ELE Times
Setting Up PCM and I2S Formats for Reliable SCO Loopback Transmission
In the contemporary wireless audio industry, providing crystal-clear uninterrupted sound is such a major and recurrently faced problem. Depending on the nature of Bluetooth headsets ethereally connecting with other apparatus modules over wireless ambience or in the car for in-roads communication purposes, or in gaming devices, it is imperative that, from the engineers’ standpoint, audio signals need to stay unstuck from distortion. To validate and optimize further, SCO (Synchronous Connection-Oriented) loopback transmissions can be put to use.
In this manual, loopback mode is described. Why do we need loopback testing in Bluetooth audio? And how does one configure PCM or I2S for an SCO loopback using the Infineon AIROC Bluetooth controllers?
What is a Loopback Mode?
Loopback mode is a constraint and verification method for wireless audio. Rather than train the audio signal back to a set destination (e.g., speakers, headphones, etc.), the signal is looped back to the originating source. This allows the developers to check the signal quality, such as verifying hardware configurations and troubleshooting towards identifying any mismatch, without dependence on external devices for tests.
Normal vs. Loopback Mode:
Normal Mode: Audio is transmitted to the output device.
Loopback Mode: Audio is redirected back to the source for testing.
Test Environment
To configure SCO loopback transmission, you’ll need:
AIROC CYW20706 headset demo (PCM_OUT source) → GitHub demo project
Linux mbt tool for HCI command input → GitHub mbt tool
AIROC CYW89072 (or any supported Infineon Bluetooth controller) with firmware
Step-by-Step Setup for SCO Loopback Transmission
Step 1: Program the CYW20706 and Bring Up the Demo
- Flash the CYW20706 using ModusToolbox.
- Use the client control tool to run the demo.
- Pair a phone with the CYW20706 and start playback.
Step 2: Connect Hardware
Wire the CYW20706 PCM_OUT pin to the CYW89072 PCM_IN pin.
Step 3: Download Firmware
./mbt download [filename].hcd –minidriver
Step 4: Enable Loopback Mode
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
PCM Configuration
8K PCM
./mbt input_command 1cfc050001000101
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
16K PCM
./mbt input_command 7efc03010200
./mbt input_command 6dfc0400010102
./mbt input_command 1cfc050002000101
./mbt input_command 1efc050000030000
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
I2S Configuration
8K I2S
./mbt input_command 7efc03000200
./mbt input_command 6dfc0401010001
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
16K I2S
./mbt input_command 7efc03010200
./mbt input_command 6dfc0401010102
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
Pin Configuration Notes
For controllers like CYW555xx or CYW43xx, an additional command may be required to route PCM/I2S to default pins:
./mbt input_command 61fc0501b9b8b8b8
By default, the setup assumes TDM2 pins are in use. If you are using alternative pins, adjust the commands accordingly.
Key Takeaway
SCO loopback transmission is an invaluable tool for validating wireless audio performance. By configuring PCM or I2S formats with Infineon’s AIROC Bluetooth controllers, engineers can easily verify signal integrity, fine-tune system performance, and ensure a smooth end-user audio experience.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Infineon Technologies.)
The post Setting Up PCM and I2S Formats for Reliable SCO Loopback Transmission appeared first on ELE Times.
Looking Into What Makes Glasses Smart: A Guide to the Flexible PCBs in Smart Glasses
As emerging glasses and systems bring the virtual and physical worlds closer together than ever before, making navigation, entertainment, and even gaming way easier and more exciting, it is the power of electronics that makes it happen. In such a scenario, let’s examine the technology that makes it possible, seamless, and modern. As we move into the topic, it’s essential to emphasize that the PCB is the most crucial central platform that connects and organizes all the electronic components in a smart glass or an AR/VR device.
What type of PCB is used in Smart Glasses?
Due to the need for flexibility, adaptability, and reliability, the majority of smart glasses today are manufactured using Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs). These are thin, lightweight circuit boards made from pliable materials that bend easily without breaking. As opposed to the rigid circuit boards, FPCBs are made with the intent to empower technology with convenience.
What makes FPCBs the go-to Choice?
PCBs enable engineers to redefine electronics with unique shapes. As it can withstand repeated bending cycles, by default, it becomes an ideal choice for compact and curved designs of smart glasses or AR/VR gear. It is a prime example of how technology integrated with aesthetics and need can empower a whole segment of innovation and seamlessness.
Smart Glasses and FPCBs are a match made in heaven, as FPCBs not only constitute the central platform, which is what a PCB usually does, but also enable the engineers to render various specific characteristics of glasses into the segment of Smart Glasses.
Electrical yet Appealing & Convenient: Secrets
To make a device fitted with so many components, yet maintain it for optimal use as a glass, necessitates a plethora of considerations to be ticked. This takes us to the next part of our story, which is the types of FPCBs depending on the materials it is made of. These materials render significant properties to the FPCBs, enabling them to not only facilitate technology but also combat its ills.
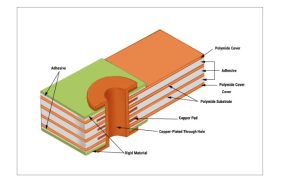 Structure of an FPCB
Structure of an FPCB
Primary materials used in these applications are:
- Polyimide (PI): The most commonly used substrate for flexible PCBs, polyimide offers outstanding thermal stability (up to 400 °C) and high mechanical strength. It can withstand thousands of bending cycles, making it ideal for the constantly moving and compact environment of smart eyewear.
- Polyester (PET): A more economical alternative to polyimide, PET provides decent flexibility but is less durable. It works best in static or low-bend applications, and is often chosen for simpler or less demanding wearable designs.
- Copper Foil: Copper is the standard conductor in flexible PCBs. Among the types, rolled-annealed (RA) copper is preferred over electrodeposited (ED) copper because of its superior flexibility and fatigue resistance—key for handling repeated bends in devices like smart glasses.
- Adhesives and Coverlays: Adhesives secure the layers of a flexible PCB, while coverlays (thin protective films) safeguard the circuitry. Both must retain flexibility and adhesion under stress to prevent issues like delamination during everyday use.
Engineers frequently favor polyimide-based substrates for their durability, particularly in premium AR glasses where long-term reliability is essential. Beyond strength, the choice of material also influences signal performance—polyimide’s low dielectric loss makes it well-suited for high-frequency applications such as 5G connectivity in smart devices.
Design Considerations with FPCBs
Since smart glasses can be subjected to repeated bending and need proper signals to enable their proper usage, it is important to design them accordingly to suit future needs. In engineering terms following considerations rank the highest:
Bending Radius:
- Maintain ≥10× PCB thickness for dynamic bends, ≥3× for static.
- Example: 0.1 mm PCB → 1 mm minimum dynamic bend radius.
Trace Layout & Spacing:
- Route traces perpendicular to bend lines.
- Avoid vias/components in bend zones.
- Keep ≥0.1 mm spacing to prevent shorts during flexing.
Tear-Drop Pads:
- Use tear-drop geometry at trace–pad junctions to minimize stress concentration and cracking.
Layer Stack-Up:
- Use symmetrical stack-ups to keep the neutral axis centered.
- Reduces stress on multilayer FPCs, especially in curved frame designs.
In AR glasses, an FPC can route signals from the microdisplay in the lens to the control unit in the frame, flexing around corners without adding bulk. This ability to combine compact routing with mechanical flexibility makes FPCs fundamental to wearable design.
Is it all Always Good with FPCBs?
To give a straight answer, no. Neither is the case with any technology in the world. Let’s look into certain challenges that FPCBs have to offer when it comes to Smart Glasses:
- Maintaining Signal Integrity: With FPCBs having thin dielectric layers, high-frequency signals for wireless connectivity can face significant challenges. To counter this, manufacturers often turn towards low-loss materials like modified polyimide and ensure precise impedance control, targeting values like 50 ohms for optimal performance.
- Ensuring Bend Durability: Repeated flexing can fatigue copper traces. Mitigation strategies include using rolled-annealed (RA) copper and reinforcing bend zones with stiffeners or extra coverlay layers to better distribute mechanical stress.
- Miniaturization: Smart eyewear requires ultra-compact PCBs with high-density interconnects. Techniques like laser-drilled microvias (as small as 0.05 mm) enable dense, high-performance circuit layouts.
By leveraging these methods, manufacturers can deliver flexible PCBs that meet the strict demands of smart eyewear—combining durability, miniaturization, and high-speed signal integrity where Flexible PCBs are central to smart eyewear, enabling sleek, lightweight designs. Success depends on material choice, proper bend-radius design, and precise rigid-flex assembly—key factors for building reliable, innovative wearables
The post Looking Into What Makes Glasses Smart: A Guide to the Flexible PCBs in Smart Glasses appeared first on ELE Times.
For more secure AI and ML models: Infineon’s OPTIGA Trust M backs Thistle Technologies’ Secure Edge AI solution
Infineon Technologies AG provides its OPTIGA Trust M security solution to Thistle Technologies for its new cryptographic protection for on-device AI models to its security software platform for embedded computing products based on the Linux operating system (OS) or on a microcontroller. The new capabilities in the Thistle Security Platform for Devices, along with Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security solution as tamper-resistant hardware-based root-of-trust, protect the valuable intellectual property (IP) in the AI models deployed in edge AI applications, and in the training data sets on which they are based.
The Thistle Security Platform for Devices that includes the Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security solution, provides ready-made, cloud-managed security components which integrate seamlessly into Linux OS-based devices and microcontrollers. Instead of building and maintaining a one-off cybersecurity stack, OEMs can deploy a proven, continuously updated foundation in hours, and scale it across large, heterogeneous fleets of devices. The Security Platform enables both secured boot and over-the-air (OTA) updating, and is compatible with a broad range of microprocessors, systems-on-chip (SoCs) and microcontrollers. Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security controller enables secured key provisioning, tamper-resistant key storage, and efficient cryptographic operations for encryption and decryption, taking care that only trusted, authenticated, and verified AI models are deployed in edge AI applications.
Thistle has extended its solution to include built-in protection for on-device AI models and data, using cryptographic keys stored in Infineon’s tamper-resistant security controllers, OPTIGA Trust M. The three key features of the new Thistle Secure Edge AI solution are:
- Hardware-backed model encryption – AI model encryption key is secured by OPTIGA Trust M security solution. Each device has a unique AES 256-bit key securely stored in OPTIGA Trust M, which is used to secure the AI Model encryption key. This means that the AES key is used for encryption and decryption inside the OPTIGA Trust M only. Even if a device is lost, decommissioned, or disassembled, the manufacturer’s IP embedded in the model is still efficiently protected. At launch, this feature is enabled on the Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security solution.
- Secured model provenance – in OTA updates, the Thistle platform enables cryptographically signed, tamper-evident delivery of AI models and firmware directly from the training platform to the device, taking care that every installed instance of a model can be traced and verified.
- Signed data and data lineage – device-generated or collected data can be signed on-device and tagged with provenance metadata. This means that downstream systems which might use the data to train or refine AI models can check the provenance of the data, and of the version of the model that the device was running when it generated the data.
Animesh Ranjan, Head of Partnerships & Ecosystem at Infineon says: “At Infineon, we are pleased to expand our collaboration with Thistle Technologies to deliver stronger protection for AI models running at the edge. By combining the OPTIGA Trust M security solution with the Thistle Security Platform, we enable device makers to safeguard their AI with hardware-anchored security that is both practical and scalable.”
Window Snyder, Chief Executive Officer of Thistle Technologies, says: “It is always our goal to make robust security capabilities accessible for device makers. With Infineon’s OPTIGA Trust M and the Thistle Security Platform, manufacturers can protect AI models and data with proven cryptography and deploy at scale quickly. Together we give customers a straightforward way to ship devices that can securely verify, encrypt, and update AI models.”
The post For more secure AI and ML models: Infineon’s OPTIGA Trust M backs Thistle Technologies’ Secure Edge AI solution appeared first on ELE Times.
Breaking Boundaries: Advanced Patterning Paves the Way for Next-Gen Chips
A cutting-edge semiconductor industry or techscape is now seeing chip features being shrunk smaller than the dimensions measured in mere atoms. Such a leap requires advanced patterning, which is a vital process involving high-precision lithography, deposition, and etching techniques working together to scale devices beyond the scope of conventional methods.
These advanced patterning processes will be used in future logic, DRAM, and NAND devices to cram more transistors into smaller dies thereby leading to faster speed, lower power consumption, and enriched functionality. Through the means of advanced patterning, one further increases yields, minimizes defects, and cuts costs at sub-half-micron nodes.
Why Does Advanced Patterning Matter?
Advanced patterning unlike the conventional method was made to help pass resolution limits that come with conventional photolithography. It can provide enhanced layouts as well as finer controls such that the application of Moore’s Law can continue with great force by semiconductor manufacturers.
Benefits include:
- Higher performance and density: More functionality in smaller chip areas.
- Improved yields: Larger process windows reduce defects.
- Sustainability: Advanced processes deliver better energy and cost efficiency.
Patterning Techniques in Action
Single Patterning versus Multipatterning
Single Patterning has been the simplest and most cost-effective method, but this only applies when the scanner is able to resolve the smallest features.
Multi-Patterning (be it Double, Triple, or Quadruple) pushes resolution limits by applying multiple exposures and photomasks. Cases of such techniques are Litho-Etch-Litho-Etch (LELE) and Litho-Freeze-Litho-Etch (LFLE) for creating feature sizes required by very dense chip designs.
Self-Aligned Patterning
Self-aligned processes, including SADP, SAQP, and SALELE, use sidewall spacers or etched references to define features smaller than those that can be lithographically defined while improving placement accuracy and pattern fidelity.
EUV Lithography
Next is Extreme Ultraviolet lithography with the shortest wavelength of 13.56 nm. EUV can produce sub-10-nm features required for nodes like 7 nm, 5 nm, etc., while resisting challenges are still there in things like resist sensitivity, defect control, and edge placement error (EPE).
Step Over the Patterning Challenges
As chips scale toward 3 nm and smaller, tolerances go down to just a few atoms. Controlling EPE caused by stochastic photoresist defects, photon limitations, and scanner imperfections is one of the biggest hurdles. Even a single misplaced edge can lead to yield loss in wafers containing billions of transistors.
Lam Research enables advanced logic and memory scaling through a suite of precision patterning technologies, including Akara for ultra-accurate etching, VECTOR DT for wafer flatness enhancement, Corvus for vertical ion edge control, Kyber for cost-effective line edge roughness reduction, and Aether for efficient dry EUV photoresist processing.
The Road Ahead
As the semiconductor roadmap pushes toward the angstrom era, advanced patterning is no longer optional it is the foundation of innovation. With companies like Lam Research leading the charge, the industry is unlocking the ability to build smaller, faster, and more sustainable chips that will power AI, advanced computing, and next-generation devices.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Lam Research.)
The post Breaking Boundaries: Advanced Patterning Paves the Way for Next-Gen Chips appeared first on ELE Times.
New GST Rates Bring Relief to Electronics Industry from September 22
The Government of India has taken a landmark step towards rendering the tax structure simpler and thereby easing the financial burden upon the common man while while Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi unveiled the next generation of GST reforms during the festive season, marking a pivotal moment in India’s economic transformation. The changes in GST rates have come into force on Monday, September 22; the news has come as a relief for the electronics industry.
As per the reports, the government has announced major concessions on taxes on many household electronics and technology products:
Electric Accumulators: The GST rate has been reduced from 28% to 18%, substantially lowering the cost of backup power solutions for digital devices and small appliances. This change is expected to boost the adoption of energy storage systems in homes and offices, especially in areas with unreliable power supply.
Composting Machines: With a reduction from 12% to 5%, the rates now encourage a wider acceptance of organic waste management and waste-to-energy solutions.
Two-Way Radios: Taxes have been shrunk from the erstwhile 12% to a meagre 5%. On one hand, such tariff change led to lowered procurement costs for the security forces, including the police department, paramilitary units, and defense establishments.
Industry experts wish these reforms have far-reaching benefits. According to the Industry experts, reduction will foster domestic demand, increase the sale of electronic goods and further enlarge the market for local producers.
Rationalised GST under the new reforms will, therefore, be better placed to make the electronics sector accessible, affordable, and competitive while also striving to sustain digitisation and empowerment on the government level.
The post New GST Rates Bring Relief to Electronics Industry from September 22 appeared first on ELE Times.
Vishay Intertechnology to Showcase Solutions for AI and EV Applications at PCIM Asia 2025
Company to Highlight Broad Portfolio of Semiconductor and Passive Technologies in a Series of Reference Designs and Product Demos Focused on AI Servers, Smart Cockpits, Vehicle Computing Platforms, and More
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. announced that the company will be showcasing its latest semiconductor and passive technologies at PCIM Asia 2025. In Booth N5, C48, visitors are invited to explore Vishay’s differentiated products and reference designs tailored to the rapidly evolving demands of AI infrastructure and electric vehicles (EV).
At PCIM Asia, Vishay’s exhibits will highlight the company’s solutions for server power supplies, DC/DC converters, power delivery units, BBUs, mainboards, and optical modules in AI infrastructure and applications, as well as smart cockpit and vehicle computing and ADAS platforms for next-generation EVs. To meet the needs of these high growth sectors, the company is focused on expanding its capacity and optimizing its global manufacturing footprint to broaden its portfolio.
Vishay AI solution components on display at PCIM Asia will include power MOSFETs with extremely low on-resistance in PowerPAK 8×8, 10×12, SO-8DC double-sided cooling—for high efficiency thermal management—1212-F, and SO-8S packages; microBUCK buck regulators with 4.5 V to 60 V input; 50 A VRPower integrated power stages in the thermally enhanced PowerPAK MLP55-31L package; SiC diodes in TO-220, TO-247, D2PAK, SMA, and SlimSMA packages; TVS in DFN and SlimSMA packages; surface-mount TMBS rectifiers with ultra-low forward voltage drop of 0.38 V; IHLE series inductors with integrated e-field shields for maximum EMI reduction that handle high transient current spikes without saturation, and low DCR and high voltage power inductors; the T55 vPolyTan polymer tantalum chip capacitor with ultra-low ESR; thin film chip resistors with operating frequencies up to 70 GHz; Power Metal Strip resistors with high power density and low ohmic values, TCR, inductance, and thermal EMF; and PTC thermistors with high energy absorption levels up to 340 J.
Highlighted Vishay automotive solutions will consist of reference designs, demos and components solutions. Reference designs for automotive applications will include active discharge circuits for 400 V and 800 V; a 22 kW bidirectional 800 V to 800 V power converter for OBCs; an intelligent battery shunt built on WSBE Power Metal Strip resistors, with low TCR, inductance, and thermal EMF, and a CAN FD interface for 400 V / 800 V systems; a 4 kW bidirectional 800 V to 48 V power converter for auxiliary power; a compact 800 V power distribution solution; and a 48 V eFuse.
Highlighted Vishay Automotive Grade components for smart cockpit, vehicle computing and ADAS, and other automotive applications include fully integrated proximity, ambient light, force, gesture, and transmissive optical sensors; Ethernet ESD protection diodes; surface-mount diodes in the eSMP package; MOSFETs with extremely low on-resistance in PowerPAK 8x8LR, SO-10LR, 1212, and SO-8L packages; IHLP series low profile high current power inductors that handle high transient current spikes without saturation; the T51 vPolyTan polymer tantalum chip capacitor with ultra-low ESR; metallized polypropylene DC-Link film capacitors with high temperature operation up to +125 °C; and Automotive Grade EMI suppression safety capacitors with the ability to withstand temperature humidity bias (THB) testing of 85 °C / 85 % for 1000 h.
The post Vishay Intertechnology to Showcase Solutions for AI and EV Applications at PCIM Asia 2025 appeared first on ELE Times.
Towards Greener Connectivity: Energy-Efficient Design for 6G Networks
The need for sustainable mobile networks is stronger today than ever before. Increasing operational costs, tightening environmental rules, and international commitments toward sustainable development are all compelling telecom operators, as well as infrastructure vendors, to repaint their perspective on how networks are created and powered. Since wireless infrastructure uses more than any other type of infrastructure in terms of energy use, the transition from 5G to 6G is an opportunity to make sustainability one of the prime considerations alongside speed and capacity.
According to ITU-R Recommendation M.2160 on the IMT-2030/6G Framework, sustainability remains one of the key aspirations, where mobile systems are expected to be designed so that they use minimum power, emit least greenhouse gases, and utilize their resources efficiently. Contrary to what happened in previous generations where energy efficiency was considered after the fact, 6G has the potential to incorporate green-by-design concepts from the start so as to deliver both excellent performance and little environmental impact.
Energy-Saving Features in 5G: Achievements and Limitations
Innovations such as RRC_INACTIVE mode, Idle Mode Signaling Reduction, Discontinuous Reception (DRX), Discontinuous Transmission (DTX), and Carrier Aggregation control helped reduce unnecessary signaling and lower energy use.
The later 5G releases enhanced on such features as:
- Dynamic SSB transmission control based on cell load.
- On-Demand SIB1 broadcasting.
- Cell switch-off and micro-sleep for base stations.
- Improved RRC_INACTIVE mobility.
- Partial activation of antenna ports.
- BWP operation for UEs.
- Dynamic PDCCH monitoring control.
- SCell dormancy in carrier aggregation.
- Low-power receivers for UEs.
However, some structural shortcomings exist: for instance, frequent SSB bursts (every 20 ms) allow only shallow sleep, and persistent antenna activation wastes energy even when traffic is low. Many legacy UEs are incapable of supporting these new modes of efficiency, and high-traffic scenarios still do not have robust network-level mechanisms for saving energy. These gaps necessitate a fundamental rethink of energy efficiency in 6G.
Less ON, More OFF is the Principle on Which 6G Is Built:
In 6G, energy efficiency will become a paramount design concern instead of a mere secondary feature. The phrase “Less ON, More OFF” becomes the banner under which unnecessary transmissions are done away with and base stations and UEs are put to sleep when at all possible.
Samsung Research finds three main enablers:
Carrier-Dependent Capabilities
6G introduces Energy-Saving Network Access (ENA), which dynamically controls SSB transmission.
Multi-toned SSBs: Normal (NM-SSB), Energy-Saving (ES-SSB), and On-Demand (OD-SSB) provide extremely flexible signaling in contrast to 5G-Fixed SSBs-on.
ES-SSB usually delays the transmission periodicity (e.g., 160 ms); the OD-SSBs are transmitted only on demand, reducing base station standby energy.
- Dynamic Time/Frequency/Spatial/Power Adaptation
Here, DSA is the active adaptation of the number of active antennas and beam directions based on real-time demand.
It avoids over-provisioning and wasting idle power and is particularly applicable for high-frequency bands in which power scales with antenna density.
- Energy-Aware Network Management and Exposure (EANF)
Interfacing with the central orchestration layer for real-time monitoring of energy consumption, in order to initiate power-aware policies for scheduling, load balancing, and carrier activation.
Further, in the realm of AI-RAN, better traffic predictions will enable the optimization of beam configurations and event-driven measurements, thereby also reducing signaling, and hence power consumption.
Energy Conservation for UEs in 6G
User devices remain at the core of the 6G energy-saving scheme. Network-UE joint power saving opens the way for more proactive strategies whereby the network predicts UE activity, traffic patterns, and battery status to join in coordinating wake-up intervals.
Some of these key innovations include:
- Ultra-low-power wake-up receivers that keep energy use at a minimum.
- Context-aware wake-up signals powered by ML techniques evaluating and adapting timing and frequency.
- Collaborative scheduling between the network and the UE to reduce idle consumption without degradation of user experience.
Performance and Energy Gains
Internal studies with 24-hour traffic profiles demonstrated:
- ENA cuts energy consumption by 43.37% at low traffic and reaches 20.3% average savings.
- DSA further reduces power consumption by another 14.4%, scaling the antenna ports with demand.
- Together, ENA + DSA can reach an energy saving of ~21.2% while also enhancing the user-perceived throughput (UPT) by up to 8.4%.
In this way, such results show that 6G energy savings are not just about switching off and saving power-they also include efficiency improvements and network responsiveness enhancements.
Conclusion:
Rather from being a small improvement, the 6G energy-saving vision represents a paradigm shift. Networks can enter low-power modes more frequently when ENA, DSA, and EANF cooperate, which minimises waste and maintains service quality. 6G offers faster and more dependable connectivity as well as a sustainable foundation for the upcoming ten years of wireless evolution by fusing AI-native intelligence, signalling innovation, and hardware flexibility.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Samsung.)
The post Towards Greener Connectivity: Energy-Efficient Design for 6G Networks appeared first on ELE Times.
Building Trustworthy Software with AI: The Generate-and-Check Paradigm
Whether it be designing products and creative content or software engineering, artificial intelligence is steadily changing how we engineer and interact with technology. But although AI can speed up the development process, the real price of the measure lies in trusting its output, particularly when dealing with safety-critical applications. How can AI-generated software be ensured to be correct, secure, and efficient within real-world parameters?
Bosch Research recognizes the immense promise of the generation-and-execution approach in driving innovation and practical impact. This synthesis combines generative AI to suggest solutions and systematic checks to enforce correctness, safety, and performance. Balancing AI creativity occurs with a touch of strictness-a balance that lands well upon software engineering.
How Generate-and-Check Works
Think of solving a crossword puzzle: you may try out different words, but each suggestion is validated against the length of the clue and the letters already in place. Similarly, in software engineering, AI can generate new code or refactor existing code, while automated checks verify compliance with rules and desired outcomes.
Those rules can be either very simple like the coding style enforcement or highly advanced, like formal verification of software properties. From this perspective, rather than verifying every possible system state, safety, correctness, and adherence to requirements are ensured by verifying AI proposals.
Less error-prone AI assistance, and much less reliance on human supervision all the time.
Use Case 1: Smarter Code Refactoring
Refactoring is a perfect application for generate-and-check. The AI proposes improvements, e.g., migrating to more efficient frameworks, while automated checks verify the equivalence of the new version with the old code.
This approach is somewhat different from the traditional ones based mostly on unit tests as it guarantees behavioral invariance, i.e., that the refactored code behaves exactly the same but better in terms of maintainability or efficiency. Tools developed at Bosch Research allow you to profile this too, to make sure that performance has stayed the same or improved after the changes have been made.
Use Case 2: Reliable Software Translation
On the other hand, software translation remains an area where AI excels but demands human monitoring. The idea of translating legacy code into a safer or new-age language seems nice, but oftentimes traditional transpilers would fail in preserving the idiomatic essence of the target environment.
Yet with generate-and-check, AIs can translate idiomatically while automated tools check for functional correctness, safety, security, and performance. This finally offers a chance to modernize codebases in great bulk without stealthily inserting vulnerabilities.
Embedding into the Developer Workflow
AI becomes valuable for developers if their tools support integration with existing toolchains. Generate-and-check would appear in various forms:
IDE plugins for quick, low-latency assistance during coding.
Background workflows for longer tasks, such as legacy migration, where AI proposals can be rolled out as pull requests. Each PR can provide evidence, such as performance metrics or validation checks, preserving developers’ agency albeit under automated rigor.
This guarantees that AI will continue to be an aid rather than a substitute, offering reliable recommendations while developers make the ultimate choices.
Looking Forward:
The generate-and-check paradigm is a mentality shift for trustworthy AI in software engineering, not merely a technical approach. AI offers safer, better, and more efficient software development by combining its generating capacity with reliable verification.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Bosch.)
The post Building Trustworthy Software with AI: The Generate-and-Check Paradigm appeared first on ELE Times.
Energy Harvesting for IoT: Powering Self-Sustaining Sensors
The growth of IoT depends on billions of sensor nodes that must operate reliably without frequent maintenance. Powering them through traditional batteries alone is costly and unsustainable, especially when replacements are required at scale. Energy harvesting offers an attractive path toward self-sustaining devices, enabling sensors to draw power from their surrounding environment light, motion, heat, sound, or even radio waves.
Yet, deploying energy harvesting systems is not without hurdles. Limited standards, variable energy sources, and integration complexity raise questions around long-term reliability and return on investment. Selecting the right harvester technology depends heavily on the environment in which the sensor will operate.
Choosing the right energy source
Energy harvesters have infrastructure-specific physical phenomena, and their utility strongly depends on the situation:
- Photovoltaic (PV): Good in the presence of light, including new-generation indoor PV cells capable of producing electricity at just 50 lux.
- Vibration/kinetic: Good where there is some regular motion involved-type actions on the roads, or in machinery environments.
- Thermoelectrics (TEG): How does this generate power? Temperature difference, obviously, which is why it finds use in industries or on the wearer.
- Acoustic: Uses sound waves. Probably better in a noisy industrial setup.
- RF energy harvesting: From Wi-Fi sources, cellular, or even dedicated transmitters, they usually provide very low powers, just enough to wake a device.
Therefore, to power devices capable of some form of heavy industrial application, it is generally necessary to instrument several harvesters acting simultaneously, depending on conditions of daylight, silence, and noise-this, in fact, introduces added complexity to design.
Building blocks of self-sustaining IoT nodes
An energy-harvesting IoT node contains:
- Harvester/s- for gathering ambient energies.
- PMIC- to regulate, store, and distribute energy.
- Energy storage- battery or capacitor to buffer power.
- Sensor, MCU/SoC and wireless interface- for low-power operation.
The new PMICs have become increasingly versatile now, supporting a variety of harvester types and enabling their dynamic optimization. When complemented with features such as the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT), ultra-low quiescent currents (sub-100 nA), and adaptive duty cycling, the nodes are able to effectively optimize performance with respect to erratic energy input.
Choosing storage depends on the application’s requirements:
- Batteries: High energy density, therefore, good for sustained powering, but lifespan in terms of charge cycles is limited.
- Capacitors (including supercapacitors): They can charge and discharge quickly and have a very long lifecycle, but low energy storage.
Leakage currents, environmental condition, and duty cycle also decide which is the best option. Real testing is a must, as datasheet specifications can never accurately predict real operating environments.
Energy management in action
Moving beyond the hardware, there is a rise in advanced software techniques. Reinforcement learning (RL) allows energy allocation to be optimized by teaching sensor nodes when to send data, when to go into sleep mode, and how to adjust power depending on the energy available. Machine learning merges with the efficiency of hardware to make IoT systems more autonomous, thus improving resilience.
Toward a sustainable IoT ecosystem
Energy harvesting could potentially eliminate its frequent replacement, reduce environmental damages, and thus extend the lifetime of the device. Success lies in an all-encompassing design approach that involves choices such as ultra-low-power components, energy-efficient communication protocols, and adaptive power management capable of handling the variability of real-world conditions.
Any IoT device that is to become truly self-sustaining needs just the right harvesters working along with smart PMICs and optimized storage.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Avnet.)
The post Energy Harvesting for IoT: Powering Self-Sustaining Sensors appeared first on ELE Times.
Powering Sustainable Manufacturing: How UPS Systems Drive Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is a must for India’s manufacturing sector. Increasing energy costs, intermittent grid disruptions, and maintaining operational integrity are being cited as pressure points leading industry to rethink its energy strategies. UPS systems came up as one of the solutions supporting efficiency and sustainability.
According to the India UPS Market Report by Astute Analytica, the Indian UPS market was valued at USD 8.79 billion in 2024 and is purportedly expected to more than double to USD 18.28 billion by 2033, therefore, growing at a CAGR of 8.61%. Growth can be attributed mainly to the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which require stable power supply without interruptions for automation, robotics, and real-time data-driven operations.
Mission-Critical Power for Industry 4.0
In modern manufacturing operations, sensors, robots, and smart controllers work in an integrated manner. A slight power interruption can either allow predictive maintenance systems to cease working, delay robotic operations, or even halt production lines altogether. The UPS now offers a good 95 percent or better efficiency reduction in energy wastage and operating costs with lithium-ion batteries.
Backup power is just one of the many interesting ways that today’s UPSs are providing energy-conservation services. Transformer-less designs, modular architectures, and an ECO mode help optimize plant-wide performance by minimizing heat generation, cooling load requirements, and some of the energy wastes in static operations, while also preserving stability and resilience.
Supporting Resilience and Efficiency
Most modern UPS are meant for dynamic industrial loads such as heavy motors and stamping equipment and provide protection against surges, overcurrent fault conditions, and voltage sags. Also, in their modular construction and scalable nature, manufacturers can increase capacity only when needed, so as to reduce wastes and maximize uptime.
IP4X+ UPS systems are also becoming of utmost importance in the aspects of powerifiers in industrial environments that deal with dust, high temperature, and moisture on a daily basis.
UPS as Part of Energy Management Strategy
UPS are starting to play a more active role in broader energy management schemes. Real-time monitoring, predictive fault analysis, load sharing, and peak shaving facilities place UPS manufacturers in a position to integrate the UPS with a smart grid or automation platform.
This is also inline with India’s drive towards intelligent energy infrastructure. The smart grid market of India is forecasted to reach USD 19.33 billion by 2033 with the government providing a 20 billion USD opportunity for grid modernization through a plan of 250 million smart meter rollouts by 2027.
Facilitating Renewable and Sustainable Manufacturing
UPS are crucial for renewable energy endeavors in the Indian context. By interfacing with solar power and battery storage, and regenerative loads such as CNC machines, UPS solutions assist in providing clean backup power while unleashing the ability to recapture energy for downstream use, thus further reducing carbon footprints and operational costs.
January 2025 saw India’s renewable energy capacity at 217.62 GW and holds a promising view of 500 GW by 2030 with the backing of 50 GW of energy storage. UPS integration with these initiatives ensures uninterrupted, green, and scalable industrial power.
Innovations and Emerging Trends
An industry UPS evolving fast:
- Lithium-ion is becoming popular nowadays as it offers the advantage of a longer life, more efficiency, and less maintenance cost compared to lead-acid batteries.
- Modular UPS solutions are now common since manufacturers may benefit from scalability and versatility being paramount in a dynamic manufacturing environment.
- AI-powered systems are now being used for maintenance scheduling and asset optimization.
Challenges Ahead
Whilst having numerous pros, the implementation poses certain challenges. SMEs are raised with issues, from the exceptionally high upfront costs to the lack of expertise regarding installation and upkeep. Other barriers to implementation include battery lifecycle management, constant need for component replacement, and skilled manpower shortage.
Conclusion
From being an emergency backup, UPS has now evolved to become a strategic asset for energy-efficient, resilient, and sustainable manufacturing in India. They are shaping the evolution towards Industry 4.0 and beyond through their interfacing with smart grids, renewable sources, and automation systems.
While cost and complexity may deter smaller enterprises initially, the long-term benefits greater operational continuity, reduced energy costs, and compliance with sustainability goals make UPS adoption indispensable for India’s industrial growth journey.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content by Pankaj Singh, Head of Data Center & Telecom Business Solutions, Delta Electronics India.)
The post Powering Sustainable Manufacturing: How UPS Systems Drive Energy Efficiency appeared first on ELE Times.
Rohde & Schwarz announces new frequency models up to 54 GHz for R&S ZNB3000 vector network analyzer
Designed to combine precision and speed in a scalable platform, the R&S ZNB3000 vector network analyzer from Rohde & Schwarz helps engineers and researchers accelerate innovation in high-performance RF applications and signal integrity testing. By extending the maximum frequencies up to 32 GHz, 43.5 GHz and 54 GHz, Rohde & Schwarz addresses even more applications with the R&S ZNB3000, from RF component testing for 5G, 6G and Wi-Fi applications to advanced high-speed interconnect testing for AI data centers and next-generation RF component testing for satellite communications in the Ka band and V band.
Optimized for high-speed interconnect testing for AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) applications in data centers demand ultra-fast, high-bandwidth interconnects to efficiently handle massive data loads. Technologies such as high-speed Ethernet (IEEE 802.3ck) require testing solutions that can operate at frequencies up to 50 GHz to ensure optimal signal integrity. The new PCIe 7.0, Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, currently under development, will double the supported data rates up to 128.0 GT/s. This requires testing at higher frequencies, as well.
Covering up to 54 GHz, the R&S ZNB3000 is designed to meet these requirements, enabling precise characterization of high-speed PCBs, cables, and interconnects used in AI data center infrastructure. At EuMW 2025, Rohde & Schwarz demonstrates the new 54 GHz model of the R&S ZNB3000 for the first time in public. The setup, which includes a PCIe cable as the device under test (DUT), showcases how to ensure the reliability of high-speed interconnects for AI-driven workloads.
Industry-leading performance and flexibility
The R&S ZNB3000 family offers best-in-class RF performance with a high dynamic range of up to 150 dB, high output power, and low trace noise of less than 0.0015 dB RMS. These attributes ensure highly accurate and fast measurements, even at higher frequencies. The new models retain the series’ characteristic features, including:
- Ultra-fast measurement speed:Maximizes throughput and reduces the cost of testing.
- Low start frequency of 9 kHz:Enables precise time-domain analysis for signal integrity and high-speed testing.
- Flexible frequency upgrade concept:Customers can start with a base unit and expand the maximum frequency later by purchasing upgrade options, ensuring a targeted investment approach.
Expanding to new RF applications
The new high-frequency models also support advanced RF component testing for SatCom applications in the Ka and V bands, such as filters, mixers, amplifiers, switches and beamformers, which operate at these high frequencies. It also enables RF component testing for 5G, 6G and Wi-Fi applications. This makes the R&S ZNB3000 an ideal choice for both production environments and research labs working on next-generation technologies.
The post Rohde & Schwarz announces new frequency models up to 54 GHz for R&S ZNB3000 vector network analyzer appeared first on ELE Times.
Infineon power modules enhance energy efficiency in Goldwind’s grid-forming wind turbines
Infineon Technologies AG and Goldwind Science & Technology Co., Ltd. expand their collaboration, enabling a stable and reliable flow of electricity in wind power generation. Infineon will supply Goldwind with its XHP 2 1700 V IGBT5 power modules with .XT technology that will enhance energy efficiency in Goldwind’s grid-forming GW 155 – 4.5 MW wind turbines. Infineon’s power modules deliver high power density, reliability, and robustness, ensuring a long operational lifetime for wind energy systems. By optimizing energy efficiency, they help to reduce energy costs and enhance the profitability of Goldwind’s wind turbines.
Grid-forming wind turbines act as stabilizers within the energy grid. Unlike conventional turbines that passively follow the grid, the grid-forming technology allows wind farms to mimic the stabilizing properties of traditional rotating generators. By using power electronics, grid-forming wind turbines can generate a stable frequency and maintain grid voltage, even when the load in the power grid changes. The International Energy Agency estimates that renewables will account for almost half of global electricity generation by the end of the decade, with the share of wind and solar photovoltaics doubling to 30 percent. Grid-forming capabilities will therefore become essential to ensure a stable and reliable flow of electricity despite fluctuations in energy generation.
“The emergence of grid-forming wind turbines enables wind farms to evolve from simple power suppliers into stabilizing pillars of the energy grid.” said Ye Jiqiang, Vice President of the Wind Power Industry Group and General Manager of the Supply Chain Center at Goldwind. “We look forward to further deepening our long-term collaboration with Infineon, leveraging efficient and reliable cutting-edge technology to advance renewable energy systems.”
“Collaborating with Goldwind to support their grid-forming wind turbines underscores Infineon’s commitment to strengthening global energy systems and further advancing renewable energy integration,” said Dominik Bilo, Executive Vice President and Chief Sales Officer Industrial & Infrastructure at Infineon. “Together, Infineon and Goldwind are driving decarbonization by enhancing the reliability and efficiency of wind power generation.”
Infineon’s XHP 2 1700 V IGBT5 power modules use the .XT interconnection technology. This technology is characterized by improved wire bonding, reliable chip attachment, and high-reliability system-soldering, enabling power modules to support increased cycling loads at higher temperatures compared to standard joining technology. The power modules feature low stray inductance and a design well-suited for paralleling, simplifying development for customers and enabling greater flexibility for platform upgrades. They provide exceptional lifetime even under challenging operating conditions such as those in wind turbines. As a result, they minimize unplanned downtimes and maximize wind energy harvested. Today, Infineon products are used in every second newly installed wind turbine worldwide.
Infineon and Goldwind have been collaborating since 2007 to advance more compact, highly reliable, and grid-friendly wind power converters. Infineon has already supplied Goldwind with its fifth-generation PrimePACK IGBT modules. Thanks to their high power density and exceptional cycling performance, these solutions have enabled Goldwind’s 6 MW full-power wind turbine models to meet stringent global standards for reliability, energy efficiency, and safety, while reducing operational and maintenance costs.
The post Infineon power modules enhance energy efficiency in Goldwind’s grid-forming wind turbines appeared first on ELE Times.
Microchip Introduces Flexible New Family of Gigabit Ethernet Switches with TSN/AVB and Redundancy For Industrial Applications
Microchip’s next generation LAN9645xF and LAN9645xS GbE switches are highly configurable with multiple ports and advanced features
Ethernet technology provides the high-speed, reliable communication needed to connect and control industrial devices in real time. Its scalability and flexibility to support protocols such as TSN ensures seamless integration for demanding industrial environments. Microchip Technology announced the launch of its next generation of LAN9645xF and LAN9645xS Gigabit Ethernet Switches with multi-port configurations and feature options for maximum reliability and flexibility.
The LAN9645xF/S switches offer multiple configurations for specific application needs and are available in 5-, 7-, and 9-port options with up to 5 integrated 10/100/1000BASE-T PHYs. This flexibility is further enhanced by the ability to operate in either stand-alone unmanaged system configurations or in managed mode with full Linux Distributed Switch Architecture (DSA) support on a connected host.
The LAN9645xF device supports advanced features such as Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and Audio Video Bridging (AVB) in managed mode of operation. This variant enhances network reliability with hardware-assisted redundancy that meet IEC 62439-3 standard for Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) and High-availability Seamless Redundancy (HSR), enabling seamless failover and zero packet loss during faults. While the LAN9645xS device supports standard Ethernet switching with some Precision Time Protocol (PTP) support and is intended to be used as a low-cost unmanaged switch.
“Our LAN9645x F/S devices help our customers lower their system costs while implementing advanced TSN and redundancy features by combining many features into a single solution,” said Charlie Forni, corporate vice president of Microchip’s networking and communications business unit. “We back our products with global technical support and a full suite of development tools to make it easier for our customers to design and deploy their industrial networks.”
Microchip’s LAN9645xF/S delivers adaptable, high-performance networking solutions for industrial Ethernet applications, as well as for markets like aerospace and defense, data centers and sustainability. Additionally, the Ethernet devices seamlessly integrate with Microchip’s ecosystem including MCUs, memory and timing solutions, enabling reliable and scalable networks for demanding environments.
The post Microchip Introduces Flexible New Family of Gigabit Ethernet Switches with TSN/AVB and Redundancy For Industrial Applications appeared first on ELE Times.
Cross-Reference Search Made Simple: Smarter Alternatives for Semiconductor Selection
A New Approach to Component Selection
Designing reliable electronic applications starts with choosing the right semiconductor components. However, even if the best part has been chosen, supply issues, growing costs, or discontinued products may result in upset causes. In such moments, being capable of developing quick alternative identification will prove paramount.
Cross-reference tools come into play here. By cross-matching components fitting the same usage from two different manufacturers, this tool has enabled engineers and non-engineers alike to make informed substitutions, be it for sustainability, design flexibility, or supply chain risk mitigation.
Making Cross-Reference Searches Easier
The idea of comparing electrical characteristic values, package sizes, and performance parameters involved first going through datasheets and catalogs. That drudgery is something ROHM’s cross-reference tool completely abolishes, providing side-by-side comparisons at a glance.
Unlike generic listings found on distributor websites, the ROHM tool displays key specifications in a well-structured table, so the user can effectively cut down on wasted time and uncertainty.
Understanding the Limits
While convenient, no cross-reference tool is perfect. Compatibility suggestions can sometimes focus only on physical fit, not functional equivalence. That’s why verification of performance, certification, and long-term availability remains essential. ROHM addresses this by ranking alternatives based on performance similarity and supporting industrial and long-life applications through its Product Longevity Program, updated annually with estimated supply periods.
Real-World Success Stories
Case 1: Got Faster Selection- Engineers used ROHM’s clear comparison tables to cut down selection time and even directly incorporated these tables into internal reports.
Case 2: Usable for Non-Engineers- Non-technical staff members used it to suggest alternatives after simply searching with part numbers.
Case 3: Reliable During Shortages- Urgent replacements were sorted with ranked lists from ROHM, supplemented by pictures and specifications.
Conclusion
Cross-reference search tools are transforming how engineers and businesses handle component selection. By combining speed, accuracy, and reliability, ROHM’s proprietary cross-reference tool developed from customer feedback empowers users to make smarter, faster, and more confident decisions.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Rohm Semiconductor.)
The post Cross-Reference Search Made Simple: Smarter Alternatives for Semiconductor Selection appeared first on ELE Times.
From Compute to Memory: Redefining AI Performance with Next-Gen Memory and Storage
Artificial Intelligence has come a long way, transforming what was once called a far-fetched notion into a makeover across industries. The conscious discourse has always been about computing accelerators such as CPUs, GPUs, or NPUs, while an invisible, but equally important, element is quietly shaping the future for AI: memory and storage. At Micron, this shift in perception has only served to deepen our commitment to innovation with a fresh standpoint whereby memory and storage became no longer just supporting elements but key drivers influencing AI in performance, scalability, and efficiency.
Breaking Through the Memory Wall
Scaling AI models into billions and even trillions of parameters makes the need for high-speed access to data shoot up exponentially. This really brings to the fore the age-old memory wall problem-the ever-widening gap between the fast processor and the comparatively slower memory bandwidth/latency. For AI workloads, in particular, large-scale training and inference, this can very well be a serious bottleneck.
Micron is attacking this challenge head-on through a full suite of products that ensure memory and storage become accelerators rather than impediments for AI performance.
Micron’s AI-Ready Portfolio
Near Memory: High Bandwidth Memory (HBM) and GDDR reduce latency and ensure fast access to AI model parameters by closely integrating with CPUs.
Main memory that balances capacity, low latency, and power efficiency for workloads like training and inference includes DIMMs, MRDIMMs, and low-power DRAM.
Expansion Memory: By increasing scalable memory capacity, Compute Express Link (CXL) technology reduces total cost of ownership.
High-performance NVMe SSDs and scalable data-lake storage are two storage alternatives that can be used to meet the I/O needs of AI applications that depend significantly on data.
These innovations come together to form Micron’s AI data center pyramid, which increases throughput, scalability, and energy efficiency by addressing bottlenecks at every level.
Why AI Metrics Are Important
AI performance is assessed using common system-level KPIs across platforms, including mobile devices and hyperscale data centers:
Time to First Token (TTFT): The speed at which a system starts producing output.
A metric for inference throughput is tokens per second.
A measure of power efficiency is tokens per second per watt.
Memory and storage both have a significant impact on these parameters, guaranteeing that AI workloads are carried out quickly, reliably, and with the least amount of energy consumption.
Enhanced Central AI Memory and Storage Set Up
The very frontier that used to separate compute from memory is getting blurred. Given the blend of demand for energy-efficient yet high performing solution, LPDDR and other low-power memories that were being used in mobile are now gradually entering into the data center space. Micron’s portfolio of DDR, LPDDR, GDDR, and HBM memories is marketed to new levels of being optimized for every step of AI inference-from embedding to decoding, thus eliminating bottlenecks.
Conclusion:
AI is being viewed as the era for bigger models and faster processors; it is a point of rethinking compute, memory, and storage interoperability. Memory is indeed a performer in the guest list of AI scalability and efficiency, thanks to the DRAM and NAND memory innovations from Micron. Breaking memory wall and setting new system-level metrics will help make the next step for AI performance, thanks to Micron.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Micron.)
The post From Compute to Memory: Redefining AI Performance with Next-Gen Memory and Storage appeared first on ELE Times.
Redefining Data Infrastructure: Optical Circuit Switches Could Transform AI Data Centers
The surge in demand for large-scale AI training is straining today’s cloud infrastructure, pushing electrical packet switches (EPS) toward their performance and power limits. As GPUs scale into massive clusters to support ever-growing large language models, the need for faster, more efficient data transport is becoming critical. Optical Circuit Switches (OCS) are emerging as a powerful alternative, offering high bandwidth over long distances with far lower energy consumption.
Unlike EPS even those integrated with co-packaged optics OCS relies on all-optical connections to link GPUs through switched ports and optical transceivers. This enables GPU clusters to operate as a unified, high-performance computing fabric while delivering significant efficiency gains.
Applied Ventures recently co-led a Series A funding round for Salience Labs, a startup pioneering OCS solutions based on Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) technology. Their Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) are available in two configurations: a high-radix switch designed for HPC workloads and a lower-radix version optimized for AI data centers. This flexibility allows hyperscalers, GPU makers, and even financial trading firms to balance cost, performance, and scalability.
The urgency of these innovations is underscored by energy trends. The U.S. Energy Information Administration projects data centers will consume 6.6% of U.S. electricity by 2028, more than double the share in 2024. Networking equipment switches, transceivers, and interconnects represents a growing portion of this footprint.
To address this, companies are rethinking chip and system design:
- Google’s TPU aims for a 10× cost-efficiency advantage over GPUs by tailoring silicon to specific AI tasks.
- Lumentum projects that without optical efficiency improvements, training GPT-5 could require 122 MW, nearly six times more than GPT-4. Energy-efficient optical interfaces combined with OCS could cut that by 79%, aligning power use with GPT-4 levels.
- Arista Networks estimates energy-efficient optical modules could save up to 20W per 1,600Gbps module.
By combining scalability with low-latency, long-reach connectivity, OCS technology could reshape how tens or hundreds of GPUs interconnect, enabling them to act as one massive supercomputer while containing the energy surge.
Conclusion:
Optical Circuit Switches are more than an incremental upgrade they represent a fundamental shift toward sustainable high-performance computing. With almost very high bandwidth, low latency, and massive energy savings, OCS will stand tall in next-generation AI data centers so that performance scaling is not done at the unsustainable power cost.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Applied Materials.)
The post Redefining Data Infrastructure: Optical Circuit Switches Could Transform AI Data Centers appeared first on ELE Times.
PerfektBlue: Bluetooth Vulnerabilities Put Millions of Vehicles at Risk
Researchers uncover a chain of flaws in a widely used automotive Bluetooth stack, exposing infotainment systems to remote compromise
In July 2025, cybersecurity researchers disclosed PerfektBlue, a set of four vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-45431 to -45434) found in OpenSynergy’s BlueSDK, a Bluetooth stack widely integrated into modern infotainment systems. The flaws affect millions of vehicles across brands including Volkswagen, Mercedes-Benz, and Skoda, enabling attackers to execute malicious code over Bluetooth Classic connections.
Attack Path and Impact
PerfektBlue can only be exploited at close range, requiring the attacker to be within 5-7 meters of a target vehicle and establish Bluetooth pairing. This limits the possibility of large-scale exploitation; however, a successful attack would open the IVI system to the hacker(s), leaking data such as:
- GPS data & Vehicle location
- Listening through in-car microphones
- Contact lists & communication logs
Safety-critical functions like braking and steering remain segmented. Yet, as past incidents (e.g., the 2015 Jeep Cherokee hack) have shown, weak network isolation could allow lateral movement if additional vulnerabilities exist.
Root Causes in Bluetooth Stack Design
PerfektBlue includes one memory corruption flaw and three logic-level vulnerabilities stemming from protocol mismanagement. Combined, they create a pathway to remote code execution once pairing succeeds.
The flaws illustrate ongoing issues in Bluetooth stack security:
- Multi-layer protocols such as L2CAP, RFCOMM, and AVRCP handle vast amounts of untrusted data.
- Implementations in C heighten memory safety risks.
- The wireless and real-time nature of Bluetooth complicates fuzz testing, letting subtle bugs persist across generations.
Delays in Fixing and Deployment
The vulnerabilities were first reported in May 2024, and a patch was issued by September 2024. Yet disclosure did not occur until July 2025, largely because automakers lagged in deploying updates.
Challenges included:
- Complex supply chains with limited visibility on software components.
- No software bills of materials (SBOMs)-thus OEMs were not aware that they even depended on BlueSDK.
- Highly manual service updates rather than OTA.
Wider Implications and Next Actions
As long as vehicle safety systems remain isolated, infotainment are not benign to breaches. Attackers could track drivers, eavesdrop on conversations, and steal sensitive data, or in poor circumstances, pivot to other systems if the segmentation is weak.
As a countermeasure, experts advised the automakers to:
- Consider Bluetooth stacks as high-value attack surfaces.
- Standardize the use of SBOMs so that the third-party software can be identified and tracked.
- Give priority to OTA update pipelines to reduce patch deployment delays.
- Integrate protocol fuzzing and binary analysis in the development lifecycles.
PerfektBlue is a reminder that connected vehicles remain vulnerable to wireless exploits. Without stronger defenses and adoption of patches faster, the automotive industry is repeating the same mistakes of past cybersecurity lapses.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Keysight Technologies.)
The post PerfektBlue: Bluetooth Vulnerabilities Put Millions of Vehicles at Risk appeared first on ELE Times.
Vishay Intertechnology Launches Industry’s First Automotive Grade Ceramic Capacitors With Y1 Rating in SMD Casing
Devices Offer Y1 Rating of 500 VAC and 1500 VDC, High Capacitance to 4.7 nF, and High Humidity Robustness
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. introduced a new series of Automotive Grade AC line rated ceramic disc safety capacitors that are the industry’s first with a Y1 rating to be offered in a surface-mount casing. Combining their Y1 rating of 500 VAC and 1500 VDC with high capacitance to 4.7 nF, the Vishay BCcomponents SMDY1 Automotive Series devices are designed to provide EMI / RFI suppression and filtering in harsh, high humidity environments.
AEC-Q200 qualified with PPAP available, the capacitors released, will be used in on-board chargers (OBC), traction inverters, battery management systems (BMS), e-compressors, and AC/DC converters in electric (EV), hybrid electric (HEV), and plug-in hybrid electric (PHEV) vehicles. For these applications, the devices offer high humidity resistance with a Class IIB humidity grade (in accordance with IEC60384-14 annex I) and can withstand the 85 / 85 / 1000 h test.
Allowing for surface-mount assembly with a reflow soldering process, SMDY1 Automotive Series capacitors reduce production costs. Unlike leaded components, the devices offer a low, flat profile on the PCB to enable flat casings or backside PCB mounting without the clearance space required by through-hole capacitors.
RoHS-compliant and halogen-free, the components consist of a copper-plated ceramic disc and feature encapsulation made of flame-resistant epoxy resin in accordance with UL 94 V-0. The devices are available in two case sizes: the C case with a creepage distance of 10 mm and the D case with a creepage distance of 14.5 mm.
The post Vishay Intertechnology Launches Industry’s First Automotive Grade Ceramic Capacitors With Y1 Rating in SMD Casing appeared first on ELE Times.
India’s Export Growth Hits 6.18% in Early FY 2025–26, Driven by Electronics, Pharma, and Gems
During the first five months of FY 2025–26, notwithstanding non-uniform global demand, India’s external trade sector continued to show resilience. Provisional data published by the Ministry of Commerce & Industry state that the cumulative exports both for merchandise and services aggregated to US$ 349.35 billion during April to August 2025, registering a 6.18% year-on-year growth when compared to US$ 329.03 billion during the same period in 2024.
The Ministry, however, went on to say that growth was led by electronics, engineering goods, gems & jewellery, petroleum products, and pharmaceuticals, where services continued to be another key anchor. More importantly, India’s overall trade deficit has narrowed, pointing to a better external balance.
Merchandise exports reached US$ 184.13 billion, a modest 2.52% rise from US$ 179.60 billion last year. Within this, non-petroleum exports showed stronger momentum, climbing to US$ 158.07 billion from US$ 147.25 billion, a 7.35% increase that reflects resilience in India’s core manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
During the same time period, imports were US$ 390.78 billion, up just 2.49% from US$ 381.30 billion the previous year. The country’s trading condition improved as seen by the trade deficit for April–August 2025, which decreased from US$52.27 billion in 2024 to US$41.42 billion.
August 2025:
August proved to be a very successful month for exports, with total shipments totaling US$69.16 billion, up 9.34% from the previous year. In contrast, imports dropped 7% to US$79.04 billion, which significantly decreased the monthly deficit.
- Merchandise exports: US$ 35.10 billion (vs. US$ 32.89 billion in Aug 2024)
- Merchandise imports: US$ 61.59 billion (vs. US$ 68.53 billion)
- Services exports: US$ 34.06 billion (vs. US$ 30.36 billion)
- Services imports: US$ 17.45 billion (vs. US$ 16.46 billion)
- Trade deficit: US$ 9.88 billion, significantly lower than US$ 21.73 billion in August 2024
Sector-Wise Export Drivers (August 2025):
- Electronics: +25.93%, reaching US$ 2.93 billion (vs. US$ 2.32 billion in 2024)
- Engineering goods: +4.91%, totaling US$ 9.90 billion (vs. US$ 9.44 billion)
- Gems & jewellery: +15.57%, valued at US$ 2.31 billion (vs. US$ 2.00 billion)
- Petroleum products: +6.54%, at US$ 4.48 billion (vs. US$ 4.20 billion)
- Pharmaceuticals: +6.94%, climbing to US$ 2.51 billion (vs. US$ 2.35 billion)
India’s export base is diverse, as evidenced by the double-digit rise in cereals, coal & minerals, tea, dairy, poultry, ceramic items, and rice, in addition to these main categories.
The services sector remained a bright spot in India’s external trade. Between April and August 2025:
- Services exports were estimated at US$ 165.22 billion, rising from US$ 149.43 billion last year.
- Services imports stood at US$ 84.25 billion.
- This led to an increase in the surplus from US$ 68.25 billion to US$ 80.97 billion.
This surplus illustrates the worldwide competitiveness of Indian IT services, digital solutions, consulting, and financial services and continues to serve as a crucial buffer against India’s merchandise trade deficit.
Exports in August expanded strongly across both traditional and new destinations:
- UAE: +23.42%
- USA: +7.15%
- Netherlands: +17.87%
- Hong Kong: +62.46%
- China: +22.38%
The sharp rise in shipments to Hong Kong from gems & jewellery and electronics and greater growth to China above all signify an emerging trade linkage of India with Asia, while UAE and USA have stood as reliable supporting engines for export demand.
Key Sources of Imports
On the import front, India saw larger inflows from Russia, Saudi Arabia, Ireland, Iraq, and Qatar. While energy imports seemed to remain the largest from Russian and Middle Eastern suppliers, Ireland became an important source for specialized and high-value imports.
Conclusion:
The Ministry of Commerce & Industry emphasized that the narrowing of the trade deficit alongside the strong growth in the merchandise and services sector testifies to India’s ability to evolve with the shifting global trade dynamics. Electronics, pharmaceuticals, and engineering products are expected to continue to be the main pillars, while agricultural exports add further support.
The post India’s Export Growth Hits 6.18% in Early FY 2025–26, Driven by Electronics, Pharma, and Gems appeared first on ELE Times.
TI unlocks premium motor control in everyday applications with ultra-low-cost real-time MCUs
An expansion of TI’s comprehensive C2000 portfolio, the new MCUs transform the performance of household appliances and power tools
What’s new
Texas Instruments (TI) introduced its most affordable C2000 real-time microcontrollers (MCU), enabling engineers to design products with industry-leading performance at a lower cost. The F28E120SC and F28E120SB MCUs deliver 30% faster computing power compared to previous C2000 MCUs for single motor and power factor correction systems, helping transform the performance of home appliances, from washing machines and dishwashers to vacuum cleaners and power tools.
Powered by TI’s proprietary InstaSPIN field-oriented control (FOC) software and advanced algorithms, these new MCUs enable smoother, quieter and more efficient motor performance. Their advanced capabilities – including high-speed sensorless FOC, high-torque zero-speed startup and sophisticated vibration compensation – deliver highly precise, responsive motor control for everyday applications.
Why it matters
Today’s consumers demand appliances and power tools that operate as efficiently, smoothly and quietly as possible. Yet, historically, system designers have had to compromise by using MCUs with less computing performance and analog integration to meet cost targets.
The F28E12x series of MCUs helps solve this challenge by delivering the performance needed to enable premium motor-control features at a lower price than competing devices. These MCUs eliminate additional components by integrating TI’s C28x digital signal processor core and industry-leading analog peripherals, including a high-speed analog-to-digital converter and programmable gain amplifier, helping simplify designs and lowering costs.
“Since their introduction in the 1990s, TI C2000 MCUs have allowed designers to control both simple and complex motors with low latency and high reliability,” said Vivek Singhal, vice president and general manager, Application-Specific Microcontrollers at TI. “Adding fully featured, ultra-low-cost MCUs to the C2000 portfolio enables new markets to access the industry-leading real-time performance that TI is known for. Using this technology, appliance and power-tool manufacturers can deliver seamless, quiet motor operation, previously considered a luxury, at an affordable price point.”
Moreover, TI’s F28E12x series facilitates fast execution of the sensorless FOC algorithm, enabling motor speeds over 120,000rpm, or 2kHz electrical frequency. The ability to run a motor at high speeds reduces gear transition noise and improves reliability, enabling engineers to design products with smooth, quiet operation. The MCUs can also run a vibration compensation algorithm to achieve up to 60% speed ripple reduction, counteracting the acoustic noise and vibrations caused by an imbalanced load in applications such as washing machines.
The post TI unlocks premium motor control in everyday applications with ultra-low-cost real-time MCUs appeared first on ELE Times.



