Новини світу мікро- та наноелектроніки
EEVblog 1723 - AlienTek DM40 Multimeter/Oscilloscope Review
onsemi releases EliteSiC MOSFETs in T2PAK top-cool package
My class AB amplifier
 | So, I'm developing a guitar amplifier for a friend, and I need a high power (as for my standards) amp to make it loud. So I made this one, the most powerful discrete amp to date, that can deliver 20Vpp to 8 ohm speaker without distortion at 24V supply. I had a problem with connecting everything for tests and idle current calibration because PCB is , so i had to improvise. I put a power diode into ground terminal of amp, connected a big clip of function generator ground, then connecred small clip of power supply ground, and scope ground to power supplu ground clip. The effect is this big tangle of wires and connectors, but it worked as intended. The design is a variation of amp from 70s record player but with changed voltage rating and conversion from class B to AB. It's suprisingly stable and silent when input is floating, so I like it. [link] [comments] |
The Big Allis generator sixty years ago

Think back to the 1965 electrical power blackout in the Northeast United States of just over sixty years ago. It was on November 9, 1965. There was a huge consequence for Consolidated Edison in New York City.
Their power-generating facility in Ravenswood had been equipped with a generator made by Allis-Chalmers, as shown in the following screenshots.

Figure 1 Ravenswood power generating facility and the Big Allis power generator.
That generator was the largest of its kind in the whole world at that time. Larger generators did get made in later years, but at that time, there were none bigger. It was so big that some experts opined that such a generator would not even work. Because of its size and its manufacturer’s name, that generator came to be called “Big Allis”.
Big Allis had a major design flaw. The bearings that supported the generator’s rotor were protected by oil pumps that were powered from the Big Allis generator itself.
When the power grid collapsed, Big Allis stopped delivering power, which then shut down the pumps delivering the oil pressure that had been protecting the rotor bearings.
With no oil pressure, the bearings were severely damaged as the rotor slowed down to a halt. One newspaper article described the bearings as having been ground to dust. It took months to replace those bearings and to provide their oil pumps with separate diesel generators devoted solely to maintaining the protective oil pressure.
So far as I know, Big Allis is still in service, even through the later 1977 and 2003 blackouts, so I guess that those 1965 revisions must have worked out.
John Dunn is an electronics consultant, and a graduate of The Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn (BSEE) and of New York University (MSEE).
Related Content
- Modern Distribution Grid Technologies
- Power grid blackouts: Are they preventable and predictable?
- Teardown: The power inverter – from sunlight to power grid
- Inventions that were almost ahead of their time
The post The Big Allis generator sixty years ago appeared first on EDN.
Optimized analog front-end design for edge AI
Courtesy: Avnet
| Key Takeaways:
01. AI models see data differently: what makes sense to a digital processor may not be useful to an AI model, so avoid over-filtering and consider separate data paths 02. Consider training needs: models trained at the edge will need labeled data (such as clean, noisy, good, faulty) 03. Analog data is diverse: match the amplifier to the source, consider the bandwidth needs of the model, and the path’s signal-to-noise ratio |
Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) have expanded the market for smart, low-power devices. Capturing and interpreting sensor data streams leads to novel applications. ML turns simple sensors into smart leak detectors by inferring why the pressure in a pipe has changed. AI can utilize microphones in audio equipment to detect events within the home, such as break-ins or an occupant falling.
For many applications that rely on real-world data, the analog front-end (AFE) is one of the most important design elements as it functions as a bridge to the digital world. At a high level, AFEs delivering data to a machine-learning back-end have broadly similar design needs to conventional data-acquisition and signal-processing systems.
But in some applications, particularly those in transition from IoT to AIoT, the data is doing double-duty. Sensors could be used for conventional data analysis by back-end systems and also as real-time input to AI models. There are trade-offs implied by this split, but it could also deliver greater freedom in the AFE architecture. Any design freedom must still address overall cost, power efficiency, and system reliability.
The importance of bandwidth and signal-to-noise ratio
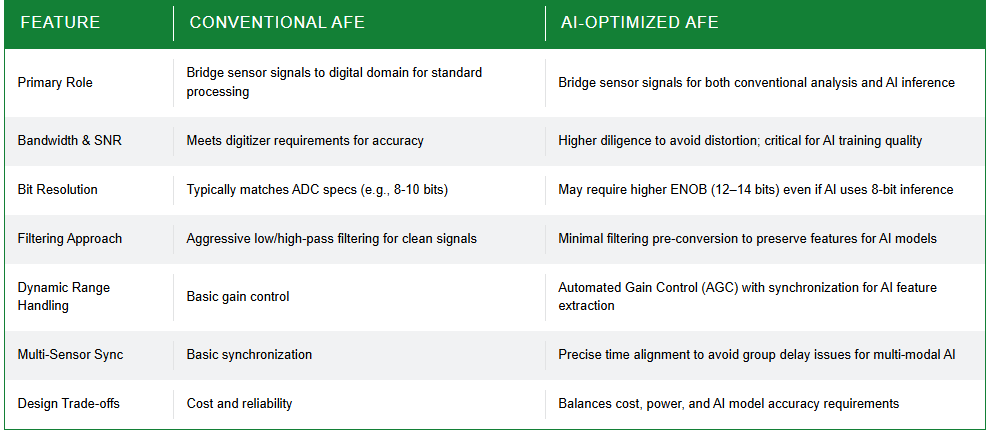
Accuracy is often an imperative with analog signals. The signal path must deliver the bandwidth and signal-to-noise ratio required by the front-end’s digitizer. When using AI, designers will be more diligent when avoiding distortion, as introducing spurious signals during training could compromise model training.
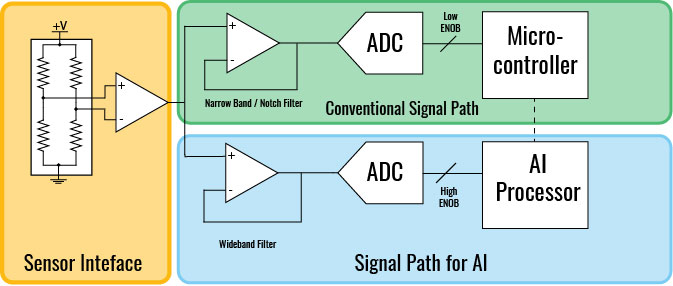 The classic AFE may need to change to accommodate the sensor and digital processing sections, and the AI model’s needs which may be different. (Source: Avnet)
The classic AFE may need to change to accommodate the sensor and digital processing sections, and the AI model’s needs which may be different. (Source: Avnet)
For signals with a wide dynamic range, it may make sense to employ automated gain control (AGC) to ensure there is enough detail in the recorded signal under all practical conditions. The changes in amplification should also be passed to the digitizer and synchronized with the sensor data so they can be recorded as features during AI training or combined by a preprocessing step into higher-resolution samples. If not, the model may learn the wrong features during training.
Interfacing AI systems with multi-sensor designs
Multi-sensor designs introduce another consideration. Devices that process biological signals or industrial condition-monitoring systems often need to process multiple types of data together. Time-synchronized data will deliver the best results as changes in group delay caused by filtering or digitization pipelines of different depths can change the relationship between signals.
The use of AI may lead the designer to make choices they might not make for simpler systems. For example, aggressive low- and high-pass filtering might help deliver signals that are easier for traditional software to interpret. But this filtering may obscure signal features that are useful to the AI.
| Design Tip – Analog Switches & Multiplexers
Analog switches and multiplexers perform an important role in AFEs where multiple sensors are used in the signal chain. Typically, devices are digitally addressed and controlled, switches selectively connect inputs to outputs, while multiplexers route a specific input to a common output. Design considerations include resistance, switching speed, bandwidth, and crosstalk. |
For example, high-pass filtering can be useful for removing apparent signal drift but will also remove cues from low-frequency sources, such as long-term changes in pressure. Low-pass filtering may remove high-frequency signal components, such as transients, that are useful for AI-based interpretation. It may be better to perform the filtering digitally after conversion for other downstream uses of the data.
Techniques for optimizing energy efficiency in AFEs
Programmable AFEs, or interchangeable AFE pipelines, can improve energy optimization. It is common for edge devices to operate in a low-energy “always on” mode, acquiring signals at a relatively low level of accuracy while the AI model is inactive. Once a signal passes a threshold, the system wakes the AI accelerator and moves into a high-accuracy acquisition mode.
That change can be accommodated in some cases by programming the preamplifiers and similar components in the AFE to switch between low-power and low-noise modes dynamically.
A different approach often used in biomedical sensors is to use changes in duty cycles to reduce overall energy. In the low-power state, the AFE may operate at a relatively low data rate and powered down during quiet intervals. The risk arises of the system missing important events. An alternative is to use a separate, low-accuracy AFE circuit that runs at nanowatt levels. This circuitry may be quite different to the main AFE signal path.
In audio sensing, one possibility is to use a frequency-detection circuit coupled with a comparator to listen for specific events captured by a microphone. A basic frequency detector, consisting of a simple bandpass filter and comparator, may wake the system or move the low-power AFE into a second, higher-power state, but not the full wakefulness mode that engages the back-end digital AI model.
In this state, a circuit such as a generalized impedance converter can be manipulated to sweep the frequency range and look for further peaks to see if the incoming signal meets the wakeup criteria. That multistage approach will limit the time during which the full AI model needs to be active.
Breaking down analog front-ends for AI
Further advances in AI theory enable more sophisticated analog-domain processing before digitization. Some vendors have specialized in neural-network devices that combine on-chip memory with analog computation. Another possibility for AFE-based AI that results in a lower hardware overhead is reservoir computing. This uses concepts from the theory of recurrent neural networks. A signal fed back into a randomly connected network, known as the reservoir, can act as a discriminator used by an output layer that is trained to recognize certain output states as representing an event of interest. This provides the ability to train an AFE on trigger states that are more complex than simple threshold detectors.
Another method for trading off AFE signal quality against AI capability is compressive or compressed sensing. This uses known signal characteristics, such as sparsity, to lower the sample rate and, with it, power. Though this mainly affects the choice of sampling rate in the analog-to-digital converter, the AFE still needs to be designed to accommodate the signal’s full bandwidth. At the same time, the AFE may need to incorporate stronger front-end filtering to block interferers that may fold into the measurement frequency range.
Optimizing AFE/AI trade-offs through experimentation
With so many choices, experimentation will be key to determining the best tradeoffs for the target system. Operating at higher bandwidth and resolution specifications is a good start. Data can be readily filtered and converted to the digital domain at lower resolutions to see how they affect AI model performance.
The results of those experiments can be used to determine the target AFE’s specifications in terms of gain, filtering, bandwidth, and the ENOB needed. Such experiments also provide opportunities to experiment with more novel AFE processing, such as reservoir computing and compressive sensing to gauge how well they might enhance the final system.
The post Optimized analog front-end design for edge AI appeared first on ELE Times.
X-FAB’s XbloX accelerates time-to-market for scalable, high-performance SiC MOSFETs
Introducing Wi-Fi 8: The Next Boost for the Wireless AI Edge
Courtesy: Broadcom
Wi-Fi 8 has officially arrived—and it marks a major leap forward for next-generation connectivity.
Wi-Fi has come a long way. Earlier generations (Wi-Fi 1 through 5) focused mainly on delivering content to users: streaming video, online gaming, and video calls. But today’s digital world runs in both directions. We create as much data as we consume. We upload high-resolution content, collaborate in real time, and rely on on-device AI for everything from productivity to entertainment. That makes the “last hop” between devices and wireless networks more critical than ever.
Wi-Fi 8 is built for this new reality. Evolving from the advances of Wi-Fi 6 and 7, it offers reliable performance at scale, consistently low latency, and significantly stronger uplink capacity—precisely what modern, AI-driven applications need to run smoothly and responsively.
Why Wi-Fi 8 Matters
The internet has shifted from passive browsing to immersive, interactive, and personalized experiences. Devices now sense, analyze, and generate data constantly. By the end of 2025, hundreds of millions of terabytes will be created every day, much of it from IoT, enterprise telemetry, and video. A lot of that data never even makes it to the cloud—it’s handled locally. But guess what still carries it around? Wi-Fi.
Uplink matters
Traditional traffic patterns skewed roughly 90/10 downlink/uplink. Not anymore. AI apps, smart assistants, and continuous sync push networks toward a 50/50 split. Your Wi-Fi can’t just be fast going to you—it has to be equally fast, fair, and predictable going from you.
Real-time Wi-Fi
In the age of AI, Wi-Fi has to be far more real-time. Take, for example, agentic apps that work with voice inputs. We all know today’s assistants can feel clunky—they buffer, they miss interruptions. To get to your true agentic assistant with a “Jarvis-like” back-and-forth, networks need ultra-low latency, less jitter, and fewer drops.
With the right broadband and Wi-Fi 8, those thresholds become possible.
What’s New in Wi-Fi 8
Wi-Fi 8 delivers a system-wide upgrade across speed, capacity, reach, and reliability. Here’s what that means in practice:

Higher throughput—more of the time: Wi-Fi 8 achieves higher real-world speeds with smarter tools. Unequal Modulation ensures each stream runs at its best rate, so one fading link doesn’t drag the others down. Enhanced MCS smooths out the data-rate ladder to prevent sudden slowdowns, while Advanced LDPC codes hold strong even in noisy conditions. The result: faster, steadier performance across the network.
More network capacity in busy air: In crowded spaces, Wi-Fi 8 is built for cooperation. Inter-AP Coordination helps access points schedule transmissions instead of colliding. Non-Primary Channel Access (NPCA) taps into secondary channels when the primary is congested, while Dynamic Subband Operation (DSO) lets wide channels serve multiple narrower-band clients at once. Dynamic Bandwidth Expansion (DBE) then selectively opens wider pipes for Wi-Fi 8 devices without disrupting legacy clients—unlocking more usable capacity where it’s needed most.
Longer reach and stronger coverage close to the edge: Connections go farther with Distributed Resource Units (dRU), which spread transmit energy for noticeable gains at the fringe. And with Enhanced Long Range (ELR), a special 20-MHz mode extends coverage up to 2× in line-of-sight and about 50% farther in non-LoS—keeping links alive even at the outer edge of the network.
Reliability and QoS that stick: Real-time apps get the consistency they need thanks to smarter quality-of-service features. Low-Latency Indication prioritizes AR/VR, gaming, and voice traffic, while Seamless Roaming keeps calls and streams intact during movement. QoS enhancements and Prioritized EDCA reduce latency and prevent bottlenecks across multiple streams. Plus, enhanced in-device coexistence coordinates Wi-Fi with Bluetooth, UWB, and more to avoid self-interference. Together, these features make the network feel smoother and more reliable.
Wi-Fi 8 Real-World Impact
So what does all this look like in everyday use? Assume a busy apartment building, or an office full of devices roaming between access points. Signals aren’t perfect, interference is everywhere, but Wi-Fi 8 keeps things flowing. It does this by coordinating access points, smoothing out delays, and reducing radio clashes—so your most important traffic doesn’t get stuck in line.
Picture this: It’s a busy evening in a modern family home. One person is streaming a live sports match in 8K on the big screen, another is deep into an online game while streaming to friends, and a third is working on a project that involves real-time AI voice assistance.
Meanwhile, the smart doorbell detects someone approaching. But instead of just pinging a vague “motion alert,” the AI-powered camera recognizes whether it’s a delivery driver dropping off a package, a neighbor stopping by, or a family member arriving home. The alert is contextual and useful.
In older Wi-Fi environments, that mix of high-bandwidth streams, real-time gaming, and constant AI inference could lead to stutters, buffering, or dropped packets at the worst moments. With Wi-Fi 8, all of it just works. The 8K stream stays crisp. The gamer experiences smooth, low-latency play. The AI assistant responds instantly without awkward delays. And the doorbell notification comes through without competing for airtime—because the network can intelligently prioritize, coordinate, and balance all that traffic.
That’s the difference Wi-Fi 8 brings: a reliable home network, no matter how many devices or demands are piled on at once.

Why it works: Wi-Fi 8 increases throughput and, at the same time, greatly reduces the 99th percentile latency tail. By coordinating APs, elevating delayed packets, and reducing radio self-contention, it shortens queues, avoids collisions, and keeps critical traffic flowing—even when signals aren’t perfect.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi 8 represents far more than an incremental upgrade—it marks a fundamental shift in how wireless networks will power the AI-driven world. As our homes, offices, factories, and devices generate and process more data than ever, the need for reliable uplink performance, real-time responsiveness, and intelligent coordination becomes non-negotiable. Broadcom’s new ecosystem brings these capabilities to life, ensuring that next-generation applications—from immersive entertainment and autonomous IoT to true conversational AI—can operate smoothly, consistently, and securely.
With Wi-Fi 8, the wireless edge finally catches up to the ambitions of modern computing. It isn’t just faster Wi-Fi; it’s the foundation for the seamless, AI-enabled experiences we’ve been waiting for—and a major leap toward the connected future we’re building every day.
The post Introducing Wi-Fi 8: The Next Boost for the Wireless AI Edge appeared first on ELE Times.
Design specification: The cornerstone of an ASIC collaboration

Engaging with an ASIC development partner can take many forms. The intended chip may be as simple as a microcontroller, as sophisticated as an AI-based edge computing system-on-chip (SoC), or even a large language model (LLM) AI accelerator for data centers. The customer design team may include experienced ASIC design, verification, and test engineers or comprise only application experts. Each customer relationship is different.
Yet they all share one fundamental need. The customer and the ASIC developer must agree, in greater detail, on what they are trying to build. That is the role of design specification documents. At Faraday, this document is the cornerstone of conversations between customers and chip design teams, covering critical decisions throughout the design process. The topics can range from initial feasibility estimation through sign-off and beyond.
If the design specification is so important, an obvious question arises: how do you construct a specification that will result in a successful ASIC design experience? However, the real answer is that a successful design specification is a joint effort between the customer and the ASIC development partner.
So, there must be a comprehensive, cooperative, checklist-driven procedure for creating a design specification. It allows to mesh smoothly with customers’ design teams, whether they are starting with only a wish list of features or with a detailed design plan. It also works across a wide range of sizes and complexities in today’s ASIC landscape.
What design specification does
The design specification will serve many purposes during the ASIC design. Fundamentally, it will list the design requirements for the ASIC implementation team. As such, it will serve as a shopping list of silicon IP to be included in the design, an outline of the architecture that integrates that IP, and a guide for integration, verification, and testing.
Less obviously, the design specification can be a point of reference for discussions that will take place between the customer and the design team. What exactly should this block do? How much power can we allocate to this function? Does this alternative approach to implementation work for you? All these discussions can begin with the design specification.
Also, the specification can be invaluable for tasks where the customer is often uninvolved. For example, knowing the design intent and how the chip will be used can be priceless in developing verification plans, self-test architectures, test benches, and manufacturing test strategies. Information from the design specification is vital for detailed design activities, such as determining clock architectures and power-management strategy, in which the customer would typically not be directly involved.
Key elements of design specification
So, what goes into the design specification? There are several important categories of information. The most obvious is a set of functional requirements—what the chip is supposed to do. Often, this will be a list of features, but it may be much more detailed. It’s also essential that the specifications include performance, power, and area requirements.
These will influence many conversations, from our initial feasibility assessment to foundry and process selection, library selection, and power-management strategies. And much of this information will be included in the specifications.
It’s also essential to capture a description of the system in which the chip will operate, including the other components. For example, which SPI flash chip will be used for an external flash? The minor differences in SPI protocols between memory chips can determine which SPI controller IP we select.
Another essential kind of system information is more physical: the thermal and mechanical environment. Heat sinks, passive or forced-air cooling, and so on will influence power management and package design.
Not just what, but how
The specification is not just a list of requirements. It also jointly develops design plans for implementing the chip. Chief among these is the gross architecture.
The architecture of an ASIC may be implicit in its function. For instance, a microcontroller may be a CPU core, some memory on a memory bus, and some peripheral controllers on a low-speed peripheral bus. However, a more elaborate SoC may have several CPU cores clustered around a shared cache and a hierarchy of buses, determined by the bandwidth and latency requirements of particular data flows between the memory and IP instances. If the customer hasn’t already decided on architecture, the design team will develop a proposal and review it with the customer.

Figure 1 An example of the proposed architecture for the customer is highlighted in a comprehensive diagram that describes the architecture and provides additional information. Source: Faraday Technology Corp.
In some cases, the customer will already have architecture in place. This may be because the chip extends to an existing product family. Or it may use a network-on-chip (NoC) scheme or something entirely original, such as a data-flow architecture designed to accelerate a particular algorithm. In these cases, ASIC designer’s role is to ensure that the information in the specification is complete enough to capture the design intent unambiguously, to drive the selection of IP with the proper interfaces, and to adequately inform about the chip layout.
The specification may also include information about specific IP blocks. If a block is a controller for a standard interface—say, a USB controller—then there needs to be enough additional information. For instance, it should be a Gen3 USB host with power delivery to allow the design team to select the appropriate IP.
In some cases, a functional block may be something unique. This often happens when the IP is customer specific. In these cases, the customer must provide enough detail for the design team to create and test the block. This may be simply a detailed functional description. Or it may require pseudo-code or Verilog code for critical portions of the block.
Pulling it together
Altogether, the design specification becomes an agreed-upon statement of what the customer requires and what the design team is designing. But which parts of the document come from the customer, which are jointly written, and which are supplied by ASIC designer for the customer to review vary widely from case to case.
At Faraday, we have developed a formal process, called e-cooking, to collect the data. The process begins with a request for a quote from our sales organization. This RFQ will often contain much of the information we need for the design specification.
With RFQ in hand, we assign an engineer to the project in a role we call a technical consultant (TC). TC begins working through a design checklist to transfer information from the RFQ to the design specification.
When an item is missing or requires more detail, TC will contact the customer, explain what further information we need and why, and obtain the necessary data. If the item requires information the customer can’t provide—for instance, a choice of logic libraries—TC can ask the Faraday design team for input, which we then share with the customer for review.
The completed design specification document is a blueprint for the chip design. It will provide information regarding architectural and IP selection, verification, test plans, and packaging choices. It will also explain the statement of work, which describes which design tasks will be done by the customer and which by ASIC designer.

Figure 2 Technical consultants and engineers enter all project information into the e-cooking system, a tool that tracks the chip’s content. Source: Faraday Technology Corp.
The e-cooking process aims to capture customers’ design intent and the work they have already done toward implementation (Figure 2). The designers enter information into the tool, such as the actual cell size and name, silicon area, quantity, spacing, and I/O.
Next, ASIC designer reviews any suggestions for changes or additional data with the customer team. That brings clarity on what ASIC designer intends to implement at the start of the project. By the end of the project, the only surprises are how smoothly the two teams worked together and how well the delivered chip met customers’ expectations.
Barry Lai heads the System Development and Chip Design department at Faraday Technology Corp., a leading provider of ASIC design services and IP. With 20 years of experience in IC design, Barry specializes in SoC integration, specification definition, digital design, low-power design, and integration automation.
Related Content
- Best practices for structured-ASIC design
- Arrow and Avnet launch ASIC design services
- Why ASIC Design Makes Sense for LLM-On-Device
- An FPGA-to-ASIC case study for refining smart meter design
- A 12-point overview of the advantages of custom analog ASICs
The post Design specification: The cornerstone of an ASIC collaboration appeared first on EDN.
All I need is a 470uf capacitor
 | Can't run down to RS anymore [link] [comments] |
Vehicle to Grid (V2G) Charging in EVs: Understanding the Basics
Much of the research around emerging technologies in Electric vehicles is looking within the EV system and lack a comprehensive review of EV integration and its impact on Power system planning and operation, across transmission and distribution levels.
Shift Toward Bidirectional Energy Flows
Vehicle to Grid (V2G) charging is a phenomenal step taken in direction of placing EVs on the energy landscape where they can contribute to grid stability. V2G integration provides a paradigm shift from an era of unidirectional energy flow and introduces bidirectional energy transfer between EVs and energy grid. EVs essentially act as renewable energy storage units facilitating load balancing, peak shaving and frequency regulation within the grid.
Core Components of V2G Systems
- EV as Portable Energy Storage: The V2G system primarily consist of EV as a potable energy storage system fitted with a battery management system (BMS).
- EVSE, Chargers and Communication Interfacee: The Electrical vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) is connected to the EV, including a bidirectional charger and a communication interface that allows data flow between EV, grid and the user.
- Supporting Infrastructure: It also integrates a transformer to manage voltage levels, a smart meter for precise monitoring and an aggregator platform for coordination of combined energy sources from many EVs.
Variants of Bidirectional Charging
In addition to V2G, bidirectional energy transfer covers V2H (vehicle-to-home) and V2L (vehicle-to-load) charging.
Global Deployment Landscape
Adoption Examples: Virta Global, is a European country headquartered at Helsinki, Finland that is leading in providing V2G solutions. It has installed seven V2G chargers at its premises in Finland. Virta has installed 20 chargers at a Nissan manufacturing plant in the UK.
Economic Considerations
Battery Cycling and Infrastructure Costs: There are, however, cost considerations to be considered with V2G charging. The batteries in a V2G setup are subject to wear and tear due to frequent charging and discharging cycles. Advance chargers and communication systems add to the cost, even though a part of it is offset by revenue opportunities gained from selling stored energy.
Impact on Power Networks
- Grid Benefits and Load Management: The electrical network is largely benefited by V2G charging during load shifting, load building, power conservation, peak clipping, valley filling and flexible loads. As increasingly EVs get integrated into the system, power imbalances on the load side are bound to occur. The ancillary services provided by the V2G setup help in alleviating certain congestions on the network.
Role of Aggregators and Control Models
Aggregation for Frequency Control: Aggregation of numerous EVs into grid through V2G setup for primary frequency control is a critical to larger EV integration into the transportation system. Aggregators assist in providing services to individual EVs and serve the purpose of a bigger and more appropriate load for utility.
Models Used in Research
Studies are ongoing on several aggregated models for large-scale EV integration. Some researchers use an independent distributed Vehicle to grid regulation arrangement while others use master slaves grid regulation technique for microgrid (MG) in islanding mode.
Modified Droop Controller Approach
However, modified droop controller method is considered better than others where the reference signal is controlled and monitored uninterruptedly by a droop controller possessing feedback mechanism. Such controller is known as Modified droop controller.
Technical Capabilities of V2G Systems
- Active and Reactive Power Support: In V2G system, the vehicle can provide active power regulation, current harmonic filtering, reactive power support and tracing of adjustable renewable energy sources.
- Ancillary Services: With the help of these, ancillary services such as frequency and voltage control can be facilitated.
Microgrid-Level Power Balancing
Optimized Charging Schedules: A better balance of power in a microgrid can be achieved by Vehicle to grid systems. With the help of intelligent charging schedules, the vehicle can discharge during peak hours, charge during off-peak hours, thereby improving the load curve.
Voltage and Frequency Regulation
Up and Down Regulation
Regulation of voltage and primary frequency are crucial for energy markets. When the voltage supply from the grid is high, the EV battery is in charging state known as down regulation. On the contrary, when supply from the grid is low, EV battery is in discharging state also known as up regulation. This may affect the frequency. The primary purpose of frequency control is to maintain equilibrium between generation and demand within specific time duration. Regulation services can be provided within V2G systems to reduce pressure on the power grid.
Harmonic Filtration and Power Quality
Need for Harmonic Control: Maintaining the quality of power supplied back to the grid through Harmonic filtration is essential for any emerging V2G technology.
Advances in Digital IIR Filters: Recently, real-time digital infinite impulse response (IIR) filters are developed for the same. IIR filters generate reference signals at the power calculation stage. Digital filters offer various advantages over passive and active filters in inverter output signals of V2G applications like real-time processing, adaptability, improved performance with better noise reduction, increased control and lower costs.
V2G Applications in Fuel-Cell EVs
IIR Filters in FCEVs: Digital IIR filters are mostly implemented in Fuel Cell Electric vehicles (FCEVs) because they require less memory and have less computational complexity.
Global Research Initiatives
The European Union’s Hydrogen Mobility Europe 2 (H2ME2) project is researching and developing V2G technology for FCEVs to demonstrate the technology in a real-world setting. Other companies, such as Toyota and Hyundai, have also announced plans to develop V2G technology for their FCEVs. Moreover, companies like Texas instruments are researching on application of digital IIR filters.
Conclusion: EVs as Grid Assets
Electric vehicles can act both as a load and a potential power source which can be integrated into the power system when required. Adequate studies on the stresses that a power distribution system can experience due to large scale EV adoption are imperative and equally imperative is to come up with alternatives like V2G technology that can overcome some of these challenges.
The post Vehicle to Grid (V2G) Charging in EVs: Understanding the Basics appeared first on ELE Times.
I made my own open-source FPGA board.
 | I wanted to get started with FPGAs by making my own development board, and thus I made Arctyx Nano! https://github.com/Keyaan-07/Arctyx-Nano - everything is open-sourced under MIT License! Arctyx Nano is a low-cost, open source FPGA development board carrying the ICE40-UP5K FPGA from lattice along with the RP2350A in a raspberry pi pico form factor. It consists of 6 LEDs and one RGB LED. All the pins on both the ICs are used in one way or another. I am currently using APIO open-source toolchain to verify, simulate and build projects and to upload using APIO, i have to figure it out. This is my first FPGA PCB and i would love feedback on my design! This board was created as a project for hackclub blueprint, check it out!! [link] [comments] |
Small pcb pile
 | submitted by /u/goldfish_in_the_wall [link] [comments] |
The insides of a phone in a dorm room in Poland
 | submitted by /u/GRAPHENE9932 [link] [comments] |
High-voltage SiC MOSFETs power critical energy systems

Navitas is now sampling 2.3-kV and 3.3-kV SiC MOSFETs in power-module, discrete, and known-good-die (KGD) formats. Leveraging fourth-generation GeneSiC Trench-Assisted Planar (TAP) technology, these ultra-high-voltage devices offer improved reliability and performance for mission-critical energy-infrastructure applications.

According to Navitas, the TAP architecture uses a multistep electric-field management profile that significantly reduces voltage stress and improves blocking performance compared with trench and conventional planar SiC MOSFETs. In addition to increased long-term reliability and avalanche robustness, TAP incorporates an optimized source contact that enables higher cell-pitch density and improved current spreading. Together, these advances deliver better switching figures of merit and lower on-resistance at elevated temperatures.
Packaging options include the SiCPAK G+ power module, which uses epoxy-resin potting to deliver more than a 60% improvement in power-cycling lifetime and over a 10% improvement in thermal-shock reliability compared with similar silicone-gel–potted designs. Discrete SiC MOSFETs are offered in TO-247 and TO-263-7 packages, while KGD products provide system manufacturers with greater flexibility for custom SiC power-module development. AEC-Plus–grade SiC devices are qualified to standards that exceed conventional AEC-Q101 and JEDEC requirements.
To request samples of the ultra-high-voltage SiC MOSFETs, contact Navitas at info@navitassemi.com.
The post High-voltage SiC MOSFETs power critical energy systems appeared first on EDN.
Thermistors suppress inrush currents

S series NTC thermistors from TDK Electronics handle steady-state currents up to 35 A and absorb energy up to 750 J. They enable reliable inrush current suppression in switch-mode power supplies, frequency converters, photovoltaic inverters, UPS systems, and soft-start motors.

The S series includes two leaded variants—the S30 and S36—with disk diameters of 30 mm and 36 mm, respectively. The S30 features 7.5-mm lead spacing and a maximum power handling of 19 W, while the larger S36 has 19-mm lead spacing and extends power handling to 25 W. Both variants are rated for a wide climatic category of 55/170/21 in accordance with IEC 60068-1 requirements.
The S30 (ordering code B57130S0M000) and S36 (B57136S0M100) families cover basis resistance values of 2 Ω to 15 Ω and 2 Ω to 20 Ω, respectively. They support continuous currents ranging from 12 A to 25 A (S30) and 10 A to 35 A (S36). Permissible capacitances can reach up to 13,050 µF at 240 VAC (see datasheet for details). The table below summarizes the key electrical characteristics of the S30 and S36 variants.

To access the datasheets for the S30 series and S36 series, click here.
The post Thermistors suppress inrush currents appeared first on EDN.
Compact 1.25-kV MLCCs ensure stability

Murata has begun mass production of 1.25‑kV multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) with a capacitance of 15 nF in a 1210-size (3.2×2.5 mm) package. These MLCCs use a Class 1 ceramic dielectric (C0G, also known as NP0), making them a strong choice for onboard chargers in electric vehicles and power supply circuits in high-performance consumer devices.

Leveraging Murata’s ceramic and electrode materials, along with thin-layer molding and precision stacking technologies, these chip capacitors are optimized for the latest SiC MOSFETs. Thanks to the inherent advantages of C0G per EIA standards—low loss and stable capacitance across a temperature range of -55°C to +125°C—they are suitable for both resonant and snubber circuits.
For added design flexibility, 1.25‑kV MLCCs in the 1210 package are also available in capacitances from 4.7 nF to 12 nF. All of the new devices, including the 15‑nF chip, are offered with tolerances of ±1%, ±2%, and ±5%.
Datasheets for the new high-voltage MLCCs in the 1210 package can be accessed here.
The post Compact 1.25-kV MLCCs ensure stability appeared first on EDN.
Enhanced hybrid caps handle increased ripple current

Taiyo Yuden has launched the HVX(-J) and HTX(-J) series of conductive polymer hybrid aluminum electrolytic capacitors. These updated models offer a higher rated ripple current and a lower profile than previous HVX and HTX capacitors. They also meet the AEC-Q200 standard, ensuring reliability for automotive applications.

With increasing current demands in automotive power sources, there is growing need for hybrid capacitors that combine higher ripple current ratings, compact profiles, and a variety of sizes. The HVX(-J) and HTX(-J) series address this need, offering 36 different types. For example, the RAHTX331M1TFH0002JX achieves 3400 mA RMS at 135 °C—a 70% increase over the previous model’s 2000 mA RMS at the same temperature. Devices in the series are available in five package sizes, ranging from 8 mm in diameter and 10 mm in height to 12.5 mm in diameter and 13.5 mm in height.
The new hybrid capacitors offer rated voltages of 25 VDC to 63 VDC, capacitance values from 47 µF to 1000 µF, and high rated ripple currents at 135°C ranging from 2200 mA RMS to 4000 mA RMS. These performance characteristics make them well suited for noise suppression and power smoothing in automotive power-supply circuits, including control systems such as electric power steering and safety-critical applications like ADAS.
More information on the HVX(-J) and HTX(-J) series can be found here.
The post Enhanced hybrid caps handle increased ripple current appeared first on EDN.
Chip antennas boost Wi-Fi and UWB signal integrity

Three chip antennas from Taoglas—the ILA.257, ILA.68, and ILA.89—provide Wi-Fi 6/7, ultra-wideband (UWB), and ISM connectivity. Manufactured using a low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) process, the antennas deliver high radiation efficiency and frequency stability in ultra-compact packages. According to Taoglas, they also require a smaller keep-out area than competing antennas.

The ILA.257 is a 3.2×1.6×0.5-mm antenna for Wi-Fi 6/7, providing tri-band coverage across 2.4 GHz, 5.8 GHz, and 7.125 GHz with strong radiation efficiency and stable signal integrity. Its small footprint and minimal keep-out area make it well-suited for wearables, portable electronics, and industrial IoT devices.
Engineered for UWB operation from 6 GHz to 8.5 GHz, the ILA.68 3.2×1.6×1.1-mm antenna delivers a stable omnidirectional radiation pattern with consistent repeatability and low insertion loss. It supports applications such as indoor positioning, access control, and short-range radar in space-constrained IoT and automotive systems.
Designed for the 868-MHz and 915-MHz ISM bands, the ILA.89 supports global LPWAN and LoRa deployments with up to 47.9% radiation efficiency and 0.56 dBi peak gain. Its 4.0×12.0×1.6-mm footprint, simple layout, and regional variants help reduce design complexity and speed time-to-market for small IoT devices.
The ILA.257, ILA.68, and ILA.89 antennas are now available from Taoglas and its authorized distributors.
The post Chip antennas boost Wi-Fi and UWB signal integrity appeared first on EDN.
Handheld enclosures add integrated cable glands

OKW now offers CONNECT fast-assembly handheld plastic enclosures with optional integrated cable glands, making it easier to install power and data cables.
Cost-effective CONNECT is ideal for network technology, building services, safety engineering, IoT/IIoT, medical devices, analytical instruments, data loggers, detectors, sensors, test and measurement.
 (Source: OKW Enclosures Inc.)
(Source: OKW Enclosures Inc.)
CONNECT’s two case shells snap together for fast and easy assembly: no screws are required. This offers the choice of two ‘fronts’: one shell is convex – perfect for LEDs – while the other is flat and recessed for a compact display or membrane keypad. Inside the flat shell there are mounting pillars for PCBs and components.
CONNECT enclosures feature open apertures at each end. For these, design engineers can specify a combination of ASA+PC blank end panels and soft-touch TPE cable glands with integrated strain relief. Cable diameters from 0.134“ to 0.232“ are accommodated. The two long sides provide ample space for USB connectors.
These UV-stable ASA+PC (UL 94 V-0) enclosures are available in six sizes from 2.36″ x 1.65″ x 0.87″ to 6.14″ x 2.13″ x 0.87″. The standard colors are off-white (RAL 9002) and black (RAL 9005). Custom colors are also available.
The cable glands come in volcano (gray) and black (RAL 9005). The end parts are off-white (RAL 9002) and black (RAL 9005). Other accessories include wall holders, rail holding clamps for round tubes up to ø 1.26″, and self-tapping screws.
OKW can supply CONNECT fully customized. Services include machining, lacquering, printing, laser marking, decor foils, RFI/EMI shielding, and installation and assembly of accessories.
For more information, view the OKW website: https://www.okwenclosures.com/en/Plastic-enclosures/Connect.htm
The post Handheld enclosures add integrated cable glands appeared first on EDN.
DSO-TC3 Oscilloscope Test with Signal Generator - Signal Test - Sine wav...
 | We used the following circuit elements for measurement trials: [link] [comments] |



