ELE Times
The Semicon India program has brought new energy to the ecosystem: Jose Lok, element14
“The Semicon India program has brought new energy to the ecosystem, signaling the government’s commitment to building a resilient and self-sufficient semiconductor value chain,” says Jose Lok, Product Category Director, Semiconductors, element14, in an exclusive interaction with the ELE Times under its exclusive series ‘Powering the Chip Chain.’ As India wrapped up its largest electronics and semiconductors carnival this month, we grabbed the hot seat to discuss some very pertinent issues with Jose, representing element14, a consistent feature of Global 500 Fortune companies, with its resounding presence across 140 countries, with over 125 company locations.
Reflecting on India’s journey in electronics and semiconductors, he says, “India’s semiconductor landscape is going through a remarkable transformation.” Underlining the impact of schemes like Semicon India, PLI, and DLI, he highlights the momentum contributed by these schemes to the wholesome electronics and semiconductor ecosystem of India. This is further coupled by India’s growing influence over the global supply chain as demand peaks back home across sectors like automotive, IoT, and industrial automation.
Making Access Easier and Efficient
In the interaction, Jose touched upon the critical challenges faced by the design engineers in developing new products. He says, “Engineers often face long lead times, difficulty sourcing small quantities for prototypes, and a lack of visibility into real-time inventory,” as he underlines the pain points.
He further adds that the company has made its business in India largely by addressing these pain points and making it easier for engineers in prototyping and R&D, including its intuitive e-commerce platform and an inventory of over 950,000 products from 2,000 leading suppliers.
Emerging Opportunities
Further adding to the impact of the government schemes, he says, “The increased momentum has translated into increased demand from OEMs and design houses. It’s also creating new opportunities for companies like ours to support emerging players with the right components, kits, and engineering resources.” Further, adding to the same, he emphasizes the visibility and structure offered by these to enable distributors like element14 to work more closely with the Indian engineers and also align their plans accordingly.
element14’s India Plans
Talking about the company’s India plans, he says, “For element14, India is a strategic growth market. It represents not just an opportunity to expand but to partner with a new generation of engineers and innovators.” He also sounds quite optimistic when it comes to India’s role in the global supply chain of semiconductors, as he underlines the growing demand for components across the globe in segments like automotive, IoT, and industrial automation.
Challenges in the Indian Landscape
Every company faces one or the other challenge when it comes to scaling in a given nation under certain circumstances. For element14, these remain to be infrastructure variability, diverse needs, and timely last-mile delivery, specifically in the remote areas. He says, “Strategically, the pace of policy execution and the need for talent development in chip design and testing are areas that will require continued focus.”
Find the Part-01 at “Exclusive Feature: “We’re Using AI to Help Us Make Better, Faster, and More Accurate Decisions,” says DigiKey’s Ken Paxton”
Changing Roles
Reflecting on how the nation’s stride in electronics manufacturing impacts the distributors, he says, “The expectation from distributors has shifted beyond just availability.” The distributors are today expected to provide better technical support, along with alternative prototyping options, and also better credit terms, enabling an end-to-end partnership in the product development cycle.
As Jose puts it, “As India moves toward becoming a global electronics hub, distributors must grow into enablers of speed, reliability, and innovation.”
As India’s semiconductor ambitions gather pace, element14 is positioning itself as more than a distributor. “Our focus in India and across Asia is clear. We want to support innovation in a truly end-to-end way, from the early stages of design all the way to mass production and beyond,” says Jose. At its core, he adds, the company’s goal is “to be a reliable partner for innovation, one that grows with our customers and helps them build what’s next.”
| India’s semiconductor ambitions are backed by initiatives like the ₹76,000 crore ISM and the ₹1,000 crore DLI scheme, which focuses on fostering a strong design ecosystem. A critical part of this effort is ensuring design engineers get timely access to quality components.
To highlight how distributors are enabling this, we present our exclusive series — “Powering the Chip Chain” — featuring conversations with key industry players. |
The post The Semicon India program has brought new energy to the ecosystem: Jose Lok, element14 appeared first on ELE Times.
AI-Driven Design Automation Boosts Semiconductor Productivity
The semiconductor industry is entering a new phase where artificial intelligence is taking on some of the most complex aspects of chip development. With design cycles growing more challenging due to advanced system-on-chip (SoC) requirements, AI-driven design automation tools are proving to be a game-changer bringing higher productivity, improved performance, and faster time to market.
Rising in Complexity in SoC Development
Modern (SoC) has multiple functions integrated, making them huge optimization targets for power, performance, and area (PPA). Mock manual iterative style often cannot efficiently address design rule checks (DRCs), timing closure, and multi-block optimizations. That has created an ever-increasing demand for intelligent design solutions that can handle scaling design.
Productivity Gains Through AI-Optimized Workflows
According to industry evaluation reports, AI-enabled chip design platforms have shown transformative improvements. These reports demonstrate productivity improvements, speeding up design completion from more than five to thirty times over and reducing design rule checks (DRCs) by as much as 70%. Performances outcomes have also improved significantly, highlighting how AI can streamline bottlenecks that previously slowed down development.
Accelerating Time to Market
Products must be delivered on time in very demanding markets like display drivers, imaging solutions, and advanced electronics. This makes automated design optimization allow the engineering teams to focus on innovation rather than repetitive fine-tuning, ensuring that smarter, quicker, and more cost-efficient solutions reach the market.
AI for Competitive Edge
By implementing intelligent design automation, not only do companies improve their operations-oriented efficiency, but they also boost their actual competitive thrust. The concurrent multiple-block optimization of large (SoC) is turning into the strategic differentiator in markets where performance and speed to market define success.
Looking Ahead
AI-driven chip design automation has already gone beyond being a laboratory experiment it is fast becoming an orthodoxy in modern semiconductor engineering. The early adopters, foremost of them being Himax with Cadence’s Cerebrus Intelligent Chip Explorer, demonstrated astonishing gain in productivity and design quality. As more semiconductor companies embrace similar AI-driven platforms, the industry is poised to unlock new levels of creativity, reduce development costs, and accelerate the path to next-generation chips.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Cadence.)
The post AI-Driven Design Automation Boosts Semiconductor Productivity appeared first on ELE Times.
India’s Powerplay in Electronics Commands Global Attention at electronica India and productronica India 2025
Largest-ever edition in Bengaluru underscores India’s journey to becoming a global electronics manufacturing hub
- Featured 50,194 visitors, unprecedented international participation of 6000+ brands from 50+ countries
- Targeted international pavilions and 2,000+ structured business matchmaking sessions transformed potential into partnerships with measurable commercial outcomes.
- Conferences bridged policy, manufacturing, and innovation divides, creating actionable pathways to India’s technological leadership rather than theoretical aspirations.
Electronica India and Productronica India 2025, held at the Bangalore International Exhibition Centre (BIEC), concluded three days of significant business engagement, industry discourse, and technological exploration. The trade fairs, featuring over 6000+ global brands from more than 50 countries and attracting 50,194 trade professionals, reinforced India’s expanding role within the global electronics manufacturing landscape.
Organised by Messe Muenchen India, these co-located trade fairs continue to serve as a strategic meeting point for the entire electronics manufacturing value chain, encompassing design, components, assembly, automation, embedded systems, and quality assurance. While established global entities leveraged the platform to consolidate their regional footprint, Indian manufacturers, Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) providers, and material suppliers actively showcased advanced capabilities, often with a view toward securing international export partnerships.
Government representation, including senior leadership from Karnataka – Shri. Rahul Sharanappa Sankanur, IAS, Managing Director, Managing Director Karnataka Innovation and Technology Society (KITS), Smt. Gunjan Krishna, IAS, Commissioner, Industries and Commerce Department, Government of Karnataka and Dr. Darez Ahamed, IAS- Managing Director, Guidance Tamil Nadu affirmed ongoing state-level commitments to cultivating electronics manufacturing hubs. Concurrently, dedicated international pavilions from Japan, Taiwan, and Germany were prominent, solidifying the show’s reputation as a key gateway for international enterprises seeking to engage with India’s dynamic ecosystem.
The facilitated Buyer-Seller Forum proved highly effective, recording over 2,000 structured meetings. Sourcing teams from key sectors such as automotive, industrial automation, and consumer electronics–including leading companies such as Samsung, Spark Minda, and Jio platforms–engaged directly with component manufacturers and solutions providers. Discussions primarily revolved around optimizing lead times, establishing local inventory, implementing cost engineering strategies, and fostering supplier development – all critical aspects for global supply chain resilience.
With Rohit Sharma as the face for electronica India and productronica India 2025, the platform also expanded its reach beyond the immediate industry community. His association helped connect the event’s core message to a wider and increasingly tech-aware audience, highlighting the growing societal relevance of electronics manufacturing in India.
Exhibitor Testimonials
Exhibitors consistently reported high-quality interactions. Sanjay Kumar, Managing Director from Kyocera Asia Pacific India Pvt. Ltd an electronica India exhibitor, said, “The scale and focus here in Bengaluru this year was truly impressive. The international pavilions provided direct access to component suppliers we would typically need to visit multiple regional shows to engage with.”
For process-focused technology providers, the utility was clear Gaurav Mehta, President – Business Development from Kaynes Technology India Ltd, an exhibitor at productronica India, stated, “For a process-driven technology company like ours, productronica India gave us access to the right mix of automation buyers and R&D teams. What impressed us was not just the quantity of inquiries but their technical specificity—Indian manufacturers are now discussing Industry 4.0 integration parameters and machine learning capabilities, not merely basic automation. We received interests from across verticals like defence & aerospace, IT/IOT, Healthcare, Automotive. Semiconductor, bare PCBs, Industrial and Consumer segments.
Buyer Testimonials
Mr. Gurdeep Singh, General Manager – Strategic Sourcing Group, Samsung India Electronics Pvt Ltd – “This exhibition brilliantly showcased the immense potential for localized electronics component sourcing in India. We were particularly impressed with the focus on nurturing growing Indian manufacturing capabilities and the opportunity to identify several promising new sourcing partners. A truly invaluable experience for anyone in the industry!”
Mr. Sushil Kumar, General Manager – Procurement and Sourcing, Jio Platform Limited. – “What stood out was the access to both established names and emerging startups under one roof. This juxtaposition is invaluable—we were able to benchmark mature solutions against emerging supply chain scenarios and witness India emerging as a key global manufacturing destination.”
Mr. Prakash Palanisamy, DGM – Group Corporate Electronics Sourcing, Spark Minda Group – “We attend shows globally, but the scale and focus here in Bengaluru this year were truly impressive. The international pavilions provided direct access to component suppliers we would typically need to visit multiple regional shows to engage with.”
Beyond the exhibition floor, the 2025 edition integrated a robust schedule of supporting programs designed to foster deeper technical and strategic discussions. These included the India Semiconductor Conclave, focusing on policy and design ecosystems, and the CEO Forum, addressing procurement and MSME component strategies. A strong highlight this year was the eFuture Conference, which brought together experts to discuss emerging technologies and future roadmaps for the electronics industry. Additional sessions like the eMobility Conference, the Innovation Forum, and a Live Podcast Zone further enhanced the event’s value proposition by providing diverse perspectives and real-time insights from technologists and decision-makers.
Industry leaders underscored the event’s significance. Rajoo Goel, Secretary General of ELCINA, remarked, “This edition reflects the growing depth of the Indian electronics industry. India’s electronics sector is no longer merely an assembly hub but a burgeoning ecosystem demonstrating sophisticated capabilities across the value chain. The “substantive and targeted” nature of the discussions indicates a higher level of technical readiness and business acumen among domestic participants, making them increasingly attractive partners for international collaborations that seek specialized expertise beyond basic manufacturing.”
Dr. Reinhard Pfeiffer, CEO of Messe München GmbH, offered a global perspective: “India is no longer an emerging destination—it is becoming a critical node in the global electronics supply chain. India now plays an indispensable role not just in production volumes but also in strategic design, supply chain resilience, and technological innovation. Both of these trade fairs provide a tangible showcase, allowing international stakeholders to directly gauge India’s advancements, fostering confidence and catalysing direct foreign investment and partnerships”
Bhupinder Singh, President IMEA, Messe München and CEO, Messe Muenchen India, concluded, “The 2025 edition of electronica India and productronica India has cemented the industry’s trust in these platforms and their intent to catalyse the next phase of electronics manufacturing in India. The “trust” placed in the platform reflects its proven ability to consistently deliver valuable cross-border interactions, solidifying its role as a premier facilitator for the next, more advanced phase of electronics manufacturing in India, characterized by deeper international integration and technological collaboration.”
Starting 2026, electronica India and productronica India will transition to a bi-annual format taking place both in Greater Noida (April) and Bengaluru (September). This strategic shift aims to provide more frequent market access points and better align with evolving regional business cycles, reflecting the accelerated pace of India’s electronics sector.
The post India’s Powerplay in Electronics Commands Global Attention at electronica India and productronica India 2025 appeared first on ELE Times.
India Can Lead in Semiconductor Innovation, If We Skill Right
Author: Mr. Saleem Ahmed, Officiating Head, ESSCI
When you hold your smartphone, drive your car, or even switch on your smart TV, there’s an invisible heartbeat inside, semiconductors. These tiny chips power satellites in orbit, fighter jets in the skies, and the AI algorithms reshaping our lives. For years, India has depended on importing these critical components, an Achilles’ heel for a country that aspires to be a global tech leader. But the tide is turning. With billion-dollar investments, government incentives, and, most importantly, a young pool of engineers, India is poised to script a new chapter: becoming a semiconductor innovation powerhouse.
Yet, there’s a catch. Money can build fabs and policy can set direction, but without the right skills, the vision will remain half-written. The future of India’s semiconductor journey will not just be about silicon, it will be about skills.
The Opportunity Before India
The global semiconductor industry is racing towards a trillion-dollar valuation by 2030. India’s own market is expected to touch $64 billion by 2026, nearly three times its 2019 size of $22.7 billion, according to Counterpoint Research and the India Electronics & Semiconductor Association (IESA). At the same time, the Electronics Sector Skills Council of India (ESSCI) projects the industry will employ 1.70 lakh professionals by 2025 and create another 1.03 lakh jobs by 2030. These are not routine jobs, they’re high-paying, future-facing roles that will place young Indians at the cutting edge of global innovation.
India already has an edge: it is home to nearly 20% of the world’s chip design engineers. Leading companies have set up design and R&D centers in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Noida. The recent unveiling of a 3nm semiconductor chip designed in India showcased the sheer technical capability of our engineers and the strategic importance of Indian design centers to the global industry.
By August 2025, the Union Cabinet of India had approved a total of ten semiconductor projects under the India Semiconductor Mission (ISM), amounting to cumulative investments of approximately ₹1.6 lakh crore (around $18.2 billion) across six states. These projects cover a range of technologies and partners, including advanced fabs, packaging, and silicon carbide-based compound semiconductors.
Why Skilling is the Decisive Factor
Despite this progress, the semiconductor value chain is highly talent-intensive. The design and IP creation phase, where the most economic value resides, requires deep expertise in VLSI (Very-Large-Scale Integration), electronic design automation (EDA) tools, and system-on-chip (SoC) architecture.
Currently, India produces tens of thousands of electronics graduates every year, but only a fraction are industry-ready. The gap lies in practical exposure, specialized training, and familiarity with real-world tools. For India to move beyond being a service center and emerge as a global innovation leader, a sharper focus on semiconductor design and VLSI roles is essential.
Equally critical is the manufacturing side of semiconductors, which demands not just technical know-how but also safety and operational excellence. Specialized programs such as Industrial Safety for Semiconductor Manufacturing – Hazchem and Electrical Safety in Semiconductor Facilities are vital to prepare a workforce capable of managing the highly sensitive and hazardous environments of fabrication plants. By strengthening both design expertise and manufacturing readiness, India can build a holistic talent pipeline for the semiconductor ecosystem.
Role of ESSCI: Building the Skills Bridge
This is where ESSCI plays a transformative role. Recognizing the talent gap, ESSCI has developed 32 NSQF-aligned qualifications spanning the entire semiconductor ecosystem, from chip design to advanced packaging, cleanroom operations to safety protocols.
The courses are designed to cater to:
- Engineering graduates looking to specialize,
- Diploma and ITI students preparing to enter the workforce, and
- Professionals seeking to upskill or switch domains.
Some of the most critical roles where demand is already soaring include:
- VLSI Design Engineers – Designing advanced digital and analog circuits at nanoscale.
- Physical Design Engineers – Specializing in floor-planning, power optimization, and timing.
- Verification Engineers – Ensuring chips are error-free before fabrication.
- Analog & Mixed-Signal Designers – Vital for sensors, RF communication, and power management.
- Wafer Processing and Packaging Engineers – Especially relevant as fabs emerge in India.
Each of these roles commands global relevance and premium salaries, but only if the workforce is trained at world-class standards. The full range of programs is available on ESSCI’s website, offering aspirants a structured path to join the semiconductor workforce. Beyond curriculum design, ESSCI collaborates with industry leaders ensuring that Indian talent is benchmarked against international standards.
Why This Matters for Young Engineers
For India’s youth, the semiconductor wave represents more than jobs, it represents a chance to lead global technological change. Whether in AI, electric vehicles, 5G, space technology, or IoT, semiconductors are at the heart of every emerging sector.
A career in this industry offers:
- High-paying roles with global exposure,
- Opportunities to work on frontier technologies, and
- The satisfaction of contributing to national self-reliance and global leadership.
Conclusion:
India’s semiconductor journey has moved from dream to execution. Fabs are being built, policies are in place, and global players are betting big on India. But without a deeply skilled workforce, the dream of becoming a global semiconductor hub risks falling short.
The responsibility now lies with all stakeholders, universities, industry, government, and skill councils like ESSCI, to align efforts and ensure our engineers are not just employable, but world-class innovators.
For young Indians, the message is simple: this is your moment. Equip yourself with the right skills, embrace the semiconductor revolution, and help India design not just chips, but its future.
Because if we skill right, India won’t just participate in semiconductor innovation, it will lead it
The post India Can Lead in Semiconductor Innovation, If We Skill Right appeared first on ELE Times.
Reinventing In-Vehicle Connectivity: Driving the Future with Automotive Ethernet
Modern cars are fast becoming connected, software-driven systems with all the trappings of a mobile data center. Automotive Ethernet forms the core of this transformation, providing the required speed, scalability, and security to build next-generation vehicles. From zonal architectures to software-defined platforms, the Ethernet enables the driving experience to become safer, smarter, and more connected.
Shaping Vehicle Architecture
The industry is shifting towards zonal architectures, with centralized processors managing multiple zones within a vehicle. The numerous benefits include reduced complexity, cost reduction, and enhanced efficiencies. By 2030, it is expected that half of new vehicles would incorporate zonal systems, thereby underscoring Ethernet’s role as the backbone of automotive design.
Why Automotive Ethernet Is Important
With over a decade of leadership and ports in the hundreds of millions deployed already, ethernet has made its way into becoming the de facto standard for in-vehicle networking. Listed below are the reasons:
- speed, secure-data transmission
- low power
- standards-based reliability
- scalability for future applications
The ecosystem is continuously growing, from PHY technology that stretches twisted pair connections to switches and MCUs that empower advanced networking.
Unlocking Next-Gen Capabilities
Automotive Ethernet is the data backbone fostering innovation through development in the following areas:
- Assisted driving & safety: ADAS and LIDAR-powered systems for intelligent navigation.
- Cloud connectivity: Fast, secure data transfer between vehicles and the cloud.
- Software-defined platforms: Supporting OTA updates and feature rollouts.
- Predictive maintenance: Real-time diagnostics and personalization.
Open Standards for Interoperability
Automotive connectivity depends heavily on open standards that guarantee interoperability from platform to platform. Collaborations with global standards bodies such as IEEE are further enhancing Ethernet to provide:
- Higher data rates
- Lower power consumption
- Lower emission of noise
Ethernet technologies, well-proven in enterprise data center applications, are now being modified for automotive applications to deliver the same level of security and performance.
Looking Ahead
Ethernet will continue to provide the data backbone propelling the transformation of automobiles into sophisticated, software-defined platforms. Vehicles will become safer, more intelligent, and constantly better thanks to ongoing technological advancements.
Broadcom is assisting automakers all over the world in embracing this change and influencing the direction of connected mobility with its extensive experience and leadership in Automotive Ethernet.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Broadcom.)
The post Reinventing In-Vehicle Connectivity: Driving the Future with Automotive Ethernet appeared first on ELE Times.
Vishay Intertechnology Releases New 1 A and 2 A Gen 7 1200 V FRED Pt Hyperfast Rectifiers in SlimSMA HV (DO-221AC) Package
Reducing Switching Losses and Increasing Efficiency, Devices Combine Low Qrr Down to 105 nC With VF Down to 1.45 V and Low Junction Capacitance and Recovery Time
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. expanded its Gen 7 platform of 1200 V FRED Pt Hyperfast rectifiers with four new devices in the eSMP series SlimSMA HV (DO-221AC) package. Optimized for industrial and automotive applications, the 1 A and 2 A rectifiers not only offer the best trade-off between reverse recovery charge (Qrr) and forward voltage drop for devices in their class, but also provide the lowest junction capacitance and recovery time.
The Vishay Semiconductors rectifiers released, include the VS-E7JX0112-M3 and VS-E7JX0212-M3, and AEC-Q101 qualified VS-E7JX0112HM3 and VS-E7JX0212HM3. To reduce switching losses and increase efficiency, the devices combine fast recovery times down to 45 ns with Qrr down to 105 nC typical, forward voltage drop down to 1.45 V, and junction capacitance down to 2.5 pF. The robust rectifiers offer non-repetitive peak surge current up to 21 A in a compact package measuring 2.6 mm by 5.2 mm with a low 0.95 mm profile, compared to 2.3 mm for the competing SMA package with a similar footprint. Combined with a minimum 3.2 mm creepage distance and molding compound with a comparative tracking index (CTI) ≥ 600 (Material Group I), the devices reduce component counts and lower BOM costs based on IEC 60664-1 requirements for high voltage applications.
The VS-E7JX0112-M3, VS-E7JX0112HM3, VS-E7JX0212-M3, and VS-E7JX0212HM3 will serve as clamp, snubber, and freewheeling diodes in flyback auxiliary power supplies and high frequency rectifiers for bootstrap driver functionality, while providing desaturation protection for the latest fast switching IGBTs and high voltage Si / SiC MOSFETs. Typical applications for the devices include industrial drives and tools, on-board chargers and motors for electric vehicles (EV), energy generation and storage systems, and Ćuk converters and industrial LED SEPIC circuitry.
The rectifiers feature a planar structure and platinum doped lifetime control that guarantee system reliability and robustness without compromising on performance, while their optimized stored charge and low recovery current minimize switching losses and reduce power dissipation. RoHS-compliant and halogen-free, the devices feature a Moisture Sensitivity Level of 1 in accordance with J-STD-020 and offer high temperature operation to +175 °C.
The post Vishay Intertechnology Releases New 1 A and 2 A Gen 7 1200 V FRED Pt Hyperfast Rectifiers in SlimSMA HV (DO-221AC) Package appeared first on ELE Times.
MSI Adopts Anritsu’s High-Speed Interface Evaluation Solution
Micro-Star International Co., Ltd. (MSI), a global leading vendor for computer hardware, has selected Anritsu’s signal integrity evaluation solution, Signal Quality Analyzer-R MP1900A and Vector Network Analyzer MS46524B, for high-speed digital interfaces, including the PCI Express (PCIe) standard.
The rapid proliferation of AI and IoT technologies has driven a significant increase in data transmission volumes. As a result, high-speed digital interfaces such as PCIe, USB, and DisplayPort, widely used in servers, data centers, and consumer products, are required to support even greater speeds and capacities. Faced with this, MSI has risen to the challenge of adapting to next-generation interface standards in its server and motherboard development, ensuring digital signal quality and improving development efficiency.
To achieve this, MSI selected Anritsu’s MP1900A and MS46524B. Utilizing both products, MSI established a comprehensive environment for evaluating the digital signal quality in terms of the time domain (such as the bit error rate), as well as the frequency domain (such as S-parameters). This enabled MSI to verify the signal quality of its high-speed digital interfaces and devices when installed in systems, while also enhancing its development efficiency.
Anritsu will continue to strongly support customers in solving challenges and driving technological innovation in the high-speed digital market through the provision of cutting-edge measurement technologies and comprehensive testing solutions.
The post MSI Adopts Anritsu’s High-Speed Interface Evaluation Solution appeared first on ELE Times.
Matter 1.4.2 Introduces Stronger Security for Smart Homes
As Smart Homes are getting more connected, strong security is overdue to compliment them. Matter 1.4.2, the latest standard, provides a proactive layer of protection for preventing attacks in the first place and giving strong defenses to devices and consumers in the modern Smart Home setting.
Matter Security Evolution
Since October 2022, the Matter standard has revolutionized Smart Home connectivity, allowing devices from different vendors to be interoperable and easy to set up. Security has been a core theme behind Matter since inception. Instead of password entry, Matter allows consumers to add devices by scanning QR or NFC tags, which triggers an automated verification and commissioning process.
What Has Matter 1.4.2 Improved in Security
- Certificate Revocation
Matter devices get a unique Device Attestation Certificate (DAC) to prevent cloning. From a theoretical point of view, an attacker may attempt to extract a DAC from a legitimate device to create clones. Matter 1.4.2 now introduces a standard certificate revocation mechanism whereby manufacturers can invalidate compromised DACs: In this way, cloned devices are marked down even before any attack will take place, thus protecting consumers better.
- Validating Vendor ID (VID)
The Multi-Admin capability associated with Matter allows consumers to control devices from multiple vendors at the same time. Previously, a malicious controller may have misrepresented its vendor ID. Matter 1.4.2 prevents this through the validation of vendor identities so that only trusted controllers can gain access to the Smart Home network.
- Access Restriction Lists (ARL)
With Access Restriction Lists, certified Matter Home Routers- and Access Points (HRAP) become able to allow only authorized devices to alter sensitive network settings. This enforces the principle of least privilege-an effort to contain vulnerabilities and avoid accidental or malicious disruptions in the home network.
Proactive Home-Raised Security
Security for Smart Homes is an ever-present challenge. Infineon engineers-perhaps among others-were instrumental in the very design of these new protections in conjunction with the Matter Working Group. This group works alongside researchers worldwide in naming and fixing vulnerabilities so that they cannot be exploited. Open standards and open-source software add further layers of transparency and safety.
Looking Ahead
Matter 1.4.2 demonstrates how quickly smart home security is developing. The standard makes sure users stay one step ahead of any attackers by foreseeing future dangers and incorporating proactive safeguards.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Infineon.)
The post Matter 1.4.2 Introduces Stronger Security for Smart Homes appeared first on ELE Times.
GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag and ST’s LIS2DUX12: Let’s talk about the new era of tracking assets and safety monitoring
It’s becoming outrageously expensive not to track assets and monitor people’s safety, especially when a device like the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag, from the company GPS-Buddy, can provide so much more information than just a location on a map. Equipped with an LIS2DUX12 accelerometer from ST, it can track much more data than geographical location, such as the operation of a motor, a person’s activities, and more, thanks to an implementation that leverages our sensors and our MEMS-Studio software.
It thus opens up the GPS-Buddy RFID Tag to numerous use cases and helps future-proof its design. The tracker can even collect and label training data to build new machine learning algorithms and leverage innovative AI capabilities. Put simply, GPS-Buddy is asset tracking for those who need to track much more than just assets.
GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag and the LIS2DUX12 solving the optimization problem The GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag
Why GPS asset trackers are not always popular
The GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag
Why GPS asset trackers are not always popular
Too often, companies use assets that are hard to track. Many tools don’t use a battery or power, and even those that do may not have the space to accommodate a large tracker, or could route that power to a wireless radio. Additionally, some with motors or generating strong vibrations can disrupt regular trackers. The idea of asset tracking is far from new. Even tracking assets using a GPS is not an original idea, and avid readers of the ST Blog will remember that we featured an ST solution featuring TomTom in 2018. Yet, many companies don’t opt for a GPS tracker because they tend to be large, costly, and power hungry.
How a small sensor can have enormous consequencesTo overcome many of these challenges and make GPS asset tracking more ubiquitous, the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag settled, in part, on the LIS2DUX12. Thanks to its high-g 10,000g shock survivability, it can withstand the most rugged environments. Additionally, its small package (2 mm x 2 mm) and low power consumption (between 3 µA in ultra-low power mode and 9.3 µA in high-frequency/high-performance mode), mean that the tracker is small enough to fit on a wide range of tools, while its small battery can last for years in the field. Moreover, GPS-Buddy also offers a web-based dashboard, allowing companies to utilize their existing cloud infrastructure, thereby further reducing development and operating costs.
GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag and the LIS2DUX12 convincing skeptics Why GPS asset trackers are not always practicalAnother problem is that companies still struggle to find a practical application for asset tracking within their operations. In many instances, a smaller operation will simply absorb asset losses rather than invest in trackers. The problem is that the costs of misplacing assets are more consequential than many initially think. Indeed, while most focus only on replacement costs, there are other issues, such as rising insurance premiums, increased liabilities when the lost items are used nefariously, and damage to a brand’s reputation, to name a few. However, until more companies derive greater value from asset tracking, the technology will struggle to achieve meaningful adoption.
 Split view of the the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag
How a smart sensor can expand the meaning of “tracking”
Split view of the the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag
How a smart sensor can expand the meaning of “tracking”
To help companies realize the benefits of asset tracking, the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag does more than just asset tracking, thanks to the LIS2DUX12. For instance, besides sensing motion and vibration, the sensor’s Qvar feature, which connects two electrodes to measure quasi-electrostatic potential variations, can detect when a motor is on and an appliance is in use, rather than sitting idle. Specifically, it means that companies can now track the location of their assets and determine whether they are being utilized or not. It can help companies better monitor activities and optimize workflows to ensure more positive working conditions and vastly more optimal operations.
Moreover, GPS-Buddy utilizes software tools like the ST MEMS Studio to process data and develop machine learning applications. Specifically, the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag features four buttons: Drive (DR), Work (WK), Private (PR), and Pause (PA). By pushing one of these, the tag logs sensor data and uses those modes as labels. It thus becomes possible to train a model to better distinguish between driving and a work activity, for instance, and add to the list of what the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag can monitor. Furthermore, this is possible without hiring data scientists or spending tens of thousands of dollars on training data, since the tag itself is responsible for data collection and labeling.
How does the tracker work with people?The GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag is so versatile that the company is even using it for entirely new applications like fall detection. Indeed, thanks to the ST sensors and our machine learning capability, the Tag tracks more than assets but also people’s safety. Concretely, if a person wearing the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag falls and stays immobile for an extended period, the device triggers an alarm and sends an emergency notification to supervisors. Called the “Man Down” alarm, it can make a tremendous difference in alerting medical personnel and save valuable time, thus helping ensure the well-being of the entire crew.
A new era in asset trackingGPS-Buddy shared how their collaboration with ST is shaping their product. For example, a device like the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag requires significant optimization to fit all algorithms inside a small device that can last for years in the field. Yet, by starting with an implementation of ST’s sensor models, they can accelerate development and shorten their time to market. Our work together also leads to the implementation of new features. For instance, we are working together on a solution that can detect elevation to turn off the radio when a plane is taking off, thus saving battery life when an asset is airborne.
For end users, the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag is a way to help companies function like a tech company without being a tech company. Indeed, a landscaping business, for instance, can now benefit from a data-driven approach and optimize its operations using AI, just like a tech company would, without having to hire an army of data scientists and developers. Put simply, the GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag is emblematic of a new era that is redefining what tracking assets and people mean and how it impacts operations.
The post GPS-Buddy RFID-Tag and ST’s LIS2DUX12: Let’s talk about the new era of tracking assets and safety monitoring appeared first on ELE Times.
6G Development: Turning 5G’s Roadblocks into Future Opportunities
The global rollout of 5G was expected to be transformative, providing blazing-fast speeds with incredibly low latencies. Through quite visionary and futuristic applications, 5G would have helped in applications such as autonomous driving and telemedicine.
Having made some progress, the realization has often been short of early expectations. Many industries have yet to create palpable value, whilst those in the operator’s arena are facing the challenge of recovering massive investments made in 5G infrastructure.
Now, with accelerated 6G research, the telecom industry has undergone an unusual opportunity to address these shortfalls and, learning from the trials of 5G, set engineers and innovators on the path of designing a wireless future that is smarter, better, and more inclusive.
Key Lessons from 5G Adoption
- Too Much Promises, Not Enough Delivery
The hype around 5G had fueled expectations for revolutionary new applications. Mobile broadband speeds improved, yet many flagship applications-think massive IoT or mission-critical ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC)-have not scaled in the way expected. Particularly hesitant are enterprises, leaving operators holding significant investments but slowly gaining returns.
- Deployment Complexity
Deployment from 4G to 5G was further complicated than expected. Small cell deployments for (mmWave) frequencies, spectrum allocation complications, and the very expensive upgrades to various parts of networks caused more delays in the commercial rollout. While the 5G core gave operators and enterprises a lot of flexibility, operational costs also increased, along with deployment time, to their aggravation.
- Ecosystem Gaps
Like in many solutions, 5G has been held back by its ecosystem. The smartphones were fast to adapt, while industrial IoT and other enterprise-critical devices took their own sweet time. Unable to muster an ecosystem of applications, services, and devices, industries were left unable to embrace 5G fully-or monetize it.
How 6G Aims to Deliver Where 5G Fell Short
Building on a Stronger Foundation
There is no point in going back to the drawing board for 6G. It is a natural evolution of the 5G capabilities. Enhancements to (eMBB), massive IoT, and URLLC will come alongside AI-native and machine-learning-driven networks, making such systems smarter, more reliable, and adaptable to the real world such as AR, industrial automation, and connected healthcare.
Simplifying Network Complexity
One of the intended goals of 6G is to ease all network operations. Simplifying the core architecture will make deployment much faster, cheaper, and easier to manage; operators and enterprises now have fewer barriers.
Expanding the Ecosystem
Taking note of the slow ecosystem development in 5G, 6G R&D now places device and application readiness alongside infrastructure. This, in turn, means that industries will have the hardware and software required to harness the capabilities of 6G from day one, thus speeding up adoption in manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and transportation.
Smarter Spectrum Utilization
6G will scale spectrum efficiency on top of any mmWave operations into upper mid-band (7–24 GHz) and terahertz ranges. This means that it can deliver faster data throughput, lower latency, and wider coverage, higher on spectrum-sharing issues that made 5G under-perform in densely populated urban setups.
Sustainability and Equity
Of course, spacetime performance will identify markets on energy-efficient and global-inclusive standards. By limiting power usage and operational footprints, 6G will be geared towards sustainability. At the same time, they aim to extend reliable connectivity to underserved regions, narrowing the digital divide.
Testing’s Contribution to 6G Success
Testing that is precise, adaptable, and standards-based will be essential to the deployment of 6G. In addition to verifying 6G capabilities, tools must also guarantee 5G backward compatibility. More significantly, collaborations with skilled testing suppliers will contribute to ensuring seamless development cycles, adherence to regulations, and practical performance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, 6G presents an opportunity to address 5G’s drawbacks by emphasising sustainability, ecosystem preparedness, and pragmatism. The upcoming ten years provide engineers, operators, and businesses the chance to transform wireless communication into something quicker, easier, and more significant for communities and industries around the globe.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Anritsu.)
The post 6G Development: Turning 5G’s Roadblocks into Future Opportunities appeared first on ELE Times.
Vishay Ametherm SL2220007 Inrush Current Limiting NTC Thermistor Receives UL Recognition
Certified by UL Solutions, Device Is Verified to Meet Stringent Safety and Performance Requirements
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. announced that its Vishay Ametherm SL2220007 bigAMP inrush current limiting negative temperature coefficient (NTC) thermistor has received UL certification. The certification process—conducted by UL Solutions under File E209153, Volume 1—verified that the SL2220007 thermistor complies with the stringent UL Mark requirements for safety and performance.
“Achieving UL recognition for the SL2220007 is an important milestone that underscores our commitment to delivering high performance, safety-verified solutions,” said Eric Rauch, VP Vishay Ametherm at Vishay Intertechnology. “UL certification is a trusted benchmark worldwide. The UL Mark on the SL2220007 gives our customers added assurance that the thermistor meets the highest standards for quality, safety, and reliability for their most demanding power designs.”
The SL2220007 offers a steady-state current of 7 A while maintaining rugged reliability and long-term performance. Optimized for switching power supplies, AC motors, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), industrial inverters, and variable frequency drives, the thermistor protects circuits by absorbing high inrush current when equipment is first powered on. It provides high initial resistance that quickly drops to a negligible level as steady-state current begins to flow, enabling the device to handle up to 125 J of energy and 265 VRMS of voltage with minimal power loss.
The post Vishay Ametherm SL2220007 Inrush Current Limiting NTC Thermistor Receives UL Recognition appeared first on ELE Times.
Infineon CoolGaN technology boosts power performance in network PoE applications of Universal Microelectronics
Infineon Technologies AG provides CoolGaN power transistors to Universal Microelectronics Co., Ltd. (UMEC) for the company’s new 250 W adapter for networking Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications. Infineon´s CoolGaN transistors enable reliable, high-performance solutions and help UMEC develop safer and energy-efficient technology to address modern power system challenges. These solutions are ideal for power electronics across various industries, including telecommunications, industrial electronics, medical technology, and consumer electronics.
GaN-based power devices provide higher efficiency, reducing heat generation and energy consumption. They can operate at higher frequencies and power densities, enabling more compact designs, maximizing rack space utilization, and improving cooling in AI data centers, for example. Furthermore, reducing system size allows for more hardware content and improved air flow, which results in less wasted heat and ultimately decreases operational costs and the overall carbon footprint.
“We are excited to see our CoolGaN technology powering UMEC’s new 250 W adapter for networking applications. This collaboration demonstrates the potential of GaN to revolutionize the data center industry, enabling smaller, more efficient, and reliable power solutions,” says Johannes Schoiswohl, Head of GaN Business Line at Infineon.
“Partnering with Infineon and utilizing their CoolGaN power transistors in our new 250 W adapter has allowed us to create a product that delivers exceptional efficiency and reliability,” says Richard Lin, Power Supply Product Manager at Universal Microelectronics. “This innovation aligns with our commitment to developing cutting-edge electronic solutions that meet the evolving demands of the networking industry.”
UMEC’s 250 W adapter offers excellent efficiency of 95 percent, a power density increase of around 39 percent. The CoolGaN transistors reduce power losses, enable switching at frequencies above 200 kHz, and improve thermal behavior, which is critical for compact and high-density power supplies. These are critical performance improvements in the global virtual networking market, which is expected to grow from $48.6 billion in 2024 to approximately $200 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 26.5 percent.
Infineon’s gallium nitride power transistors are driving digitalization and decarbonization, while enabling high-frequency operation, increasing efficiency and reducing system size in a wide range of applications. They are available in voltage classes from 60 V to 700 V and in a broad variety of packages.
The post Infineon CoolGaN technology boosts power performance in network PoE applications of Universal Microelectronics appeared first on ELE Times.
Handling Signal Swings: Wide Common Mode Range in Action
Communication between devices must be reliable in modern industrial, automotive, and energy applications. Yet, engineers often encounter strange situations where everything seems to be connected well but the networks start acting strange out there in the field. Intermittent loss of communication and unexpected breakdown of nodes become tremendously expensive issues-a major reason for frustration, for such problems hardly pop their heads in the lab.
After more research, it is discovered that the sneaky evil is common mode voltage swings brought on by external circumstances. The swings push the signal outside the limits set in the original RS-485 standard, thereby maring the data exchange. Today’s extended CM range RS-485 transceivers are meant to protect networks against such eventualities.
When Noise Invades the Network
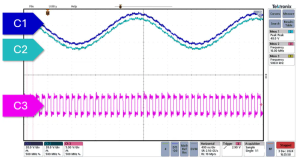
Figure 1: Scope Trace
A plain scope probe can narrate a grand story. At 500 kHz, it is not unusual to observe differential signals severely distorted due to external coupling. The transceiver receives data swathed in extraneous noise, and communication becomes unstable.
The 1983 EIA-485 standard provided for such situations by specifying a large common mode voltage range of -7 V to +12 V. Theoretically, this would be safe for signals. Practically, long cable lengths, wire resistance, and common mode external interference can move common mode levels far beyond that range.
Sources of Common Mode Swings:
A number of real-world conditions can inject interference currents into RS-485 networks:
- Motors and High-Voltage Power Supplies
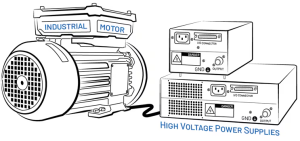
Figure 2: Common Mode Swing Sources – Motors and High Voltage Power Supplies
Motors used in industry and switching power supplies produce powerful electromagnetic fields. These fields tend to couple readily into surrounding cabling, inducing unwanted RF interference on the data lines.
- Power and Data Bundled Together
Figure 3: Common Mode Swing Sources – Cables with Power and Data Bundled Together
Running AC power cables alongside RS-485 data cables within the same cable causes capacitive coupling, which injects currents directly into the communication network.
- Ground Potential Differences Between Buildings
Figure 4: Common Mode Swing Sources – Ground Potential Differences Between Buildings
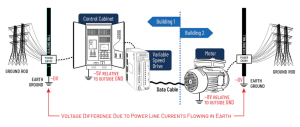
Figure 5: Ground Voltage Differences Explained
When networking across buildings, ground potential differences can create large voltage shifts. Leakage currents from safety grounds or neutral wiring often raise the common mode voltage, pushing it outside the RS-485 tolerance.
Why Extended Common Mode Range Transceivers Help
Rather than depend solely on costly shielded cables, a better solution is to implement RS-485 transceivers that have wider common mode ranges. These chips are designed to maintain reliable data transfer even when external noise forces voltages well outside the legacy standard.
Examples include:
MAX33070E – MAX33074E: Half-duplex, 3.3 V to 5 V products with ±40 V common mode tolerance
LTC2862A and LTC2863: Half- or full-duplex products with improved noise immunity
Through the implementation of these resilient solutions, engineers are able to safeguard networks against downtime, minimize field failures, and lengthen the lifespan of industrial systems.
Conclusion:
Installing and operating RS-485 networks under regulated settings is nearly impossible. Motors, power supplies, bundled cables-if anything-shift voltages around in ways that disrupt communication.
With that said, the way to go will be to design with extended common mode range transceivers that offer a safety margin against any such disruptive swings and thus ensuring communication stays steady and reliable even in the harshest industrial weather.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Analog Devices.)
The post Handling Signal Swings: Wide Common Mode Range in Action appeared first on ELE Times.
How Cloud-Integrated Printing is Revolutionizing Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive landscape has been witnessing a technological renaissance. Apart from EVs and autonomous driving, a quieter but profound change has been occurring: cloud-integrated printing. Hence, from rapid 3D prototyping to digitized supply chain management, cloud-based printing is defining new constraints in vehicle design, manufacturing, and maintenance. Analysts estimate an injection of unprecedented growth in the global cloud printing in the automotive market between 2025 and 2034; in turn, billions of dollars-worth of opportunities shall be disclosed. This means that the transformation is not only about efficiency but about sustainability, agility, and rethinking the whole concept of a factory floor for manufacturers.
Cloud Printing: With cloud printing being a mainstay of office workflows, it has now become central to automotive production. Merging next-generation hardware with managed services and cloud-based software, automotive firms can:
- Prototype cars at unprecedented velocities.
- Label and track thousands of parts globally across diverse supply chains.
- Digitize technical manuals, blueprints, and marketing collateral.
- Streamline workflows between manufacturing plants around the globe.
The cloud layer introduces a revolutionary aspect: frictionless integration anywhere, elastic production, and secure protection of sensitive designs with private or hybrid cloud models.
Market Highlights:
- North America: Holds its 30% market share in 2025 underpinned by high EV uptake and top OEMs such as Tesla, Ford, and Rivian.
- Asia-Pacific: Set to experience the quickest growth by 2034 with China, Japan, and India’s growing automotive and EV industries.
- Hardware vs. Software: Hardware has a commanding 45% market share, but cloud-based software platforms are swiftly catching up.
- Printing Types: 2D printing comprises 55% of use, but 3D printing is becoming the real growth driver.
- Applications: Parts labeling and traceability dominate, but cloud-based vehicle prototyping is the most rapidly increasing segment.
- Deployment Models: Private cloud adoption holds steady at 50%, although hybrid solutions are quickly gaining traction.
- End-Users: OEMs account for 60% of adoption, with manufacturers increasingly using 3D printing for sophisticated parts.
Trends Driving Adoption:
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Partnerships are driving faster adoption. As an example, Sharp collaborated with directprint.io in February 2025 to grow cloud printing solutions throughout the UK.
- AI-Driven Printing: AI is becoming more and more integrated into cloud platforms. Infosys and Telstra Group’s August 2025 partnership in Australia shows how machine learning is powering smarter manufacturing workflows.
- Regional Hardware Expansion: To address booming demand, Seiko Epson and other firms are increasing production, with the company opening a large-capacity printer plant in Chennai, India, in July 2025.
Hardware and Software:
Though hardware such as 3D printers and high-end scanners are seen as visible drivers of innovation, software is emerging as the real differentiator:
- Hardware: Facilitates custom part fabrication, sophisticated prototyping, and aids EV component manufacturing.
- Software: Cloud-based design systems and additive manufacturing software simplify vehicle design, enable better traceability, and enhance operational effectiveness.
2D vs. 3D Printing:
- 2D Printing: Remains the vital use cases such as documentation, blueprints, and marketing material.
- 3D Printing: The game-changer, facilitating lightweight EV components, on-demand spare parts, and quicker prototyping cycles, with growth outpacing all other segments.
Applications Driving Market Growth:
- Parts Labeling & Traceability: Critical to supply chain transparency and regulatory compliance.
- Vehicle Prototyping & Design: The most rapidly growing segment, owing to cloud-based 3D prototyping speeding up the design-to-production process.
Deployment Models: Private vs. Hybrid Cloud:
- Private Cloud: Provides control, customization, and security for proprietary IP.
- Hybrid Cloud: Fuses scalability, cost-effectiveness, and effortless data management, emerging as the preferred model for contemporary EV ecosystems.
Leading the Adoption Curve:
- OEMs represent 60% of all adopting for innovation and authentic part quality maintenance.
- In the rise: Tier-1 and 2 suppliers are increasingly turning to cloud print, particularly 3D printing, for easy and complex methods of cost-efficient part production.
Regional Outlook:
- North America as a powerhouse: Leader in cloud print adoption driven by EVs and tech-conscious OEMs.
- Asia Pacific: As fastest-growing, is nurtured by China’s EV boom and by Japan’s mature component design, with India gearing up to be an automotive manufacturing and R&D hub. Such expansions as the May 2025 launch of Konica Minolta in Australia exemplify this recent flow of energy into the region.
The Way Forward:
In the very next ten years, automotive manufacturing will be redefined. Cloud-integrated printing is more than just a tool of productivity-it stands for sustainability, innovation, and agile transformation. As 3D, AI, and hybrid cloud models converge, automakers and suppliers would rather become active in shaping the industry rather than playing catch-up.
Going Cloud-Integrated Printing today means setting the standards of tomorrow for automotive innovation.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content by Laxmi Narayan, Research Analyst, Towards Automotive.)
The post How Cloud-Integrated Printing is Revolutionizing Automotive Manufacturing appeared first on ELE Times.
Socomec Launches COUNTIS P new range of Smart AC/DC Energy Meters for Efficient Energy Management
From design to commissioning, Socomec guarantees high-performance, sustainable electrical installations
Socomec announced the launch of its latest innovation: COUNTIS P, a next-generation range of smart energy meters designed to meet the evolving needs of modern infrastructure. With over three decades of industry expertise, this launch reinforces Socomec’s commitment to innovation, sustainability, and excellence in energy efficiency and digital transformation.
Mr. Meenu Singhal, Regional Managing Director – Greater India, Socomec Innovative Power Solutions, emphasized the significance of the launch, stating, “As the energy consumption becomes increasingly complex across sectors, organizations are under pressure to manage usage more efficiently while ensuring compliance and sustainability. COUNTIS P offers a smarter, simpler way to manage energy through its compact design, AC/DC compatibility, and seamless integration with digital platforms. It empowers businesses to gain real-time insights, improve cost allocation, and drive meaningful progress toward energy efficiency goals”. He stated that this innovation demonstrates Socomec’s ongoing efforts to deliver intelligent, sustainable solutions that support customers in navigating today’s energy challenges while preparing for tomorrow’s opportunities.
The COUNTIS P range delivers precision metering, modular design, and advanced connectivity, including Modbus RTU/TCP protocols. Designed for versatility, COUNTIS P is compatible with both AC and DC systems and operates seamlessly across single-phase and complex three-phase networks. Built to perform in harsh environments, it maintains high accuracy even under extreme temperature conditions. Its plug-and-play QuickConnect installation simplifies deployment, reducing time and complexity for installers and integrators.
When integrated with Socomec’s digital monitoring platforms, COUNTIS P provides real-time energy insights that help customers track consumption, identify inefficiencies, make data-driven decisions, reduce operational costs, and support their sustainability goals. These capabilities make COUNTIS P a future-ready solution for organizations looking to optimize energy use and meet tightening regulatory standards.
In many sectors, managing sub-billing remains a critical challenge. Accurate sub-metering enables fair and transparent rebilling of energy consumption across tenants or business units. COUNTIS P meters are MID-certified, ensuring reliable accuracy and full compliance with regulatory requirements. This makes them an ideal solution for organizations seeking to avoid billing errors and ensure transparency in energy cost allocation. With features like QuickConnect technology, AC/DC compatibility, and MID certification, COUNTIS P is ideal for buildings, industry, infrastructure, and EV charging stations.
Socomec supports its customers throughout the entire lifecycle — from design to commissioning — ensuring high-performance, compliant, and sustainable electrical installations. As energy consumption becomes a critical issue for businesses, reducing kilowatt-hour usage not only lowers costs but also minimizes environmental impact. In this context, COUNTIS P stands out as a smart, reliable, and efficient tool for modern energy management.
The post Socomec Launches COUNTIS P new range of Smart AC/DC Energy Meters for Efficient Energy Management appeared first on ELE Times.
Setting Up PCM and I2S Formats for Reliable SCO Loopback Transmission
In the contemporary wireless audio industry, providing crystal-clear uninterrupted sound is such a major and recurrently faced problem. Depending on the nature of Bluetooth headsets ethereally connecting with other apparatus modules over wireless ambience or in the car for in-roads communication purposes, or in gaming devices, it is imperative that, from the engineers’ standpoint, audio signals need to stay unstuck from distortion. To validate and optimize further, SCO (Synchronous Connection-Oriented) loopback transmissions can be put to use.
In this manual, loopback mode is described. Why do we need loopback testing in Bluetooth audio? And how does one configure PCM or I2S for an SCO loopback using the Infineon AIROC Bluetooth controllers?
What is a Loopback Mode?
Loopback mode is a constraint and verification method for wireless audio. Rather than train the audio signal back to a set destination (e.g., speakers, headphones, etc.), the signal is looped back to the originating source. This allows the developers to check the signal quality, such as verifying hardware configurations and troubleshooting towards identifying any mismatch, without dependence on external devices for tests.
Normal vs. Loopback Mode:
Normal Mode: Audio is transmitted to the output device.
Loopback Mode: Audio is redirected back to the source for testing.
Test Environment
To configure SCO loopback transmission, you’ll need:
AIROC CYW20706 headset demo (PCM_OUT source) → GitHub demo project
Linux mbt tool for HCI command input → GitHub mbt tool
AIROC CYW89072 (or any supported Infineon Bluetooth controller) with firmware
Step-by-Step Setup for SCO Loopback Transmission
Step 1: Program the CYW20706 and Bring Up the Demo
- Flash the CYW20706 using ModusToolbox.
- Use the client control tool to run the demo.
- Pair a phone with the CYW20706 and start playback.
Step 2: Connect Hardware
Wire the CYW20706 PCM_OUT pin to the CYW89072 PCM_IN pin.
Step 3: Download Firmware
./mbt download [filename].hcd –minidriver
Step 4: Enable Loopback Mode
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
PCM Configuration
8K PCM
./mbt input_command 1cfc050001000101
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
16K PCM
./mbt input_command 7efc03010200
./mbt input_command 6dfc0400010102
./mbt input_command 1cfc050002000101
./mbt input_command 1efc050000030000
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
I2S Configuration
8K I2S
./mbt input_command 7efc03000200
./mbt input_command 6dfc0401010001
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
16K I2S
./mbt input_command 7efc03010200
./mbt input_command 6dfc0401010102
./mbt input_command 24fc0101
Pin Configuration Notes
For controllers like CYW555xx or CYW43xx, an additional command may be required to route PCM/I2S to default pins:
./mbt input_command 61fc0501b9b8b8b8
By default, the setup assumes TDM2 pins are in use. If you are using alternative pins, adjust the commands accordingly.
Key Takeaway
SCO loopback transmission is an invaluable tool for validating wireless audio performance. By configuring PCM or I2S formats with Infineon’s AIROC Bluetooth controllers, engineers can easily verify signal integrity, fine-tune system performance, and ensure a smooth end-user audio experience.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Infineon Technologies.)
The post Setting Up PCM and I2S Formats for Reliable SCO Loopback Transmission appeared first on ELE Times.
Looking Into What Makes Glasses Smart: A Guide to the Flexible PCBs in Smart Glasses
As emerging glasses and systems bring the virtual and physical worlds closer together than ever before, making navigation, entertainment, and even gaming way easier and more exciting, it is the power of electronics that makes it happen. In such a scenario, let’s examine the technology that makes it possible, seamless, and modern. As we move into the topic, it’s essential to emphasize that the PCB is the most crucial central platform that connects and organizes all the electronic components in a smart glass or an AR/VR device.
What type of PCB is used in Smart Glasses?
Due to the need for flexibility, adaptability, and reliability, the majority of smart glasses today are manufactured using Flexible Printed Circuit Boards (FPCBs). These are thin, lightweight circuit boards made from pliable materials that bend easily without breaking. As opposed to the rigid circuit boards, FPCBs are made with the intent to empower technology with convenience.
What makes FPCBs the go-to Choice?
PCBs enable engineers to redefine electronics with unique shapes. As it can withstand repeated bending cycles, by default, it becomes an ideal choice for compact and curved designs of smart glasses or AR/VR gear. It is a prime example of how technology integrated with aesthetics and need can empower a whole segment of innovation and seamlessness.
Smart Glasses and FPCBs are a match made in heaven, as FPCBs not only constitute the central platform, which is what a PCB usually does, but also enable the engineers to render various specific characteristics of glasses into the segment of Smart Glasses.
Electrical yet Appealing & Convenient: Secrets
To make a device fitted with so many components, yet maintain it for optimal use as a glass, necessitates a plethora of considerations to be ticked. This takes us to the next part of our story, which is the types of FPCBs depending on the materials it is made of. These materials render significant properties to the FPCBs, enabling them to not only facilitate technology but also combat its ills.
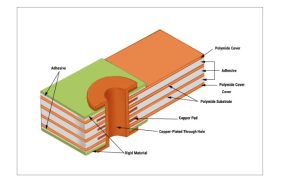 Structure of an FPCB
Structure of an FPCB
Primary materials used in these applications are:
- Polyimide (PI): The most commonly used substrate for flexible PCBs, polyimide offers outstanding thermal stability (up to 400 °C) and high mechanical strength. It can withstand thousands of bending cycles, making it ideal for the constantly moving and compact environment of smart eyewear.
- Polyester (PET): A more economical alternative to polyimide, PET provides decent flexibility but is less durable. It works best in static or low-bend applications, and is often chosen for simpler or less demanding wearable designs.
- Copper Foil: Copper is the standard conductor in flexible PCBs. Among the types, rolled-annealed (RA) copper is preferred over electrodeposited (ED) copper because of its superior flexibility and fatigue resistance—key for handling repeated bends in devices like smart glasses.
- Adhesives and Coverlays: Adhesives secure the layers of a flexible PCB, while coverlays (thin protective films) safeguard the circuitry. Both must retain flexibility and adhesion under stress to prevent issues like delamination during everyday use.
Engineers frequently favor polyimide-based substrates for their durability, particularly in premium AR glasses where long-term reliability is essential. Beyond strength, the choice of material also influences signal performance—polyimide’s low dielectric loss makes it well-suited for high-frequency applications such as 5G connectivity in smart devices.
Design Considerations with FPCBs
Since smart glasses can be subjected to repeated bending and need proper signals to enable their proper usage, it is important to design them accordingly to suit future needs. In engineering terms following considerations rank the highest:
Bending Radius:
- Maintain ≥10× PCB thickness for dynamic bends, ≥3× for static.
- Example: 0.1 mm PCB → 1 mm minimum dynamic bend radius.
Trace Layout & Spacing:
- Route traces perpendicular to bend lines.
- Avoid vias/components in bend zones.
- Keep ≥0.1 mm spacing to prevent shorts during flexing.
Tear-Drop Pads:
- Use tear-drop geometry at trace–pad junctions to minimize stress concentration and cracking.
Layer Stack-Up:
- Use symmetrical stack-ups to keep the neutral axis centered.
- Reduces stress on multilayer FPCs, especially in curved frame designs.
In AR glasses, an FPC can route signals from the microdisplay in the lens to the control unit in the frame, flexing around corners without adding bulk. This ability to combine compact routing with mechanical flexibility makes FPCs fundamental to wearable design.
Is it all Always Good with FPCBs?
To give a straight answer, no. Neither is the case with any technology in the world. Let’s look into certain challenges that FPCBs have to offer when it comes to Smart Glasses:
- Maintaining Signal Integrity: With FPCBs having thin dielectric layers, high-frequency signals for wireless connectivity can face significant challenges. To counter this, manufacturers often turn towards low-loss materials like modified polyimide and ensure precise impedance control, targeting values like 50 ohms for optimal performance.
- Ensuring Bend Durability: Repeated flexing can fatigue copper traces. Mitigation strategies include using rolled-annealed (RA) copper and reinforcing bend zones with stiffeners or extra coverlay layers to better distribute mechanical stress.
- Miniaturization: Smart eyewear requires ultra-compact PCBs with high-density interconnects. Techniques like laser-drilled microvias (as small as 0.05 mm) enable dense, high-performance circuit layouts.
By leveraging these methods, manufacturers can deliver flexible PCBs that meet the strict demands of smart eyewear—combining durability, miniaturization, and high-speed signal integrity where Flexible PCBs are central to smart eyewear, enabling sleek, lightweight designs. Success depends on material choice, proper bend-radius design, and precise rigid-flex assembly—key factors for building reliable, innovative wearables
The post Looking Into What Makes Glasses Smart: A Guide to the Flexible PCBs in Smart Glasses appeared first on ELE Times.
For more secure AI and ML models: Infineon’s OPTIGA Trust M backs Thistle Technologies’ Secure Edge AI solution
Infineon Technologies AG provides its OPTIGA Trust M security solution to Thistle Technologies for its new cryptographic protection for on-device AI models to its security software platform for embedded computing products based on the Linux operating system (OS) or on a microcontroller. The new capabilities in the Thistle Security Platform for Devices, along with Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security solution as tamper-resistant hardware-based root-of-trust, protect the valuable intellectual property (IP) in the AI models deployed in edge AI applications, and in the training data sets on which they are based.
The Thistle Security Platform for Devices that includes the Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security solution, provides ready-made, cloud-managed security components which integrate seamlessly into Linux OS-based devices and microcontrollers. Instead of building and maintaining a one-off cybersecurity stack, OEMs can deploy a proven, continuously updated foundation in hours, and scale it across large, heterogeneous fleets of devices. The Security Platform enables both secured boot and over-the-air (OTA) updating, and is compatible with a broad range of microprocessors, systems-on-chip (SoCs) and microcontrollers. Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security controller enables secured key provisioning, tamper-resistant key storage, and efficient cryptographic operations for encryption and decryption, taking care that only trusted, authenticated, and verified AI models are deployed in edge AI applications.
Thistle has extended its solution to include built-in protection for on-device AI models and data, using cryptographic keys stored in Infineon’s tamper-resistant security controllers, OPTIGA Trust M. The three key features of the new Thistle Secure Edge AI solution are:
- Hardware-backed model encryption – AI model encryption key is secured by OPTIGA Trust M security solution. Each device has a unique AES 256-bit key securely stored in OPTIGA Trust M, which is used to secure the AI Model encryption key. This means that the AES key is used for encryption and decryption inside the OPTIGA Trust M only. Even if a device is lost, decommissioned, or disassembled, the manufacturer’s IP embedded in the model is still efficiently protected. At launch, this feature is enabled on the Infineon OPTIGA Trust M security solution.
- Secured model provenance – in OTA updates, the Thistle platform enables cryptographically signed, tamper-evident delivery of AI models and firmware directly from the training platform to the device, taking care that every installed instance of a model can be traced and verified.
- Signed data and data lineage – device-generated or collected data can be signed on-device and tagged with provenance metadata. This means that downstream systems which might use the data to train or refine AI models can check the provenance of the data, and of the version of the model that the device was running when it generated the data.
Animesh Ranjan, Head of Partnerships & Ecosystem at Infineon says: “At Infineon, we are pleased to expand our collaboration with Thistle Technologies to deliver stronger protection for AI models running at the edge. By combining the OPTIGA Trust M security solution with the Thistle Security Platform, we enable device makers to safeguard their AI with hardware-anchored security that is both practical and scalable.”
Window Snyder, Chief Executive Officer of Thistle Technologies, says: “It is always our goal to make robust security capabilities accessible for device makers. With Infineon’s OPTIGA Trust M and the Thistle Security Platform, manufacturers can protect AI models and data with proven cryptography and deploy at scale quickly. Together we give customers a straightforward way to ship devices that can securely verify, encrypt, and update AI models.”
The post For more secure AI and ML models: Infineon’s OPTIGA Trust M backs Thistle Technologies’ Secure Edge AI solution appeared first on ELE Times.
Breaking Boundaries: Advanced Patterning Paves the Way for Next-Gen Chips
A cutting-edge semiconductor industry or techscape is now seeing chip features being shrunk smaller than the dimensions measured in mere atoms. Such a leap requires advanced patterning, which is a vital process involving high-precision lithography, deposition, and etching techniques working together to scale devices beyond the scope of conventional methods.
These advanced patterning processes will be used in future logic, DRAM, and NAND devices to cram more transistors into smaller dies thereby leading to faster speed, lower power consumption, and enriched functionality. Through the means of advanced patterning, one further increases yields, minimizes defects, and cuts costs at sub-half-micron nodes.
Why Does Advanced Patterning Matter?
Advanced patterning unlike the conventional method was made to help pass resolution limits that come with conventional photolithography. It can provide enhanced layouts as well as finer controls such that the application of Moore’s Law can continue with great force by semiconductor manufacturers.
Benefits include:
- Higher performance and density: More functionality in smaller chip areas.
- Improved yields: Larger process windows reduce defects.
- Sustainability: Advanced processes deliver better energy and cost efficiency.
Patterning Techniques in Action
Single Patterning versus Multipatterning
Single Patterning has been the simplest and most cost-effective method, but this only applies when the scanner is able to resolve the smallest features.
Multi-Patterning (be it Double, Triple, or Quadruple) pushes resolution limits by applying multiple exposures and photomasks. Cases of such techniques are Litho-Etch-Litho-Etch (LELE) and Litho-Freeze-Litho-Etch (LFLE) for creating feature sizes required by very dense chip designs.
Self-Aligned Patterning
Self-aligned processes, including SADP, SAQP, and SALELE, use sidewall spacers or etched references to define features smaller than those that can be lithographically defined while improving placement accuracy and pattern fidelity.
EUV Lithography
Next is Extreme Ultraviolet lithography with the shortest wavelength of 13.56 nm. EUV can produce sub-10-nm features required for nodes like 7 nm, 5 nm, etc., while resisting challenges are still there in things like resist sensitivity, defect control, and edge placement error (EPE).
Step Over the Patterning Challenges
As chips scale toward 3 nm and smaller, tolerances go down to just a few atoms. Controlling EPE caused by stochastic photoresist defects, photon limitations, and scanner imperfections is one of the biggest hurdles. Even a single misplaced edge can lead to yield loss in wafers containing billions of transistors.
Lam Research enables advanced logic and memory scaling through a suite of precision patterning technologies, including Akara for ultra-accurate etching, VECTOR DT for wafer flatness enhancement, Corvus for vertical ion edge control, Kyber for cost-effective line edge roughness reduction, and Aether for efficient dry EUV photoresist processing.
The Road Ahead
As the semiconductor roadmap pushes toward the angstrom era, advanced patterning is no longer optional it is the foundation of innovation. With companies like Lam Research leading the charge, the industry is unlocking the ability to build smaller, faster, and more sustainable chips that will power AI, advanced computing, and next-generation devices.
(This article has been adapted and modified from content on Lam Research.)
The post Breaking Boundaries: Advanced Patterning Paves the Way for Next-Gen Chips appeared first on ELE Times.
New GST Rates Bring Relief to Electronics Industry from September 22
The Government of India has taken a landmark step towards rendering the tax structure simpler and thereby easing the financial burden upon the common man while while Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi unveiled the next generation of GST reforms during the festive season, marking a pivotal moment in India’s economic transformation. The changes in GST rates have come into force on Monday, September 22; the news has come as a relief for the electronics industry.
As per the reports, the government has announced major concessions on taxes on many household electronics and technology products:
Electric Accumulators: The GST rate has been reduced from 28% to 18%, substantially lowering the cost of backup power solutions for digital devices and small appliances. This change is expected to boost the adoption of energy storage systems in homes and offices, especially in areas with unreliable power supply.
Composting Machines: With a reduction from 12% to 5%, the rates now encourage a wider acceptance of organic waste management and waste-to-energy solutions.
Two-Way Radios: Taxes have been shrunk from the erstwhile 12% to a meagre 5%. On one hand, such tariff change led to lowered procurement costs for the security forces, including the police department, paramilitary units, and defense establishments.
Industry experts wish these reforms have far-reaching benefits. According to the Industry experts, reduction will foster domestic demand, increase the sale of electronic goods and further enlarge the market for local producers.
Rationalised GST under the new reforms will, therefore, be better placed to make the electronics sector accessible, affordable, and competitive while also striving to sustain digitisation and empowerment on the government level.
The post New GST Rates Bring Relief to Electronics Industry from September 22 appeared first on ELE Times.



