationA 1.25 V reference is divided using 115 kΩ and 10 kΩ resistors to produce a 0.10 V current reference. An LM324 section compares the 1.25 V reference to the drop across a 0.25 Ω sense resistor in series with the battery return. The op amp drives an NPN transistor, which sinks base current from the PNP pass device until the sense voltage equals the reference.
The resulting charge current is 0.4 A. This current regulation is independent of battery voltage, ensuring safe charging even from deeply discharged cells.
CV loop operationA second LM324 section monitors battery voltage through a 47.5 kΩ and 20 kΩ divider. When the divided voltage reaches 1.25 V, corresponding to 4.217 V at the battery terminals, the op amp reduces drive to the pass transistor, transitioning the charger into CV mode.
The voltage loop is intentionally compensated to be slower than the current loop, ensuring a smooth handover without oscillation or overshoot. As in my case, if a commercial 1.25-V reference, e.g., TLV431, is not available, a 2k/2k potential divider connected to the common LM431-2.5-V voltage reference works reasonably well. However, since it is an integral part of both control loops, extra care should be taken to stabilize the loops to prevent oscillations.
Loop stabilityThe changeover from CC to CV crossover can cause some ringing, as shown in the measurement of U2OUT shown in the DSO capture in Figure 2. This appears as both LEDs are dimly lit, showing rapid oscillations. There are two possible remedies. The first is to dampen the voltage loop by including a small capacitance of 33 pF to 500 pF in parallel with Rtop. The second is to dampen the current loop by adding a small RC time constant from the emitter to the collector of Q2, the pass transistor driver. In LTSpice, you can probe phase margin by injecting a small AC source at the summing point or by param sweeping and observing step responses.

Figure 2 Circuit construction and measurements. Inset (a) close-up of the breadboarded circuit showing the status indication LEDs. The photograph was taken when the cell voltage was 4.09 V, which is the threshold of the CC-CV crossover (see text). (b) shows the oscillation at the node U2OUT, which drives the LEDs and forms the pass transistor pre-driver signal. The image was captured on a Tektronix TDS2024C DSO.
Charge status indicationThe output of the voltage regulating amplifier doubles as a logic-level indicator of charging state. When the battery voltage is below the regulation threshold, the output drives a red LED indicating active charging. As the battery approaches full charge and current tapers, the output level changes and illuminates a green LED. This approach eliminates the need for an additional comparator while providing clear, real-time visual feedback.
Thermal and practical considerationsWith a deeply discharged cell at approximately 2.2 V, the PNP pass transistor must dissipate roughly 1.1 W at 400 mA. Off-the-shelf, low saturation voltage transistors such as the 2SB772 will work comfortably without a heat sink. In the constructed prototype, a modest copper area was sufficient for thermal management. Although in the built version a 5W rating is used for the sense resistor, it dissipates only 40 mW, allowing a 0.25 W rated component a more than adequate margin. All active components operate within their safe operating area when supplied from a regulated 5 V source.
Experimental verificationThe charger was assembled on a prototype board and tested with a single 18650 Li-ion cell. Startup into CC mode was immediate, followed by a smooth transition to CV operation at approximately 4.22 V. Charge current tapered naturally as expected.
Supplementary files:
- A video of the circuit in operation is shown here: https://youtube.com/shorts/oSzR4XQViFs
- LTSpice simulation (.asc) file: Li-ion-ocaya-LTSpice schematic.asc
The LTspice simulation models the Li-ion cell as an ideal capacitor C in series with a small ESR = 80 mΩ, charged from a constant current I = 0.4 A source; the terminal voltage is
![]() where the capacitive core obeys:
where the capacitive core obeys:
![]()
Over a finite interval ΔV and time Δt, the approximation C = I Δt/ΔV can be made, assuming that the current is reasonably constant. The current falls progressively in reality, imparting a non-linear character to the cell voltage transient. With the cell rising from 2.2 V to 4.217 V, the ESR contributes a small, essentially instantaneous step of = 0.4 × 0.08 = 0.032 V (32 mV), after which the slope is set by I/C. Thus, if the observed CC interval Δt for the ΔV ≈ (4.217 − 2.2) = 2.017 V rise is about 5250 s (≈ 1.46 h), then C ≈ (0.4 × 5250) / 2.017 ≈ 1040 F.
This is a first-order capacitor-plus-ESR approximation, with the caveat that real Li-ion cells have voltage–state-of-charge (SoC) and temperature dependencies that make C a state-dependent quantity rather than a fixed constant.
Figure 3 plots the LTSpice simulation values of the nodes and branches named in Figure 1. In Figure 3, the battery was assumed to be deeply discharged, denoted by a state of charge of 2.2 V.

Figure 3 LTspice simulation of the key nodes and currents in the circuit. The measurements on the actual circuit closely match these plots.
The simulation shows that it transited from CC to CV charging in approximately 1 hr 21 mins after the onset of charging. The charging current tapered off thereafter and dropped to zero. The circuit current dropped to 19 mA without the battery connected, and when the charging was completed. The measured voltage across the Li-ion was 4.21 V, with only the green LED fully on, with no flickering on either LED, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4 Photographs showing the current drawn by the circuit from a 5-V bench supply, and a multimeter showing a 4.21 V SoC of the Li-ion battery when charging is completed.
Compliant Li-ion chargingThis design demonstrates that a fully compliant Li-ion charging profile can be achieved using readily available analog components. It is suitable for real-world use while remaining accessible to analysis and modification. The circuit offers a practical alternative for engineers who require simplicity, transparency, and predictability in low-power Li-ion charging applications.
P.S.: Like many enthusiasts around the world, the designer lives in a region where access to electronics stores and new components is limited. The motivation for this circuit was robustness and realizability using parts salvaged from discarded equipment.
Professor Ocaya specializes in electronics and solid-state physics, which he teaches at the Qwaqwa Campus of the UFS. He is active in computing, mathematical methods, new techniques for device characterization, material science, and microcontroller-based instrument design. He holds a C3 rating from the National Research Foundation (NRF) of South Africa.
Related Content
- Circuit’s RMS output is linearly proportional to temperature over wide range
- A battery charger that does even more
- Building a Battery Charger with the CC/CV Method
- Lead-acid battery charger
The post Build a practical 400 mA linear Li-ion charger with visible CC-CV behavior appeared first on EDN.
IIIT Hyderabad’s Smart Approach To Sand Mining Enforcement, Incorporating AI in Trucks
‘Truck art’ or the hand-painted ‘Horn Ok Please’, ‘Use Dipper at Night’ and the ‘Buri nazar waale tera mooh kala’ are an integral part of Indian highways. These artistic expressions, which lighten up many a road journey, also find an extension in hand-painted registration plates. However, such unstandardised lettering can prove to be a challenge for automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) systems. Most commercial ANPR systems are designed for standardised license plates. ANPR systems play a crucial role in modern governance, helping authorities monitor traffic, enforce regulations, prevent illegal transport, and improve public safety. From toll booths to traffic violations, ANPR enables real-time vehicle tracking without manual checks.
A Unique Number Plate Problem
Hence, when the Telangana IT Department approached IIIT-H, seeking an ANPR solution for the Telangana Mineral Development Corporation (TGMDC), their requirement was very different from typical commercial use cases.TGMDC was on the lookout for a cost-effective, robust solution tailored to monitor sand mining trucks, primarily to curb illegal mining and transport. “Typical license plates are actually easy to detect,” explains Dr. Veera Ganesh Yalla, CEO of iHub-Data and Adjunct Faculty at IIIT-H. But in India, especially with trucks, plates are often hand-painted, inconsistent, and highly variable. “They might follow black lettering on a yellow background, but from vehicle to vehicle, their design, the style, everything is unique,” he says, making off-the-shelf solutions for their detection both ineffective and expensive.

Building Smart, Not From Scratch
Commercial systems are typically very expensive, with per-camera costs of licensing and maintenance running into tens of lakhs. Leveraging prior research from Prof. Ravikiran Sarvadevabhatla’s team at the Centre for Visual Information Technology, IIIT-H, where a prototype license plate recognition system had been developed, the iHub-Data team took the research forward into real-world deployment. “The lab tech was more like a research prototype, not really for scaling or translation. So we decided to take it and see what we could do,” Dr. Yalla recalls. The team studied the workflow, rebuilt and strengthened the handwritten character recognition component. What’s unique is that they integrated the analytics as a plug-in into an open-source platform. ”If anybody wants to plug in our license plate technology into their platform, they can do it without having to rewrite their entire platform from scratch,” he notes.
Real-life Deployment
Their solution, named Vahan Eye, was piloted at Chityal on the Vijayawada–Hyderabad highway, where the team installed cameras, laid cables, and deployed the system end-to-end. The deployment tracks trucks entering Telangana and cross-checks them against a whitelist of nearly 40,000 approved vehicles. Tweaked specially to suit the needs of TGMDC, the solution offers customised dashboards. Since September, the system has been running continuously. Despite challenges such as low lighting at night and festival-related obstructions such as garlands covering the number plates, the algorithm has proven robust and continues to improve with live data.

From PoC to Public Impact
Built by a lean team of fewer than five engineers and powered by modern deep learning models, Vahan Eye demonstrates how lab research can be translated into an affordable, field-ready public solution. “Our IP is that we really figured out how to solve this whole handwritten license plate character problem,” says Dr. Yalla. Currently, the team is working on customising the solution for the Police Department for automatic detection of traffic violations by 2-wheelers.
Dr. Yalla, who began his career in the video surveillance industry with classical machine learning solutions that used support vector machines, explains that with advances in deep learning, more powerful algorithms such as YOLO and RF-Detr are now being applied, leading to significantly improved performance and accuracy. As he puts it, the goal is clear: prove the technology works, make it accessible at a fraction of commercial costs, and enable scalable adoption across government departments.
The post IIIT Hyderabad’s Smart Approach To Sand Mining Enforcement, Incorporating AI in Trucks appeared first on ELE Times.
Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, Larsen & Toubro, and Micron Join the IDTA
The India Deep Tech Alliance (IDTA) announced that Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, Larsen & Toubro, and Micron Technology have joined the Alliance. These additions further strengthen IDTA’s cross-sector collaboration model, which brings together investors, corporates, and technology-enabling partners to mobilise capital, technical expertise, market access, and policy engagement for the advancement of Indian deep tech startups.
With the addition of these global and Indian industry leaders, IDTA now spans artificial intelligence, semiconductor equipment, memory, materials, infrastructure engineering, and power systems, creating an integrated platform to support investment, technology collaboration, talent development, and startup commercialisation. With the shared goal of accelerating the growth of India’s deep tech economy, IDTA Corporate Strategic Partners aim to leverage their expertise to provide strategic and technology counsel to other IDTA members and emerging startups. Strategic advisory and ecosystem collaborations may include:
- Manufacturing and scale-up guidance for lab-to-fab transitions and production readiness.
- Technical talks, training, and access to expert resources.
- Collaborative research discussions and ecosystem initiatives with startups, researchers, and industry.
- Private industry input to policy dialogues related to national priority technology sectors.
- Mentorship, network access, and co-development opportunities in concert with investors.
IDTA is an industry-led consortium formed to mobilise capital and company-building expertise to help India-domiciled deep tech startups scale globally. It was formed to expand private sector support for strategic technology sectors, complementing the Government of India’s Research, Development & Innovation (RDI) Scheme.
This latest membership expansion follows NVIDIA joining IDTA as a Founding Member and Strategic & Technical Advisor, underscoring the Alliance’s ambition to build globally relevant, India-anchored deep tech capabilities at scale. Since its founding in September 2025, IDTA has expanded to a commitment of more than $2.5B USD in venture funding to Indian deep tech startups over the next five years, including a dedicated $1B USD allocation to Indian AI startups to be invested over the next three years. IDTA venture capital members have deployed $110M USD into 50+ companies over the past six months.
“The entry of Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, L&T, and Micron marks a pivotal step in moving India’s deep tech ambition from intent to execution,” said Arun Kumar, India Managing Partner of Celesta Capital and Chair of IDTA. “Together with NVIDIA’s role as a founding member and strategic advisor, this coalition brings unmatched depth across semiconductors, advanced manufacturing, infrastructure, and systems engineering. IDTA is designed to align capital, technology, and policy so that India can emerge not just as a participant, but as a trusted global hub for next-generation technologies.”
Quotes from New IDTA Corporate Strategic Partners:
Om Nalamasu, CTO, Applied Materials, said, “Applied Materials has a long history of working across industry, startups, academia, and research institutions to advance foundational technologies. As a materials engineering leader, we believe long‑term progress comes from sustained, ecosystem‑level collaboration. Through this alliance, we look forward to contributing our deep technology expertise to help build resilient ecosystems for India and the world.’’
Mr. Amar Kaul, Global CEO & Managing Director, CG Power, said, “India’s deep tech journey is entering a decisive phase, one where execution, industrial capability, and long-term partnerships will determine global relevance. CG Power’s participation in the India Deep Tech Alliance reflects our conviction that nation-building today requires strong, technology-led manufacturing ecosystems. Through IDTA, we look forward to contributing our expertise in industrial, power systems and semiconductors to create resilient and future-ready value chains that reinforce India’s position as a trusted global technology hub.”
Kevin Chen, Head of Lam Capital & Corporate Development, Lam Research, said: “Semiconductor manufacturing excellence depends on deep collaboration across equipment, materials, process technology, and talent. We look forward to engaging with IDTA to help Indian innovators navigate technology roadmaps, manufacturability, and global ecosystem linkages that accelerate from lab to fab.”
Prashant Chiranjive Jain, Head Corporate Centre, Larsen & Toubro, said: “The India Deep Tech Alliance represents a pivotal shift toward indigenous innovation. By synergising L&T’s engineering heritage with advanced capabilities in AI, design engineering, and quantum systems, we are committed to building a robust deep-tech ecosystem. We look forward to delivering cutting-edge solutions that position India as a global leader in the next generation of technology.”
Anand Ramamoorthy, Managing Director, Micron India, said: “Micron’s decision to join the India Deep Tech Alliance reflects our commitment to ecosystem-led collaboration to propel a vital economic engine for India. Micron’s technology and innovation expertise will play a vital role in helping advance globally competitive deep tech from India while aligning with IDTA’s support for the national RDI agenda and its focus on translating research into market impact.”
The post Applied Materials, CG Power, Lam Research, Larsen & Toubro, and Micron Join the IDTA appeared first on ELE Times.
I made a digital clock with DIY etched PCB
 | I also wrote about it here https://boxart.lt/en/blog/diy_digital_clock [link] [comments] |
ams OSRAM and Meizhi settle patent disputes over LEDs used in Spider Farmer luminaires
SDI buys PRP Optoelectronics for £9.3m
Six critical trends reshaping 3D IC design in 2026

AI compute is scaling at ~1.35× per year, nearly twice the pace of transistor scaling. Thus, the semiconductor industry has reached a hard inflection point: if we can’t scale down, we must scale up. Increasingly, engineering teams are turning to 3D ICs to keep pace with the ascent of next-gen AI scaling.
However, designing in three-dimensions also exacerbates system complexity, leaving IC and package designers with a pressing question: how do you explore millions of design considerations and still optimize and validate system performance within schedule constraints?
This article examines six trends that will help design teams overcome this challenge and help them reshape the future of 3D IC design in 2026.
Trend 1: STCO becomes crucial for multi-chiplet integration at AI scales
Advanced packages already exceed tens of millions of pins, with trajectories pointing toward hundreds of millions. At this scale, no design teams can fully comprehend the system through traditional spreadsheets or point tools. Design complexity has fundamentally shifted to system-level orchestration.
This is where system-technology co-optimization (STCO) becomes critical by incorporating packaging architectures, die-to-die interconnects, power delivery networks, thermal paths, and mechanical reliability into a unified optimization loop.

Figure 1 STCO unifies packaging architectures, die-to-die interconnects, power delivery networks, thermal paths, and mechanical reliability into a single optimization loop. Source: Siemens EDA
A core benefit is the industry’s long-awaited “shift-left” for 3D ICs: Predictive multiphysics modeling allows teams to assess performance, power, thermal headroom, and mechanical stress concurrently and address architectural risks.
To enable true STCO, EDA toolchains must evolve from siloed analysis into integrated system platforms that create a unified 3D digital twin with shared data models, giving all stakeholders a persistent, system-level view and ensuring cross-domain optimization from a single, consistent dataset.
As chiplet-based architectures scale, STCO will become a foundational requirement for achieving performance, yield, and reliability targets in next-generation AI and high-performance computing systems.
Trend 2: Co-packaged optics reshape AI system architectures
As AI clusters push beyond 100 Tb/s per node, the gap between what silicon can generate and what traditional copper interconnects can deliver is widening fast. Even with SerDes continuing to scale, copper links are approaching fundamental limits in bandwidth density and energy efficiency, turning interconnect power into a major system bottleneck.
With global AI data center power demand projected to rise 50% by 2027, efficiency gains have become non-negotiable. This pressure is accelerating momentum behind co-packaged optics (CPO). By placing optical engines directly adjacent to switch ASICs, accelerators, and chiplets, CPO collapses electrical trace lengths from inches to millimeters, dramatically reducing signal loss while improving bandwidth density, latency, and power efficiency.

Figure 2 CPO reduces electrical trace lengths from inches to millimeters to significantly lower signal loss. Source: Siemens EDA
Nvidia reports that moving from pluggable transceivers to CPO in 1.6T networks can reduce link power from roughly 30 W to 9 W per port. Industry forecasts project over 10 million 3.2T CPO ports by 2029, signaling a shift from early pilots to volume deployment. However, this transition introduces new design challenges.
Photonic ICs are highly temperature-sensitive, while 3D CPO integration adds hybrid bonding interfaces, die thinning, and vertical heat flow that create complex thermo-mechanical interactions. Thermal gradients can induce wavelength drift, alignment errors, and long-term reliability risks—making thermal-optical co-design and multiphysics analysis essential for production-scale CPO deployment.
Trend 3: Advanced packaging innovations drive integration scale-out
New power delivery architectures and vertical integration schemes continue to emerge. As thermal-compressed bonds reach their integration limits, hybrid bonds will drive the 3D interconnect to 1 µm and below. Additionally, AI and high-performance computing (HPC) suppliers are considering wafer- and panel-level architectures to place more computing closer together, and foundries are pursuing more modular wafer-scale strategies.
Material innovation is also reshaping system integration. Glass substrates are gaining traction for large-area packaging and high-frequency AI and 6G applications, supporting more reliable signaling at higher data rates while reducing package warpage by nearly 50% in large substrates.
To adapt to this pace of change, an open and scalable workflow is critical to aligning new application requirements with manufacturability, yield, and cost. So, EDA tools must support rapid design-space exploration, early multiphysics modeling, and AI-assisted optimization to navigate the exponentially expanding solution space.
Trend 4: Novel thermal solutions rise to meet AI power density challenges
Power densities in leading-edge 3D ICs have already been compared to those at the surface of the sun. With multiple chiplets stacked in extreme proximity, 3D IC power densities create intense localized hotspots and trap heat in tiers far from the heat sink. This vertical thermal confinement is pushing conventional top-down air and cold-plate cooling approaches beyond their practical limits.
To address this challenge, microfluidic cooling architectures are being heavily researched and gaining early pilot traction. By etching micron-scale channels directly into silicon dies or interposers, engineers can route coolant within tens of micrometers of active transistors, enabling localized heat extraction and significantly shortening thermal conduction paths.
At the package interface, thermal interface materials (TIM) remain one of the dominant thermal bottlenecks. TIM1—located between the die and heat spreader—is particularly critical due to its proximity to active silicon. An effective TIM must minimize thermal resistance while maintaining mechanical compliance under thermal cycling and package-induced stress.
Among near-term solutions, indium foils have emerged as leading candidates for high-performance TIM1 applications. Researchers are also exploring advanced alternatives, including phase-change materials, graphene and carbon nanotube composites, silver-filled thermal gels, and liquid metals. Some experimental approaches aim to reduce or bypass conventional TIM layers altogether by integrating cooling structures directly onto the die surface.
Ultimately, ensuring thermal, power, and mechanical reliability is an inherently interdisciplinary challenge—one that no single innovation in chip architecture, materials, or cooling design can solve in isolation. By unifying multiphysics analysis, thermal-driven floorplanning, and system-aware design within a single digital thread, Siemens Innovator3D IC and Calibre 3DThermal enable engineers to establish reliability early on the design process, evaluate trade-offs earlier, and converge faster on manufacturable, high-performance 3D IC designs.

Figure 3 Thermal solutions for 3D ICs allow engineers to evaluate trade-offs early in the design process. Source: Siemens EDA
Trend 5: AI accelerates 3D IC designs for AI
The semiconductor industry needs more than one million additional skilled workers by 2030. There simply aren’t enough domain experts to balance signal integrity, power integrity, thermal effects, and mechanical stress across complex 3D ICs.
AI offers a practical path to scale scarce engineering expertise and close the productivity gap. One high-impact application is AI-driven, design-space exploration. Modern 3D IC architectures involve thousands to millions of tightly coupled variables, spanning die partitioning, material stacks, floorplanning, interconnect topology, and power delivery design.
Machine learning and reinforcement learning techniques accelerate exploration by rapidly predicting outcomes, learning from prior iterations, and uncovering non-obvious trade-offs that deliver measurable performance, power, and reliability gains.
Another critical application is automated power-thermal co-analysis. In 3D ICs, power dissipation directly raises temperature, while temperature feeds back into leakage and dynamic power behavior. Agentic AI and ML techniques improve both accuracy and turnaround time by automating complex modeling steps.
Predictive characterization can infer cell behavior at new temperature corners, while intelligent leakage modeling extracts temperature-dependent behavior directly from data, reducing manual calibration effort and improving model fidelity.
Over the past several years, Siemens EDA has embedded industrial-grade AI directly into 3D IC design flows, from verification and multiphysics analysis to design exploration, guided by five foundational principles:
- Accuracy: Conforming to strict physical laws
- Verifiability: Transparent decision-making
- Robustness: Consistent performance with new data
- Generalizability: Applying insights across new problems
- Usability: Seamless integration with existing CAD/CAE tools
Trend 6: Integrated multiphysics workflow sets new standards for 3D IC system performance
Thermal, mechanical, and electrical effects are no longer secondary concerns that can be checked after layout. A chiplet may meet specifications in isolation yet may suffer degraded reliability when exposed to the actual thermal gradients, stress fields, power-delivery impedance, and IR-drop profiles inside a 3D stack.
This reality is driving a clear shift left in multiphysics analysis. These effects must be considered as part of early architecture decisions, chiplet partitioning, RTL modeling, and floorplanning—when the most impactful trade-offs are still on the table.
To make this practical, the industry needs standardized “multiphysics Liberty files” that capture temperature- and stress-dependent behavior of chiplet blocks. With this information available upfront, designers can verify whether a chiplet will remain within safe operating limits under realistic thermal and mechanical conditions.
Just as important, multiphysics evaluation cannot be a one-time checkpoint. 3D IC design is highly iterative, and every change—to layout, interfaces, materials, or stack configuration—can subtly reshape thermal paths, stress distributions, and electrical parasitics. Without continuous re-validation, risk accumulates quietly until it shows up as yield loss or reliability failures.
Integrated multiphysics platforms help teams stay ahead of this complexity by anchoring analysis to a shared, authoritative representation of the full 3D assembly. Working from a single source of truth allows teams to iterate confidently, uncover risks earlier, and validate decisions consistently across the entire stack.
The tools of the trade
Success in this new era requires more than a collection of isolated point tools. Design teams need a unified, end-to-end flow that brings together architecture exploration, multiphysics analysis, and cross-domain optimization in a single platform.
3D IC tools deliver exactly this integrated approach, tearing down the traditional walls between IC design, advanced packaging, and system-level validation. By giving design teams a shared source of truth and enabling them to tackle critical challenges earlier in the design cycle, these tools help engineers close on designs faster, explore more ambitious architectures, and ultimately build the silicon that will power the next generation of AI systems.
 Kevin Rinebold is technology manager for 3D IC and heterogeneous packaging solutions at Siemens EDA. He has 34 years of experience in defining, developing, and supporting advanced packaging and system planning solutions for the semiconductor and systems markets. Prior to joining Siemens EDA, Kevin was product manager for IC packaging and co-design products at Cadence.
Kevin Rinebold is technology manager for 3D IC and heterogeneous packaging solutions at Siemens EDA. He has 34 years of experience in defining, developing, and supporting advanced packaging and system planning solutions for the semiconductor and systems markets. Prior to joining Siemens EDA, Kevin was product manager for IC packaging and co-design products at Cadence.
Related Content
- Putting 3D IC to work for you
- Making your architecture ready for 3D IC
- The multiphysics challenges of 3D IC designs
- Mastering multi-physics effects in 3D IC design
- Advanced IC Packaging: The Roadmap to 3D IC Semiconductor Scaling
The post Six critical trends reshaping 3D IC design in 2026 appeared first on EDN.
Manufacturing Breakthroughs in Chip Packaging Are Powering AI’s Future
Courtesy: Lam Research
With all the attention being given to AI, it’s easy to overlook some of the core technologies enabling its capabilities. Sure, a lot more people have now heard about NPUs, GPUs and the businesses that make them, but what about the companies that enable these cutting-edge AI accelerators to be manufactured?
The Complexity of Modern Chipmaking
While most people may not realise it, chip manufacturing is incredibly challenging and requires the level of scientific breakthroughs that have powered humanity’s most advanced achievements. I mean, we’re talking about bending the laws of physics to build components that are a thousand times smaller than a grain of sand. Oh, and doing so millions of times over at incredibly high levels of quality and consistency. Plus, with the extra demands that GenAI workloads are putting on today’s latest chips, the challenges are getting even tougher.
That’s why companies providing the equipment and technologies that enable the manufacturing of these advanced chips play an essential role in driving the advanced AI capabilities we are all starting to experience.
Without their work to overcome technical challenges like the need for exascale computing, addressing the “memory wall” that can slow down AI accelerators, increasing power efficiency, and other issues that are necessary to maintain the Moore’s Law-like advances we’ve seen in these chips, the state of AI would not be where it is today. In particular, organisations like Lam Research, which build extremely complex, sophisticated machines that help process the raw silicon wafers that eventually become today’s most powerful semiconductor chips, play a big, though little-understood, part in big tech advancements like AI.
Building Next-Generation AI Chips Through Heterogeneous Integration
Lam Research makes a wide array of equipment that performs multiple tasks in the highly precise, extremely complex, and long (often 30 days or more) process of creating a modern chip. But in the era of AI accelerators, it turns out even the most sophisticated individual chip isn’t enough.
Instead, the latest GPUs and other advanced processors are being assembled through a process called heterogeneous integration, which combines multiple independent elements, known as “chiplets,” into even more sophisticated pseudo-SOCs, or Systems on Chip (advanced multi-chip packages that mimic some characteristics of an SOC). Commonly referred to as advanced packaging, the technology that enables the creation of these pseudo-SOCs requires extremely sophisticated semiconductor manufacturing.
Extraordinarily precise component stacking, chip-to-chip connections, and other key technologies allow these chips to integrate multiple independent processing elements, separate connectivity elements, memory, and more. The ultimate goal is to create the most powerful and capable multi-chip package they can in the most effective and efficient space and power envelopes possible.
Advanced Packaging Techniques
As with individual wafer processing, there are often multiple steps and multiple technologies (and approaches) involved with chip packaging. Some entail direct side-by-side connections between various chiplets and other elements, while others use various forms of stacking technology where different pieces sit on top of one another. In all cases, a critical part of the packaging process involves creating the paths through which the connections between the various elements are made. Sometimes those paths are created through film layers that act as a type of “glue” between the elements, while in other situations, it may involve creating millions of tiny holes that are filled with a metal-like material that provides something akin to a physical bridge between the layers.
In the case of Lam Research, the company has developed machines for each of those core packaging technologies. For physical bridging types—which are called through silicon vias or TSVs—Lam offers products in their Syndion, Striker ALD, and SABRE 3D lines. Each performs different parts of the process, including etching for creating the holes, deposition and filling for both lining and then injecting the new material into the holes, and then various cleaning processes along the way.
Semiconductor Manufacturing Innovations Enable AI Progress
Though little understood, the advancements in AI acceleration that have been achieved to date are strongly tied back to the manufacturing technologies that enabled them to be built. Integrating things like High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) directly beside GPU cores, for example, has had a huge impact on the performance, scale and efficiency of the latest AI accelerators, and that, in turn, is driving the impressive advancements we’ve seen in Large Language Models (LLMs) and other AI applications.
Looking forward, it’s going to be continued advancements in 3D packaging—along the lines of what Lam Research is doing with their new VECTOR TEOS 3D tool—that allow those advancements to continue. They may not be easy to see, understand, or appreciate, but semiconductor manufacturing technologies play an enormously important role in moving the tech industry and society forward.
The post Manufacturing Breakthroughs in Chip Packaging Are Powering AI’s Future appeared first on ELE Times.
Perusing a LED-based gel nail polish UV lamp

This engineer doesn’t use nail polish, but his wife does. And he deals with plenty of PCBs. What do these things have in common? Read on.
Speaking of LEDs that lose their original intensity over time and use…
In the fall of 2020, after accepting that due to the COVID pandemic she wasn’t going to be getting back inside a nail salon any time soon, my wife invested in a UV lamp so she could do her own gel polish-based nails at home. While the terminology I just used in the prior sentence, not to mention the writeup title that preceded it, might be “old news” to at least some of you, others (like me, at first) might be confused. Here goes:
Gel detailsFirst off, what is gel nail polish, both in an absolute sense and relative to its traditional counterpart? Here’s manufacturer OPI’s take:
A gel manicure is a coat of colored gel that looks deceptively similar to nail polish. It’s a thin brush-on formula, designed for high performance and a glossier finish than regular nail polish…An OPI GelColor manicure [also] lasts for up to 3 weeks…The primary difference between gel nails and a regular manicure is curing. Between each coat, you cure the color and set the gel nail polish by putting your nails under a special light.
That “special light” is a UV lamp. Initially, they were constructed using fluorescent tubes. But nowadays, mirroring the broader trend, they increasingly use LEDs instead. The one my wife first bought is Bolasen’s SunX Plus, a “Professional True 80W Salon Grade LED Nail Dryer for Gel Polish.” The link to it on Amazon’s main site now auto-forwards to a more recent battery-operated model (this one’s AC-powered), but I found a still-live product page copy on Amazon’s South Africa site (believe it or not). Here’s the associated stock artwork:

I’m not sure I want to know what the “no black hands” phrase references…




The black base shown in the stock images is missing in action; my wife found that foregoing the bottom plate expanded the lamp’s extremity-insertion gap spacing, thereby easing use. More generally, she’s now replaced this initial UV lamp with a newer successor; the original device’s intensity apparently faded over time, eventually taking excessively long to work its drying magic.
Polymer processingSpeaking of drying (or if you prefer, curing), what’s so special about UV light? Over to a blog post at the Manicurist website for an explanation:
Whether LED or UV, these lamps emit ultraviolet (UV) rays that trigger a chemical reaction called “polymerization”. Under UV exposure, the molecules in the polish bond together to form a solid and durable film known as a “polymer network”.
UV curing is more broadly used in a variety of applications and industries, as Wikipedia notes:
UV curing (ultraviolet curing) is the process by which ultraviolet light initiates a photochemical reaction that generates a crosslinked network of polymers through radical polymerization or cationic polymerization. UV curing is adaptable to printing, coating, decorating, stereolithography, and in the assembly of a variety of products and materials. UV curing is a low-temperature, high speed, and solventless process as curing occurs via polymerization. Originally introduced in the 1960s, this technology has streamlined and increased automation in many industries in the manufacturing sector.
More generally, electrical engineers out there will likely be particularly interested, for example, in UV light’s key role in the photolithography process used to make printed circuit boards!
So why, if this is a UV lamp that’s supposedly emitting light beyond the visible spectrum, is its output discernible by the human visual system (along with my smartphone’s camera)?

(cool photo, eh?)
Part of the answer may be that the LEDs in the design aren’t true UV at all, but instead leverage the lower-cost alternative referred to as near-UV. Part of it may be that the output spectral plot is sufficiently broad to still-noticeably “leak” into the violet portion of the visible range. And part of it may be that, to reassure users that the device is “on” (thereby preventing lengthy periods of peering at “pure” UV light, with likely retinal-damage consequences), the LED manufacturer added a phosphor layer to additionally generate a visible light output. Hold that thought.
Power spec uncertaintyLast (but definitely not least), before diving in, what’s with that “80W” output claim? The device actually supports two different power output modes, 80W and “low-heat” 55W, user-selectable via one of the four topside switches. When I initially plugged the lamp in without the LEDs illuminated, my Kill A Watt electricity usage meter measured 1W of power consumption:

Switch the LEDs on, in low-output mode, and I got 12W:

And in “high” mode? 23W:

12W ≠ 55W. And 23W ≠ 80W. So, what gives? At first, I wasn’t confident that my Kill A Watt was measuring power consumption correctly. But then I looked at the “wall part” that powers the lamp (in the first image of the sequence that follows, as with subsequent images in this post, accompanied by a 0.75″, i.e., 19.1 mm diameter U.S. penny for size comparison purposes):








Let’s zoom in on that last one:

Unless my math’s totally whacked, 24V times 1.5A equals 36W, not 80W, far from higher than that (to account for consumption inefficiency). So again, what gives? Was Bolasen’s marketing team being flat-out deceiving? Maybe: my cynical side certainly resonates with that conclusion.
But at the end of the day, I’ve decided to give the company the benefit of the doubt and conclude that, just as LED light bulb manufacturers do in spec’ing their devices vs incandescent precursors, Bolasen is using fluorescent UV tube intensity equivalents in rating its LED-based UV device. Online references I’ve found equate the lumens brightness rating of a 20-plus watt LED to that of an 80W fluorescent tube. Granted, that’s for visible light, but perhaps the comparison holds in the ultraviolet band as well…regardless, let me know your thoughts in the comments!
Diving insideMy background-info pontification now concluded (thank goodness, right?), let’s get to tearing down, shall we? Here’s our patient:



Raise the transport handle!


FCC-certified? Really? Call me cynical (again):


The specs say 42 total “beads” (LEDs). That matches my count in the photo that follows:

Look closely and you’ll also see, among other things, five screw heads, which I’m wagering are our pathway inside, along with an array of passive ventilation holes. Here’s the 12-LED cluster at the top (when the device is in its normal operating orientation, that is):

and the cluster-of-six at the back:

Along each side are four more clusters-of-three, such as this one:

The ones at either end, i.e., straddling the lamp’s opening in its normal orientation, are special. The one at the right side (again, in normal orientation) also includes an IR (infrared) transmitter:

while the other additionally incorporates an IR receiver:

This, dear readers, is how the lamp implements the following function (quoting the original broken English on the Amazon product page):
Use the auto-sensor, it would turn on or off automatically when you put hand/foot in or out.

Insert your appendage (hand or foot, to be precise), and its presence breaks the infrared beam that normally traverses the transmitter-to-receiver gap in an uninterrupted fashion. Voila!
OK, let’s get those five screws outta there:

and with only a bit of remaining prying to do:

we’re in!

Although this original lamp may now be too slow to operate for my wife to tolerate, it still works. I’d therefore prefer to put it back together still fully functional and then donate it for someone else to use…or maybe I’ll keep it and use it to cure resin or…hey…make my own PCBs! Regardless, I’m keeping the internal wiring intact. Don’t worry, we’ll still be able to see its guts a’plenty. Let’s start with the inside of the top half of the chassis:

The power connector pops right out of its usual location:


Now for that PCB in the center:

At left is the two-wire connection that powers the LED array. At right is the power input. And the four-wire harness coming out the bottom feeds (and is fed by) the IR transmitter and receiver. The 14-lead IC PCB-labeled U1 in the upper right corner is unmarked, alas, but is presumably the system “brains”. And at lower left is a P60NF03 n-channel MOSFET likely employed for both LED power switching and variable voltage generation (for both “80W” and “55W” modes) purposes.
Flip the PCB over:
and what now emerges into view is the multi-digit eight-segment display along with the four-switch control cluster.
Beating the heatNow for the inside of the other (lower) half. Wow, look at all those thermal-dissipating metal plates (operating in conjunction with the earlier-mentioned passive ventilation array)!

First off, here are the connections to the IR transmitter:
and IR receiver:
Now for the LED power distribution network. The two-wire harness coming from the PCB first routes to the three-LED plate that’s in the lower left, just below the six-LED plate, in the earlier overview photo:
From there it splits in two directions. The “upper” (for lack of a better word) span first routes to the aforementioned six-LED plate:
Then to a series of three mid-span three-LED plates:
And finally, to a three-LED plate at the end in proximity to the IR receiver:
The “lower” span also then cycles through its own set of three three-LED plates, the last of them alongside the IR transmitter, and terminates at the 12-LED cluster:
Dual-frequency LEDsThese one more aspect to this design that I want to make sure I highlight, which keen-eyed readers may have already noticed. Check out this closeup of one of the LED “beads”:
The yellow tint is reflective of the thin phosphor layer applied to the inside of the “bead” dome to assist in generating augmented visible light for user-operation-stupidity-prevention purposes. But peer underneath it…are there two die in there? Indeed, there are. I’d originally thought I was instead just looking at the LED’s leadframe structure:

but, in the comments to a teardown video of a different UV lamp by “Big Clive” (whose always-excellent work I’ve showcased before):
was an enlightening insight from “restorer19”:
I have the 6-led UV panel you did a video on years ago, from the same brand, and it likely uses the same LEDs – I’ve sacrificed once of the LED chips and an additional one of the phosphor domes/blobs. It appears to have two LED dies on each chip, one bonded with two wires to each end of the module, and one bonded directly downward with only one bond wire leading to it. The 2-wire die (presumably 405nm) lights a visible purple at a lower voltage (just under 3V), and the 1-wire die takes greater voltage to light up. The 1-wire die looks identical to the large one in a 365-nm LED flashlight I recently bought – the surface of the die itself seems to phosphoresce in white, and any color from the semiconductor itself is invisible. Looking at an individual LED module under magnification while powered at about 3.2V makes the two different dies obvious without being too bright to look at.
“Big Clive” had done an earlier teardown of a more elementary UV lamp containing these same dual-die LEDs (this video is, I believe, the same one that “restorer19” was referring to):
wherein he’d conjectured (at least as I interpreted his comments) that the white color, i.e. full-visible-spectrum-when-illuminated die inside might purely be for “powered on” visual user-reassurance purposes. However, a Google search using the phrase “dual die UV LED” produced an interesting (at least to me) AI Overview response:
A dual die UV LED refers to a UV-LED light source, often in nail lamps or curing devices, that combines two different LED chips (dies), usually at wavelengths like 365nm and 395nm, to effectively cure a wider range of UV-sensitive gels, including both traditional UV gels and newer LED-only gels, offering faster, more complete curing than single-wavelength lamps. These lamps are popular in nail salons for their versatility, providing professional results by ensuring all gel types, from base coats to builder gels, are fully hardened.
Key Features & Benefits
- Dual Wavelength: Uses two distinct UV wavelengths (e.g., 365nm for deeper penetration, 395nm for surface cure) for comprehensive curing.
- Broad Compatibility: Cures all gel types (UV, LED, builder, hard gels).
- Faster Curing: Significantly reduces curing time compared to older UV-only lamps.
- User-Friendly: Often includes auto-sensors, timers (15, 30, 60, 90s), and removable bases for pedicures.
- Professional Quality: Common in salons for consistent, high-quality results.
How it Works
Instead of a single type of UV emitter, a dual die lamp integrates two different LED chips within the same unit, each emitting at a specific UV wavelength, ensuring that various photoinitiators in different gels react and harden the product effectively.
In Summary: A “dual die” UV LED lamp is a modern, efficient solution for curing gel nails, combining multiple LED technologies for faster, more reliable results across the spectrum of gel products.
And, in finalizing this write-up just now prior to submitting it to Aalyia, I revisited the previously mentioned Amazon product page and noticed the following (bolded emphasis is mine):
Specifications:
- Timer: 10s/30s/60s/99s low heat mode
- Wattage: 80w(Max)
- Display: Digital Time Display
- Lamp beads: 42pcs Dual Dual Light Source
- Spectrum: 365nm+405nm
- Lifespan: 50,000H
- Voltage: 100V-240V 50Hz/60Hz
- Output: DC12V
- Lamp Size:235*223*102mm
- Ideal for: All nail gels
So, I’m guessing we now have our answer! In retrospect, I also realized that one of the earlier “stock” graphics referenced a “dual light source” and included an LED close-up revealing the dual die internal structure. That said, I’ll wrap up for now and await your thoughts in the comments!
—Brian Dipert is the Principal at Sierra Media and a former technical editor at EDN Magazine, where he still regularly contributes as a freelancer.
Related Content
- UV-C LED achieves double the efficiency
- Considerations in the selection of UV LEDs for germicidal applications
- Teardown: What caused these CFL bulbs to fail?
- LED lighting teardowns: Five lighting designs that illuminate the future of lighting
The post Perusing a LED-based gel nail polish UV lamp appeared first on EDN.
SemiQ partners with distributor NAC Semi across North America
Powering the Future: How High-Voltage MLCCs Drive Efficiency in Modern Electronics
Courtesy: Murata Electronics
Power electronics is undergoing a profound transformation. Devices are now expected to operate faster, become smaller, and achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency.
To meet these demands, wide-bandgap (WBG) semiconductors, such as silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN), are increasingly adopted over silicon-based devices. These advanced materials enable significantly higher switching frequencies and increased voltage levels. This reduces system size and boosts power density.
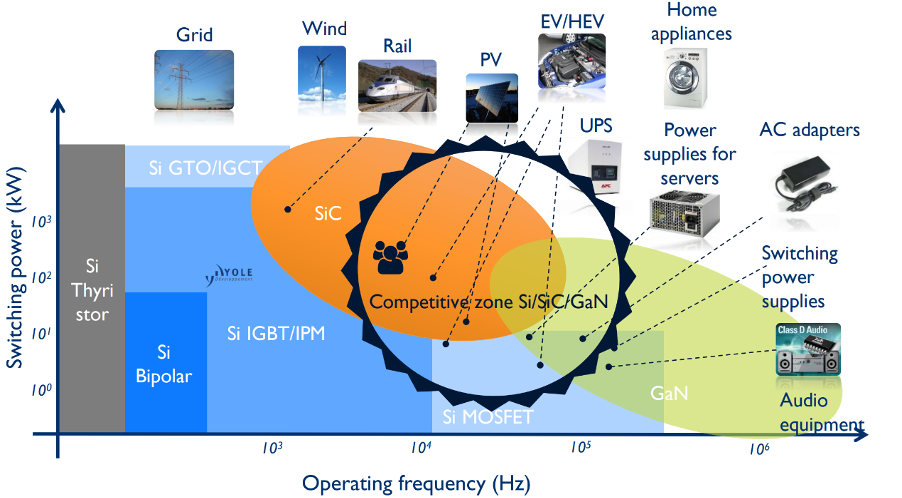 Figure 1: The typical operating frequency and switching power of various semiconductor materials (Source: Yole Group) [see MURA200 for original images]At the same time, the rapid electrification of transport, industry, and energy infrastructure is driving an unprecedented expansion in power conversion applications. This evolution exposes designers to a far wider spectrum of operating conditions.
Figure 1: The typical operating frequency and switching power of various semiconductor materials (Source: Yole Group) [see MURA200 for original images]At the same time, the rapid electrification of transport, industry, and energy infrastructure is driving an unprecedented expansion in power conversion applications. This evolution exposes designers to a far wider spectrum of operating conditions.
Critical Challenges in High-Voltage Systems
These evolving expectations place significant stress not only on active devices but also on the passive components integral to these systems. Higher switching speeds, for instance, lead to sharp voltage transients and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Increased voltages impose strict demands on insulation and overall reliability.
Multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) play a vital role in suppressing high-frequency noise, absorbing transient spikes, and protecting semiconductor devices from overvoltage stress. Therefore, the advancement of MLCCs must align with the increased performance standards required by WBG devices, necessitating enhancements in dielectric compositions and creative packaging approaches.
Taming Transient Spikes
Snubber capacitors are essential in power electronics, especially where high-speed switching induces voltage overshoot and ringing. This is particularly critical during the turn-off transitions of MOSFETs or IGBTs. This issue is heightened in SiC and GaN power semiconductors, which exhibit greater surge voltages compared to traditional silicon IGBTs.
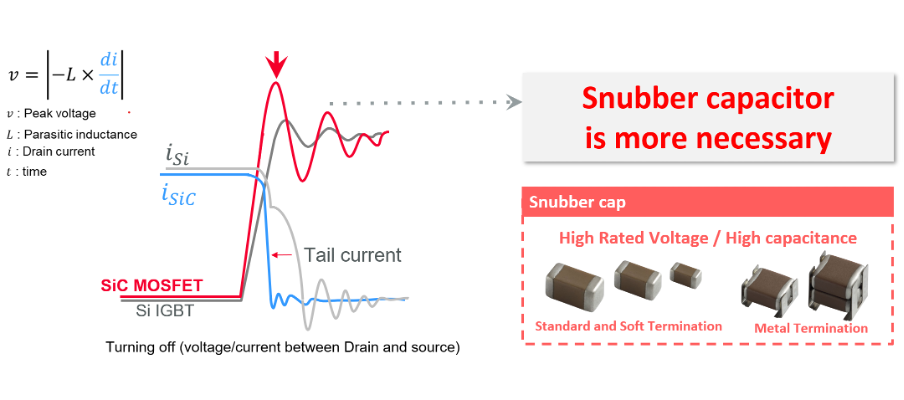 Figure 2: SiC MOSFETs exhibit a higher surge voltage than traditional Si IGBTs (Source: Murata) [see MURA200 for original images]A well-matched snubber capacitor effectively absorbs transient energy, suppresses peak voltages, and damps oscillations. Murata’s metal-termination MLCCs, such as the KC3 and KC9 series, are optimised for use in SiC-based circuits.
Figure 2: SiC MOSFETs exhibit a higher surge voltage than traditional Si IGBTs (Source: Murata) [see MURA200 for original images]A well-matched snubber capacitor effectively absorbs transient energy, suppresses peak voltages, and damps oscillations. Murata’s metal-termination MLCCs, such as the KC3 and KC9 series, are optimised for use in SiC-based circuits.
The post Powering the Future: How High-Voltage MLCCs Drive Efficiency in Modern Electronics appeared first on ELE Times.
Redefining the human experience with intelligent computing
Courtesy: Qualcomm
Enabling the devices, vehicles and machines that define tomorrow’s world.
What you should know:
- The next UI centres around you, with your AI agent seeing, hearing and acting on your behalf.
- We’re scaling AI to redefine the human experience—powering next-gen wearables and personal AI devices, and driving intelligence into robots, cars and smart homes.
- Our technologies enable extraordinary experiences that consumers and businesses depend on every day—bringing personal and physical AI everywhere.
Think of AI like coffee. You don’t walk into a café and ask for “a beverage brewed from roasted beans” — that’s assumed. You order the experience. Latte, half-pump vanilla, extra shot against a soundtrack of acoustic 90s alternative. The perfect mix to fuel your day, making you more productive, more creative, more you. AI works the same way. It’s a given, not a feature — the foundation of every experience, making each truly yours.
You are at the centre with your agent as your intelligent teammate. This is the next UI. Forget the seemingly endless scrolling and tedious tapping to complete one.single.thing only to do it again.and.again. Instead, your agent moves with you, learns from you and anticipates your needs. And thanks to AI processing on the device, it remains private, contextual and always-on. Like your favourite barista, who knows your order as soon as you walk in, including your (secret) treat every Friday.
We’re leading the charge toward the future of intelligent computing — reimagining possibilities for not only consumers, but also enterprises and industries worldwide. We’re scaling intelligence from edge to cloud, bringing AI everywhere. Our Snapdragon and Qualcomm Dragonwing platforms enable the devices, vehicles and machines that define tomorrow’s world — and redefine the human experience.
And again, I can’t say this enough, it’s all about you. Or more precisely, an “ecosystem of you” where your agent can see, hear and act on your behalf across an emerging category of AI-first intelligent wearables, along with smartphones and AI PCs.
The newest entrant in our Snapdragon X Series Compute Platforms, Snapdragon X2 Plus, delivers agentic AI experiences to aspiring creators, professionals and everyday users — broadening the already-growing Windows PC community.
Your home, too, is transforming into a responsive, intuitive environment. Understanding you and your family, your home adapts to your needs, routines and comforts. Lights, climate, security and entertainment are now intelligent with Dragonwing Q-7790 and Q-8750 processors. The backbone of these AI-enabled experiences and home automation? Connectivity, brought to you by Qualcomm, the leading wireless innovator.
But AI isn’t just personal. It’s also physical, acting alongside you.
Your car is transforming into an adaptive companion, driven by intelligence. Snapdragon is redefining automotive experiences, from enhancing safety and comfort to immersive entertainment. Private, contextual AI — sensing, processing, acting in real time — makes every drive smarter, more efficient and connected.
Advanced autonomous capabilities are also being used to power the next generation of personal service robots, all the way through to industrial full-size humanoids. Thanks to our full-stack robotics system, they will deliver intuitive and impactful assistance with precision, enhancing daily life and industry. And I’m sure they’ll learn how to make your coffee perfectly.
This is truly an exciting time in how technology is evolving around us and for us. Our innovations already power billions of devices, enabling the extraordinary experiences that consumers and businesses depend on every day. And we can’t wait to bring you more.
The post Redefining the human experience with intelligent computing appeared first on ELE Times.
The Forest Listener: Where edge AI meets the wild
Courtesy: Micron
Let’s first discuss the power of enabling. Enabling a wide electronic ecosystem is essential for fostering innovation, scalability and resilience across industries. By supporting diverse hardware, software and connectivity standards, organisations can accelerate product development, reduce costs and enhance user experiences. A broad ecosystem encourages collaboration among manufacturers, developers and service providers, helping to drive interoperability. Enabling an ecosystem for your customers is a huge value for your product in any market, but for a market that spans many applications, it’s paramount for allowing your customers to get to the market quickly. Micron has a diverse set of ecosystem partners for broad applications like microprocessors, including STMicroelectronics (STM). We have collaborated with STM for years, matching our memory solutions to their products. Ultimately, these partnerships empower our mutual businesses to deliver smarter, more connected solutions that meet the evolving needs of consumers and enterprises alike.
The platform and the kit
There’s something uniquely satisfying about peeling back the anti-static bag and revealing the STM32MP257F-DK dev board brimming with potential. As an embedded developer, I am excited when new silicon lands on my desk, especially when it promises to redefine what’s possible at the edge. The STM32MP257F-DK from STMicroelectronics is one of those launches that truly innovates. The STM32MP257F-DK Discovery Kit is a compact, developer-friendly platform designed to bring edge AI to life. And in my case, to the forest. It became the heart of one of my most exciting projects yet: the Forest Listener, a solar-powered, AI-enabled bird-watching companion that blends embedded engineering with natural exploration.
A new kind of birdwatcher
After a few weeks of development and testing, my daughter and I headed into the woods just after sunrise — as usual, binoculars around our necks, a thermos of tea in the backpack and a quiet excitement in the air. But this time, we brought along a new companion. The Forest Listener is a smart birdwatcher, an AI-powered system that sees and hears the forest just like we do. Using a lightweight model trained with STM32’s model zoo, it identifies bird species on the spot. No cloud, no latency, just real-time inference at the edge. My daughter has mounted the device on a tripod, connected the camera and powered it on. The screen lights up. It’s ready! Suddenly, a bird flutters into view. The camera captures the moment. Within milliseconds, the 1.35 TOPS neural processing unit (NPU) kicks in, optimised for object detection. The Cortex-A35 logs the sighting (image, species, timestamp), while the Cortex-M33 manages sensors and power. My daughter, watching on a connected tablet, lights up: “Look, Dad! It found another one!” A Eurasian jay, this time.
Built for the edge … and the outdoors
Later, at home, we scroll through the logs saved on the Memory cards. The system can also upload sightings via Ethernet. She’s now learning names, songs and patterns. It’s a beautiful bridge between nature and curiosity. At the core of this seamless experience is Micron LPDDR4 memory. It delivers the high bandwidth needed for AI inference and multimedia processing, while maintaining ultra-low power consumption, critical for our solar-powered setup. Performance is only part of the story: What truly sets Micron LPDDR4 apart is its long-term reliability and support. Validated by STM for use with the STM32MP257F-DK, this memory is manufactured at Micron’s dedicated longevity fab, ensuring a more stable, multiyear supply chain. That’s a game-changer for developers to build solutions that need to last — not just in home appliances, but in the harsh field environment. Whether you’re deploying an AI app in remote forests, industrial plants or smart homes, you need components that are not only fast and efficient but also built to endure. Micron LPDDR4 is engineered to meet the stringent requirements of embedded and industrial markets, with a commitment to support and availability that gives manufacturers peace of mind.
Beyond bird-watching
The Forest Listener is just one example of what the STM32MP257F-DK and Micron LPDDR4 can enable. In factories, the same edge-AI capabilities can monitor machines, detect anomalies, and reduce downtime. In smart homes, they can power face recognition, voice control and energy monitoring — making homes more intelligent, responsive and private, all without relying on the cloud.
The post The Forest Listener: Where edge AI meets the wild appeared first on ELE Times.
Eddy current in focus: A rapid revisit

Eddy currents are not just textbook curiosities; they are the hidden loops that appear whenever metal meets a changing magnetic field. From DIY levitation tricks to clever braking systems, these swirling paths of electrons keep finding new ways to surprise and inspire.
In this rapid revisit, we will zoom in on the essentials, highlight a few practical pointers, and remind ourselves why this classic effect still merits a place in every innovator’s playbook.
Eddy currents: From losses to brakes to rice cookers
Eddy currents are closed loops of electrical current induced in conductors by a changing magnetic field, as described by Faraday’s law of induction. These currents circulate in planes perpendicular to the applied magnetic field.
By Lenz’s law, eddy currents generate their own magnetic field that opposes the change which created them. This opposition manifests as magnetic drag, joule heating, and energy conversion in conductive materials are exposed to time-varying fields.
The interaction between the applied field and induced currents resists motion. A classic demonstration is a magnet falling slowly through a copper tube—its descent dampened by the opposing magnetic force. As eddy currents circulate, they dissipate energy as heat due to the conductor’s resistance. This loss is problematic in devices such as transformers, motors, and induction coils, where unwanted heating reduces efficiency.
At the same time, eddy currents enable useful applications. In magnetic braking systems, for example, a moving object’s kinetic energy is deliberately converted into heat, providing smooth, contactless deceleration.

Figure 1 A generic eddy current brake is shown with rotor eddy currents resisting motion. Source: Author
Eddy currents embody both challenge and opportunity. In power systems, they waste energy as heat and demand careful design measures such as laminated transformer cores or specialized alloys to minimize losses. Yet the same principle enables precise, contactless control in magnetic braking, induction heating, and nondestructive testing.
Léon Foucault discovered eddy currents in the early 1850s; he also demonstrated Earth’s rotation with the Foucault pendulum. From Foucault’s copper disk to today’s rice cookers and industrial drives, eddy currents illustrate how a single electromagnetic effect can hinder efficiency while powering innovation. Their discovery remains a landmark in the history of electromagnetism.
Eddy currents at work: Quick insights
On paper, eddy currents arise from changing magnetic fields. They form when a conductor moves through a magnetic field or when the field around a stationary conductor varies. In short, any change in the intensity or direction of the magnetic field can drive circulating currents. Their strength scales with the rate of flux change, the loop area, and the field’s orientation, while higher conductor resistivity weakens them.
To grasp how this works, inertia makes a useful analogy. In classical mechanics, a moving body tends to keep moving, while a stationary one stays put. Electromagnetism shows a similar stubbornness: when a conductor encounters a changing magnetic field, it responds by generating an opposing flux through induction. That flux manifests as eddy currents. Picture them as invisible coils forming inside the conductor—the material itself acting like a “built-in electromagnet” that resists change.
A familiar example is the eddy current brake used in heavy vehicles and trains. These auxiliary brakes, often engaged on downhill runs, position electromagnets near a drum on the rotating axle. Once energized, the drum develops eddy currents that push back against the changing flux, creating drag. The beauty of this system lies in non-contact braking—no friction, no wear on drums or pads. Of course, the kinetic energy does not vanish; conservation of energy dictates it reemerges as Joule heating, dissipated as heat in the drum.
The same principle appears in everyday life. Induction cooktops and induction heating (IH) rice cookers rely on high-frequency currents in their coils to generate rapidly changing magnetic fields. These fields drive eddy currents in the conductive pot walls, producing Joule heat that cooks food directly and efficiently.
As a side note, eddy current brakes and electric retarders share the same physics but differ in role. An eddy current brake is a general device found in rail systems, roller coasters, or test rigs, providing smooth, non-contact braking. An eddy current electric/electromagnetic retarder, by contrast, is an auxiliary system integrated into heavy vehicles—buses, trucks, and coaches—to control speed on long descents.
Retarders ease the load on friction brakes, preventing overheating and wear, though they still demand cooling since induced currents generate substantial heat. In short, brakes emphasize stopping power, while retarders emphasize sustained drag torque for safe downhill control.

Figure 2 An electromagnetic retarder mounts mid-shaft and delivers non-contact braking for heavy vehicles. Source: Telma
Harnessing eddy currents in dynamometers
Dynamometers often rely on eddy current action in their background to absorb and measure power. In an eddy current dynamometer, a rotating metallic disc or drum is subjected to a magnetic field; as the engine drives the disc, circulating currents are induced in the metal. These eddy currents create a resistive force proportional to speed, effectively loading the engine while converting mechanical energy into heat.
The dynamometer’s role is to provide a controlled, repeatable load while precisely measuring torque and power, enabling accurate evaluation of engine or motor performance. Their application domain spans automotive testing, industrial machinery evaluation, and research laboratories where reliable power measurement is essential.

Figure 3 An eddy current dynamometer, delivering full power at high rotation speeds, is designed for fast-rotating motors. Source: Magtrol
Eddy current sensors: From magnetic fields to motion insight
An eddy current sensor, often referred to as a gap sensor, operates by generating a high-frequency magnetic field through a coil embedded in the sensor head. When a conductive measuring object approaches this field, eddy currents are induced on its surface, altering the impedance of the sensor coil.
By detecting these impedance changes, the sensor translates variations in transmission length into a precise relationship between displacement and output voltage. Their application fields span precision displacement measurement, vibration monitoring, and shaft run-out detection, with widespread use across the automobile, aerospace, and semiconductor industries.

Figure 4 An industrial-grade contactless proximity sensor measures position by interpreting eddy currents. Source: Messotron
Put another way, the eddy current method employs high-frequency magnetic fields generated by driving an alternating current through the coil in the sensor head. When a metallic target enters this field, electromagnetic induction causes magnetic flux to penetrate the object’s surface, producing circulating eddy currents parallel to that surface. These currents modify the coil’s impedance and eddy current displacement sensors detect the resulting oscillation changes to measure distance.

Figure 5 Drawing illustrates the core mechanism of an eddy current displacement sensor. Source: Author
At this point, it’s important to distinguish between an eddy current probe and an eddy current sensor. The probe is the coil assembly that induces and detects eddy currents, typically used in non-destructive testing (NDT), while the sensor integrates the probe with electronics to deliver calibrated displacement or vibration signals in industrial applications.
Also note that the sensing field of a non-contact sensor’s probe engages the target across a defined area, known as the spot size. For accurate measurement, the target must be larger than this spot size; otherwise, special calibration is required.
Spot size is directly proportional to the probe’s diameter. In eddy-current sensors, the magnetic field fully surrounds the end of the probe, creating a comparatively large sensing field. As a result, the spot size extends to many times the diameter of the probe’s sensing coil.
Wrap-up: Bridging theory and practice in eddy currents
Time for a quick break, yet so many details remain in the fascinating world of eddy currents. I am not covering every nuance here because eddy current methods are broad and specialized, with deeper dives best reserved for dedicated sections. To anchor the essentials: eddy current examination is a nondestructive testing method based on electromagnetic induction.
When applied to detect surface-breaking flaws in components and welds, it’s known as surface eddy current testing. Specially designed probes are used for this inspection, with coils mounted near one end of a plastic housing. During inspection, the technician guides the coil end of the probe across the surface of the component, scanning for variations that reveal discontinuities.
Well, now switch on your eddy current soldering iron—or set up one yourself—and start doing something practical, like building your own probes, sensors, or experimental rigs. Hands-on exploration is the best way to connect theory with practice, and this is the perfect moment to make the leap from reading to making.
For curious makers, eddy current soldering irons are not just another tool, they are a gateway into experimenting with induction heating itself. A coil generates a rapidly changing magnetic field, inducing circulating currents in the conductive tip or sleeve. These eddy currents encounter resistance and dissipate energy as heat, delivering rapid warm-up and stable temperature exactly where it is needed.
Whether you pick up a ready-made station or build a DIY rig, you will be blending theory with practice in the most tangible way. It’s a perfect project to showcase how electromagnetic principles—Faraday’s law and Lenz’s law in action—can power real-world innovation.
 T. K. Hareendran is a self-taught electronics enthusiast with a strong passion for innovative circuit design and hands-on technology. He develops both experimental and practical electronic projects, documenting and sharing his work to support fellow tinkerers and learners. Beyond the workbench, he dedicates time to technical writing and hardware evaluations to contribute meaningfully to the maker community.
T. K. Hareendran is a self-taught electronics enthusiast with a strong passion for innovative circuit design and hands-on technology. He develops both experimental and practical electronic projects, documenting and sharing his work to support fellow tinkerers and learners. Beyond the workbench, he dedicates time to technical writing and hardware evaluations to contribute meaningfully to the maker community.
Related Content
- Maxon: Inductive encoder is based on eddy currents
- The difference between inductive proximity, displacement, and eddy-current sensors
The post Eddy current in focus: A rapid revisit appeared first on EDN.
















